Nearly 50% of environmentalists abandoned Twitter following Musk’s takeover
2023-08-15
(Press-News.org) In October 2022, Elon Musk purchased Twitter (recently renamed X), which had previously served as the leading social media platform for environmental discourse. Since then, reports a team of researchers in the journal Trends in Ecology and Evolution on August 15, there has been a mass exodus of environmental users on the platform—a phenomenon that could have serious implications for public communication surrounding topics like biodiversity, climate change, and natural disaster recovery.
“Twitter has been the dominant social media platform for diverse environmental interests to communicate and organize around advocacy goals, exchange ideas and research, and new opportunities for collaboration,” writes the US-based research team of biologists and environmental consultants.
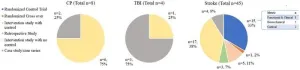
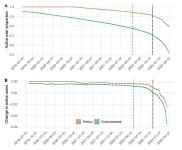
The team studied a group of 380,000 “environmentally-oriented users,” which included a wide range of people from the conservation community who had actively participated in pro-environmental discussions surrounding topics like climate change and biodiversity on Twitter. Users were considered “active” if they posted on the platform at least once within a 15-day period. The researchers found that in the 6-month period after Musk took over Twitter, only 52.5% of these environmental users were still actively using Twitter—a substantially larger drop-off rate than other “comparable online communities,” including users who discuss general politics on the platform.
“There is currently no platform equivalent to Twitter,” the team writes. “Thus, any changes in engagement by environmentally-minded users raises serious questions about where to track discourse about environmental conservation and how to mobilize pro-environmental segments of the public.”
Going forward, the authors call upon researchers to take an active role in the transition towards different modes of environmental communication—whether that be advocating for change within Twitter to help make it a useful platform for environmentalists again or collectively switching to another platform like Mastodon or Threads. They also point to resources like the Coalition for Independent Technology Research, which bring people together to voice concerns to Twitter representatives and policymakers.
“The future of Twitter as a platform for outreach and research is uncertain,” write the authors. “We need to create collaborations across industry, the non-profit sector, and academia to track public engagement with the environment across social media platforms for the benefit of primary research, applied environmental conservation, and climate mitigation.”
###
Trends in Ecology & Evolution, Chang et al. “Environmental users abandoned Twitter after Musk takeover.” https://www.cell.com/trends/ecology-evolution/fulltext/S0169-5347(23)00189-1
Trends in Ecology & Evolution (@Trends_Ecol_Evo), published by Cell Press, is a monthly review journal that contains polished, concise, and readable reviews and opinion pieces in all areas of ecology and evolutionary science. It aims to keep scientists informed of new developments and ideas across the full range of ecology and evolutionary biology—from the pure to the applied, and from molecular to global. Visit http://www.cell.com/trends/ecology-evolution. To receive Cell Press media alerts, please contact press@cell.com.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-15
Levels of grey matter in two parts of the brain may be linked to a desire to start smoking during adolescence and the strengthening of nicotine addiction, a new study has shown.
A team of scientists, led by the universities of Cambridge and Warwick in the UK and Fudan University in China, analysed brain imaging and behavioural data of over 800 young people at the ages of 14, 19 and 23.
They found that, on average, teenagers who started smoking by 14 years of age had markedly less grey matter in a section of the left frontal lobe linked to ...
2023-08-15
About The Study: In this study, most U.S. infants who required intensive care for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) lower respiratory tract infections were young, healthy, and born at term. These findings highlight the need for RSV preventive interventions targeting all infants to reduce the burden of severe RSV illness.
Authors: Natasha Halasa, M.D., M.P.H., of the Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, and Angela P. Campbell, M.D., M.P.H., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
2023-08-15
About The Study: In this study of high-use social media platforms, physicians from across the U.S. and representing a range of medical specialties were found to propagate COVID-19 misinformation about vaccines, treatments, and masks on large social media and other online platforms and that many had a wide reach based on number of followers.
Authors: Sarah L. Goff, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
2023-08-15
Inside all living cells, loosely formed assemblies known as biomolecular condensates perform many critical functions. However, it is not well understood how proteins and other biomolecules come together to form these assemblies within cells.
MIT biologists have now discovered that a single scaffolding protein is responsible for the formation of one of these condensates, which forms within a cell organelle called the nucleolus. Without this protein, known as TCOF1, this condensate cannot form.
The findings could help to ...
2023-08-15
The Lundquist Institute (TLI) at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center announced today that TLI Principal Investigator, Michael Yeaman, PhD, has been awarded a grant totaling $11.5M from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), Department of Health & Human Services. Along with his role at TLI, Dr. Yeaman is Professor of Medicine at UCLA, and Chief, Division of Molecular Medicine at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center.
This new NIH U19 Center program will decode patterns of the human immune system and microbial pathogens that result in infections that are not ...
2023-08-15
Most infants admitted to the intensive care or high acuity unit for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections during fall 2022 were previously healthy and born at term, according to a new study reported in JAMA Network Open.
The findings from this study support the use of preventative interventions in all infants to protect them from RSV, the leading cause of lower respiratory tract infections (LRTI) and hospitalizations worldwide.
RSV accounts for about 57,000-80,000 hospitalizations in children younger than 5 years with 1 in 5 RSV-positive hospitalized children being admitted ...
2023-08-15
CLEVELAND–Life’s random rhythms surround us–from the hypnotic, synchronized blinking of fireflies…to the back-and-forth motion of a child’s swing… to slight variations in the otherwise steady lub-dub of the human heart.
But truly understanding those rhythms—called stochastic, or random, oscillations—has eluded scientists. While researchers and clinicians have some success in parsing brain waves and heartbeats, they’ve been unable to compare or catalogue an untold number of variations and sources.
Gaining such insight into the underlying ...
2023-08-15
East Hanover, NJ. August 15, 2023. A team of New Jersey researchers reviewed the evidence for the impact of robotic exoskeleton devices on recovery of ambulation among individua5ls with acquired brain injury, laying out a systematic framework for the evaluation of such devices that is needed for rigorous research studies. The open access article, "Lower extremity robotic exoskeleton devices for overground ambulation recovery in acquired brain injury – A review” (doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2023/1014616), was published ...
2023-08-15
We have all felt the workings of the so called “brain-gut-axis”, how our intestines get affected, for example, by stress. But still, researchers don’t know a lot about the relation between our gut and our brain.
Research has identified genetic correlations between patients suffering from irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and psychiatric disorders, such as bipolar disorder.
By using new statistical methods, developed at NORMENT Centre, Post Doctor Markos Tesfaye at the University of Bergen and University of Oslo and his colleagues working under the leadership ...
2023-08-15
(WASHINGTON, August 15, 2023) – Early improvements in cardiac and hematologic parameters may predict better survival outcomes for patients being treated for stage IIIb AL amyloidosis, a deadly disease with a median survival of 4-6 months caused by abnormal protein buildup, according to new research released today in Blood Advances.
Amyloidosis occurs when normal proteins in the body misfold and form amyloid deposits in vital organs and tissues, which can lead to organ dysfunction, failure, and death. The prognosis for patients with advanced cardiac amyloidosis is extremely poor, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Nearly 50% of environmentalists abandoned Twitter following Musk’s takeover