(Press-News.org) DETROIT – Wanqing Liu, Ph.D., professor of pharmaceutical sciences in the Wayne State University Eugene Applebaum College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences and of pharmacology in Wayne State’s School of Medicine, received a $3 million, five-year award from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. The study, “Interaction between Genome and Heavy Metals in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease,” aims to discover and validate the gene Х heavy metal (GXM) interactions in human livers and to understand their role in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Andrea Cassidy-Bushrow, Ph.D., senior scientist and epidemiologist in the Department of Public Health Sciences at Henry Ford Health, is the co-principal investigator on the study.
NAFLD is the most common chronic liver disease, affecting more than 30% of the U.S. population. NAFLD is characterized by a spectrum of histological changes with multiple cells involved. There are no approved drug treatments available currently for the disease.
“There is an urgent need to identify both the genetic and environmental risk factors of NAFLD to aid in developing diagnostic, prevention and therapeutic strategies,” said Liu. “Over the past decade, a number of genetic risk alleles have been identified, but a growing body of research demonstrates that exposure to heavy metals increases NAFLD risk. However, more research is needed to assess the correlation between various naturally occurring accumulated metals in human livers and the NAFLD histology.”
Liu and Cassidy-Bushrow said that critical knowledge about how naturally and chronically accumulated metals interact with the liver genome and together to confer risks for NAFLD is lacking. Their preliminary studies in human liver tissues have successfully demonstrated that multiple metals are indeed correlated with NAFLD.
“By leveraging our previously collected data, we have begun to identify numerous metal-response genes, expression quantitative traits loci and allele-specific expression loci, which are further enriched to NAFLD and its related pathways,” said Cassidy-Bushrow. “We aim to expand our study to a large-scale, highly detailed and integrated analysis to thoroughly understand the role of GXM interactions in NAFLD in humans.”
The project also involves Hongmin Ni, M.D., associate professor of pharmacology, toxicology and therapeutics at the University of Kansas Medical Center, as a co-investigator. Ni will supply human liver tissue and isolated liver cells for a cell-specific, in vitro analysis of genome-metal interactions.
The collaborative study will generate important data that has the potential to identify high-risk metals and their essential response genes, ultimately promoting the development of new strategies for NAFLD diagnosis, prevention and treatment, as well as advance research for other related diseases.
The project number for this National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences of the National Institutes of Health grant is ES034410.
###
About Wayne State University
Wayne State University is one of the nation’s pre-eminent public research universities in an urban setting. Through its multidisciplinary approach to research and education, and its ongoing collaboration with government, industry and other institutions, the university seeks to enhance economic growth and improve the quality of life in the city of Detroit, state of Michigan and throughout the world. For more information about research at Wayne State University, visit research.wayne.edu.
END
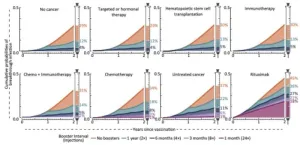
New Haven, Conn. — For many, the threat of the COVID-19 pandemic seems over. However, for patients whose immune systems are compromised by cancer or by cancer therapies, fear of COVID-19 infection and severe disease remains very real.
Currently, CDC guidance recommends that immunocompromised patients receive COVID-19 booster shots “as needed.” While this flexibility is useful for patients with complex medical conditions, more specific guidance is lacking as to when additional COVID-19 boosting would be most effective.
New ...
“Our findings may provide a useful therapeutic approach for treating breast cancer patients who may suffer from early relapse and intrinsic resistance.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 16, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on June 12, 2023, entitled, “Are cis-spliced fusion proteins pathological in more aggressive luminal breast cancer?”
A vast majority of breast cancers (~70%) are estrogen receptor-alpha positive (ER+), for which endocrine therapy is the common ...
Markers that indicate the presence of Parkinson’s disease in patients on average seven years before clinical presentation have been identified by a UCL and Moorfields Eye Hospital research team.
This is the first time anyone has shown these findings several years before diagnosis, and these results were made possible by the largest study to date on retinal imaging in Parkinson’s disease.
The study, published today in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology, identified markers of Parkinson’s in eye scans with the help of artificial ...
When a sabertooth tiger called out, what noise did it make – a mighty roar or a throaty purr? A new study from North Carolina State University examined the data behind the arguments for each vocalization and found that the answer was more nuanced than they thought – and that it could depend on the shape of a few small bones.
Modern cats belong to one of two groups: either the pantherine “big cats,” including the roaring lions, tigers and jaguars; or Felinae “little cats,” which include purring ...
Two Georgia Tech researchers, Alex Robel and Shi Joyce Sim, have collaborated on a new model for how water moves under glaciers. The new theory shows that up to twice the amount of subglacial water that was originally predicted might be draining into the ocean – potentially increasing glacial melt, sea level rise, and biological disturbances.
The paper, published in Science Advances, “Contemporary Ice Sheet Thinning Drives Subglacial Groundwater Exfiltration with Potential Feedbacks on Glacier Flow”, is co-authored by Colin Meyer (Dartmouth), Matthew Siegfried (Colorado School of Mines), and Chloe Gustafson (USGS).
While there are pre-existing methods to understand ...
Children’s views of inequality may be influenced by how its causes are explained to them, finds a new study by a team of psychology researchers. The work offers insights into the factors that affect how larger social issues are perceived at a young age and points to new ways to reduce bias toward lower-status economic groups.
“When making sense of social inequalities, adults may consider the structural forces at play—for example, people may cite policies related to legacy admissions when thinking about how disparities first arise,” says Rachel Leshin, a New York University doctoral student and the lead ...
Plants are not exposed to herbivores without defenses. When an insect feeds on a leaf, thereby wounding it and releasing oral secretions, a signaling cascade is elicited in the plant, usually starting with a rapid increase in the amount of the plant hormone jasmonic acid and its active isoleucine conjugate. Jasmonic acid regulates various reactions in plants, including defenses against herbivores and responses to environmental stress.
Mutants with disadvantageous properties do not necessarily disappear
An important thesis of evolutionary theory is natural selection and the conclusion that mutants with disadvantageous properties disappear ...
The Arizona Bioindustry Association announced that renowned Valley fever researcher John Galgiani, MD, professor and director of the Valley Fever Center for Excellence at the University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson, is the 2023 recipient of the AZBio Pioneer Award for Lifetime Achievement.
The Pioneer Award is the highest honor awarded by Arizona’s bioscience community and is extended to an Arizonan whose body of work has made life better for people at home and around the world. Galgiani’s four decades of Valley fever research, ...
The University of Arkansas celebrated an important milestone with the groundbreaking on a building that Chancellor Charles Robinson suggested might someday rival the U of A’s most iconic structure, Old Main, in significance to the university and the state of Arkansas.
Robinson and other university leaders, including University of Arkansas System President Don Bobbitt and members of the U of A System Board of Trustees, as well as researchers and industry leaders, gathered at the Arkansas Research and Technology Park in South Fayetteville to celebrate construction of the national Multi-User Silicon Carbide ...
With opioid overdose deaths surging in the United States, many communities are in desperate need of solutions to bring down the body count. Among the most promising is strengthening prison reentry programs for highest-risk users, a Rutgers-led study has found.
“For people who use drugs and have been in prison for several years, the reentry period can be chaotic and disorienting,” said Grant Victor, an assistant professor in the Rutgers School of Social Work and lead author of the study published in the Journal of Offender Rehabilitation.
“Closing ...