(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan – How is a donut similar to a coffee cup? This question often serves as an illustrative example to explain the concept of topology. Topology is a field of mathematics that examines the properties of objects that remain consistent even when they are stretched or deformed—provided they are not torn or stitched together. For instance, both a donut and a coffee cup have a single hole. This means, theoretically, if either were pliable enough, it could be reshaped into the other. This branch of mathematics provides a more flexible way to describe shapes in data, such as the connections between individuals in a social network or the atomic coordinates of materials. This understanding has led to the development of a novel technique: topological data analysis.
In a study published this month in The Journal of Chemical Physics, researchers from SANKEN (The Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research) at Osaka University and two other universities have used topological data analysis and machine learning to formulate a new method to predict the properties of amorphous materials.
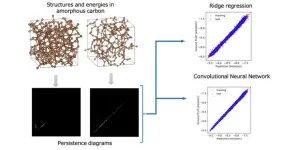
A standout technique in the realm of topological data analysis is persistent homology. This method offers insights into topological features, specifically the "holes" and "cavities" within data. When applied to material structures, it allows us to identify and quantify their crucial structural characteristics.
Now, these researchers have employed a method that combines persistent homology and machine learning to predict the properties of amorphous materials. Amorphous materials, which include substances like glass, consist of disordered particles that lack repeating patterns.
A crucial aspect of using machine-learning models to predict the physical properties of amorphous substances lies in finding an appropriate method to convert atomic coordinates into a list of vectors. Merely utilizing coordinates as a list of vectors is inadequate because the energies of amorphous systems remain unchanged with rotation, translation, and permutation of the same type of atoms. Consequently, the representation of atomic configurations should embody these symmetry constraints. Topological methods are inherently well-suited for such challenges. "Using conventional methods to extract information about the connections between numerous atoms characterizing amorphous structures was challenging. However, the task has become more straightforward with the application of persistent homology," explains Emi Minamitani, the lead author of the study.
The researchers discovered that by integrating persistent homology with basic machine-learning models, they could accurately predict the energies of disordered structures composed of carbon atoms at varying densities. This strategy demands significantly less computational time compared to quantum mechanics-based simulations of these amorphous materials.
The techniques showcased in this study hold potential for facilitating more efficient and rapid calculations of material properties in other disordered systems, such as amorphous glasses or metal alloys.
###
The article, “Persistent homology-based descriptor for machine-learning potential of amorphous structures,” was published in The Journal of Chemical Physics at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0159349
END
Topology's role in decoding energy of amorphous systems
Researchers show how topological data analysis can be used to predict the properties of amorphous materials using machine learning, which could pave the way for more computationally efficient methods suitable for industrial applications
2023-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Small urban greening projects can dramatically increase number of insect species in cities
2023-08-22
By increasing the diversity of indigenous plants in urban areas, researchers from the University of Melbourne have seen a seven times increase in the number of insect species in just three years, confirming the ecological benefits of urban greening projects. The findings are published in the British Ecological Society journal, Ecological Solutions and Evidence.
The study, conducted in a small greenspace in the City of Melbourne, found that an increase in the diversity and complexity of plant communities leads to a large increase in insect biodiversity, a greater ...
Which is easier to remember, symbols or words?
2023-08-22
Everyday symbols like &?!#@$ are highly memorable, according to new research.
The new study led by the University of Waterloo aimed to investigate how well symbols are remembered compared to words with the same meaning.
“Our work is ground-breaking as it highlights how humans remember graphic symbols and logos,” said Myra Fernandes, co-author and professor of Cognitive Neuroscience at Waterloo. “Symbols are particularly useful as they can be used as logos in advertising, as well as offer a faster ...
Study finds no effect of LEED certification on federal buildings’ energy efficiency
2023-08-22
In 2010, the U.S. government announced a multi-billion-dollar plan to improve the energy efficiency of its buildings, including a focus on LEED certification. Used worldwide, LEED—Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design—is a system that rates buildings on energy efficiency. A new study examined the effects of LEED certification on energy efficiency in federal buildings. The study found no effect on average energy consumption, primarily because many other factors come into play when rating energy.
The study, by researchers ...
Water harvesting in Death Valley: Conquering the arid wilderness
2023-08-22
Korea is regarded as a “water-stressed nation.” Although the country receives an annual precipitation of approximately 1,300mm, it is characterized by concentrated periods and specific regions, thereby giving rise to challenges stemming from water scarcity. The lack of drinking water extends beyond mere inconvenience, posing life-threatening implications for certain individuals. In March 2023, the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) released a report highlighting the plight of roughly 190 million children in Africa who suffer from an absence of safe water, resulting in the tragic daily loss of 1,000 children under the age of five.
Nations across the globe ...
Driverless cars are no place to relax, new study shows
2023-08-22
Early data on activities that will be unsafe to undertake in automated vehicles has been released. From doing work to watching the world, from social media to resting – preliminary results are in.
Research led by RMIT University looked at what happens if a driver is suddenly required to take control of an automated vehicle, such as in an emergency.
The series of papers examines how experience and three types of distractions (work, social media and rest) impacted on the driver’s ability to respond.
Study lead author in the School of Engineering, Dr Neng Zhang, said ...
CORRECTION: MRI scans improve prostate cancer diagnosis in screening trial
2023-08-22
The REIMAGINE study, published today in BMJ Oncology, is the first study to use MRI scans with prostate specific antigen (PSA) density to assess the need for further standard NHS tests. Of the 29 participants found to have serious prostate cancer, 15 had a ‘low’ PSA score that would have meant they were not referred for further investigation under the current system.
Currently, men over 50 in the UK can ask for a PSA test if they are experiencing symptoms or are concerned about prostate cancer. ...
Short-term use of immunosuppressants not linked to cancer risk
2023-08-22
Relatively short-term use of immunosuppressant medications to control an inflammatory disease was not associated with an increased risk of later developing cancer, according to new research led by scientists at the University of Pittsburgh and Mass Eye and Ear, a member of the Mass General Brigham health care system, and published today in the journal BMJ Oncology.
The findings should provide reassurance to patients and clinicians who may hesitate to prescribe the medications because they are known to increase the risk of cancer in people who ...
New study reveals the most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis, affects 15% of the global population over the age of 30
2023-08-22
**Embargoed until 23.30 [UK time] / 6.30pm [ET] Monday, August 21, 2023** Peer-reviewed / Systematic review and meta-analysis
The Lancet: New study reveals the most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis, affects 15% of the global population over the age of 30
Aging, population growth, and obesity are key drivers
● By 2050, nearly 1 billion people are projected to have osteoarthritis.
● Obesity is a major contributor to osteoarthritis. In 2020, obesity was responsible
for approximately 20% of the disability of osteoarthritis.
● Osteoarthritis increases with age. For ages 70+, the condition ranked seventh
among causes ...
Estrogen receptor mutation study suggests potential treatments for endometrial cancers
2023-08-22
Researchers at Huntsman Cancer Institute identified potential new treatment options for people with endometrial cancer. Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecological cancer and high levels of estrogen promote its development. The study, published in Molecular Cancer Research discovered that estrogen receptor mutations found in endometrial cancers cause large changes in endometrial cancer cells.
Estrogen is a reproductive hormone that binds and activates estrogen receptors. Cancer can cause estrogen receptors to remain in a state of constant activity. That increases shedding of the endometrial ...
UC Davis MIND Institute gets $4.7 million NIMH grant to test autism intervention in community
2023-08-22
UC Davis MIND Institute researchers have received a $4.7 million, five-year grant from the National Institutes of Mental Health to study a child-focused autism intervention in community agencies. The Early Start Denver Model (ESDM) is a comprehensive intervention for autistic children ages 1-4. It addresses all areas of development and emphasizes communication and social interaction through everyday activities.
ESDM was tested in research studies at the MIND Institute and shown to improve communication skills and daily living skills. The new grant will allow MIND Institute experts to train behavior analysts in community agencies to use the model, to see if it is effective ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
[Press-News.org] Topology's role in decoding energy of amorphous systemsResearchers show how topological data analysis can be used to predict the properties of amorphous materials using machine learning, which could pave the way for more computationally efficient methods suitable for industrial applications