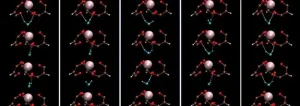
(Press-News.org) What was once the final frontier of the human genome — the Y chromosome — has just been mapped out in its entirety.
Led by the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), a team of researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and many other organizations used advanced sequencing technologies to read out the full DNA sequence of the Y chromosome — a region of the genome that typically drives male reproductive development. The results of a study published in Nature demonstrate that this advance improves DNA sequencing accuracy for the chromosome, which could help identify certain genetic disorders and potentially uncover the genetic roots of others.
DNA sequencing isn’t as simple as reading genetic material from a genome’s beginning to its end. DNA gets chopped up when it is extracted from cells, plus even the best sequencing equipment can only handle relatively small bits of DNA at a time. So, researchers and clinicians rely on special software to piece together fragments of sequenced code in the correct order like a puzzle.
A reference genome is a separate, already pieced-together genome that serves as a guide, similar to the pictures on the front of puzzle boxes. And because 99.9% of our species’ genetic code is shared, any human genome would closely match a reference.
Last year, a team from the Telomere-to-Telomere (T2T) consortium, which is made up of experts from dozens of organizations such as NIST, generated the most complete reference genome at the time by using new sequencing technologies to crack previously indecipherable regions of the genome. But cells used in that work did not contain the most puzzling of all, the Y chromosome.
“Chromosomes all contain sections of very repetitive DNA, but well over half of the Y chromosome is like that,” said study co-author Justin Zook, who leads NIST’s Genome in a Bottle (GIAB) consortium. “If you use the puzzle analogy, a lot of the Y chromosome looks like the backgrounds often do, where all the pieces look really similar.”
With this new endeavor, T2T was not starting at zero as the GIAB had already gotten the ball rolling.
The GIAB’s mission is to produce test materials, or benchmarks, that can be used to evaluate sequencing technologies or methods. The materials themselves are highly accurate readouts of specific genes that can act as an answer key for checking the results of a particular sequencing method.
NIST has rigorously analyzed several individual human genomes to create their benchmarks. While GIAB has not yet produced a benchmark for the Y chromosome specifically, the consortium has studied one genome extensively, accumulating the largest collection of Y chromosome data prior to the new study.
That data served as a jumping-off point for the new study’s authors, who focused their analysis on the best understood GIAB Y chromosome. They examined the sample with a combination of cutting-edge technologies — namely high fidelity and nanopore sequencing — that make the DNA fragment puzzle pieces larger and thus easier to assemble.
A machine-learning analysis tool and gamut of other advanced programs helped the team identify and assemble the pieces of the chromosome. More than 62 million letters of genetic code later, the authors had spelled out the GIAB Y chromosome front to back.
The researchers pitted their complete Y chromosome sequence, named T2T-Y, against the most widely used reference genome’s Y chromosome parts, which are riddled with stretches of absent code. Using them both as guides for sequencing a diverse group of over 1,200 separate genomes, they found that T2T-Y drastically improved the outcomes.
T2T-Y, in combination with the group’s previous reference genome, T2T-CHM13, represents the world’s first complete genome for the half of the population with a Y chromosome.
The newest addition could be useful in identifying and diagnosing the few known conditions related to genes in the Y chromosome. But what’s more is the new reference’s potential to shed light on new genes and their function.
“There are certainly aspects of fertility and some genetic disorders that are connected to genes in the Y chromosome,” Zook said. “But because it’s been so hard to analyze up to this point, we may not even know yet just how important the Y chromosome is.”
At NIST, Zook and his fellow GIAB researchers have developed a new benchmark based on the X and Y chromosomes assembled by T2T to help translate the potential impact of the new reference material into reality.
END
Researchers fully sequence the Y chromosome for the first time
2023-08-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New research shows how cancer rewires a key immune pathway to spread
2023-08-23
A study led by researchers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) and Weill Cornell Medicine discovered a new relationship between cancer cells and the immune system, and shows how cancer can selfishly hijack a normally helpful immune pathway.
Usually, activation of this key immune pathway — called the STING pathway — triggers a strong inflammatory response that protects the body from foreign and unhealthy cells. But prolonged activation of the same pathway leads to a desensitization and ultimately to a “rewiring” of cellular signaling, which aids and abets cancer’s spread, the researchers found.
“You might think of ...
Graphene discovery could help generate hydrogen cheaply and sustainably
2023-08-23
Researchers from The University of Warwick and the University of Manchester have finally solved the long-standing puzzle of why graphene is so much more permeable to protons than expected by theory.
A decade ago, scientists at The University of Manchester demonstrated that graphene is permeable to protons, nuclei of hydrogen atoms.
The unexpected result started a debate in the community because theory predicted that it would take billions of years for a proton to permeate through graphene’s dense crystalline structure. ...
Adding immunity to human kidney-on-a-chip advances cancer drug testing
2023-08-23
By Benjamin Boettner
(Boston) — A growing repertoire of cell and molecule-based immunotherapies is offering patients with indomitable cancers new hope by mobilizing their immune systems against tumor cells. An emerging class of such immunotherapeutics, known as T cell bispecific antibodies (TCBs), are of growing importance with several TCBs that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved for the treatment of leukemias, lymphomas, and myelomas. These antibody drugs label tumor cells with one of their ends, and attract immune cells with another end to coerce them into tumor cell killing.
One major challenge in the development of TCBs and other immunotherapy ...
Fungus gnats as pollinators not pests
2023-08-23
Many plants and crops rely on insects to pollinate them so they can reproduce. A new study has shown that several flowering plants from the group Euonymus are pollinated by fungus gnats, a dipteran insect. Specifically, they pollinate Euonymus plants which have red-petaled flowers with short stamens and yogurt-like scent. Although fungus gnats are known to pollinate hundreds of plant species, this study shows that the particular traits of red Euonymus flowers were likely to have been acquired via pollination syndrome, evolving over a process of natural selection to be pollinated specifically by fungus gnats. This research highlights the important role of Diptera, which are commonly regarded ...
Solar powered irrigation: a game-changer for small-scale farms in sub-Saharan Africa
2023-08-23
In sub-Saharan Africa 80% of agricultural production is from smallholder farmers, who face constraints on increasing farm productivity resulting in a large yield gap. Extensive rain-fed agriculture (90% of all cropland) under unpredictable and erratic rainfall pattern is a leading cause of the low productivity and food insecurity in Africa, together with a low degree of mechanization. This has been reinforcing a persistent poverty trap, triggered by cyclical famines that are jeopardizing local development opportunities.
In a new IIASA-led study as part of the research project Renewables for African Agriculture (RE4AFAGRI), an international ...
Looking out for kids: a case for better pediatric trauma interventions
2023-08-23
In the weeks following the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, public health directives called for masking, social distancing, social isolation, and stay-at-home orders. Apart from the severe medical consequences as a direct result of the pandemic, the ensuing social isolation had far-reaching impacts on children. The pandemic control measures affected the pediatric population by increasing mental distress, limiting physical activity, changing sleep patterns, and reducing emergency room visits. Unfortunately, the scope of pediatric trauma during the pandemic remains ...
SwRI investigates the efficiency impact of smart-technology-enabled vehicles
2023-08-23
SAN ANTONIO — August 23, 2023 — A Southwest Research Institute project funded by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has demonstrated an average of 15% energy savings when vehicles outfitted with connected and automated vehicle systems, or CAVs, are introduced into traffic.
CAVs use wireless smart technology to communicate with other CAVs and traffic infrastructure. SwRI’s eco-driving framework uses custom software and predictive powertrain algorithms to enable human drivers to make more efficient driving ...
Nemours Children’s Health researchers to present at World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery
2023-08-23
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. (August 23, 2023) – Researchers from Nemours Children’s Health will present a range of studies at the World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery, Aug. 27 – Sept. 1 in Washington D.C., the leading global conference in the field. Nemours Children’s presentations will highlight advances in complex congenital heart disease, prevention, cardiomyopathy in rare diseases, and the benefit of integration with other areas like psychology and telehealth.
"In pediatric cardiac surgery, the Nemours Children’s Cardiac Center has pioneered a number of procedures, and we are pleased to share our new findings with researchers and clinicians ...
Unravelling the water dynamics and structure of water-coordinated metal complexes
2023-08-23
Lanthanide-containing complexes are important compounds for sophisticated nuclear-fuel processing and medical imaging. Moreover, they often have interesting symmetric crystal structures and associated dynamics that render unique properties for practical applications.
The seven-coordinate lanthanide complex Ho(III) aqua-tris(dibenzoylmethane) or Ho-(DBM)3·H2O was first reported in the late 1960s. It has a three-fold symmetric structure with holmium (Ho) at the center of three propeller-shaped dibenzoylmethane (DBM) ligands and a water (H2O) ...
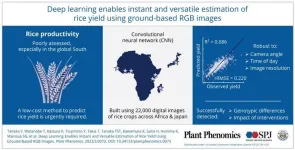
Artificial intelligence can now estimate rice yields, according to new study
2023-08-23
With the rise in global demand for staple crop products projected to substantially increase by 2050 due to population growth, rising per capita income, and the growing use of biofuels, it is necessary to adopt sustainable agricultural intensification practices in existing croplands to meet this demand. However, estimation processes currently employed in the global South remain inadequate. Traditional methods like self-reporting and crop cutting have their limitations, and remote sensing technologies are not fully utilized in this context.
However, recent advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, particularly deep learning with convolutional ...