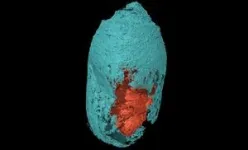
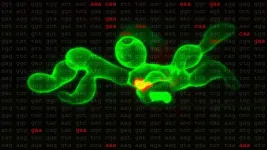
(Press-News.org) Associate Professor Tim Thomas and Professor Anne Voss from WEHI (Melbourne, Australia) have been awarded the 2023 UNSW Eureka Prize for Scientific Research.
The prize recognises their groundbreaking research in developing a new class of drugs that can put cancer cells ‘to sleep’ without triggering the harmful side effects caused by conventional cancer treatments, like chemotherapy and radiation.
The Australian Museum Eureka Prizes are among Australia’s most distinguished science awards, honouring excellence across the areas of research and innovation, leadership, science engagement, and school science.
At a glance
Associate Professor Tim Thomas and Professor Anne Voss awarded the 2023 UNSW Eureka Prize for Scientific Research.
The pair identified a novel approach to cancer treatment that can put cancer cells ‘to sleep’, without the harmful side effects caused by conventional therapies.
The Eureka Prize for Scientific Research is awarded for outstanding curiosity-driven scientific research.
Breakthrough treatment
Chemotherapy and radiation are two common treatments used to destroy or stop the growth of cancer cells, to prevent tumours from spreading. But these treatments can also affect healthy cells and damage the cells’ DNA, leading to debilitating side effects, including nausea, fatigue and hair loss. The new class of drugs developed by Associate Professor Thomas and Professor Voss have an unprecedented ability to stop cancer cells from reproducing and spreading – without damaging the cells’ DNA. Professor Voss, Joint-Head of WEHI’s Epigenetics and Development Division, said the pair was honoured and humbled to be Eureka Prize recipients.
“This win is a testament to the collaborative power and the unwavering commitment of so many colleagues that has underpinned our work towards findings better treatments for a disease that still impacts millions of people worldwide,” she said.
“The best anti-cancer treatments currently available to patients can still impact their quality of life. “This new class of drug compounds stop cancer cells from dividing and proliferating by switching off their ability to continue the cell cycle. This stops the cancer cells in their track, preventing them from spreading.
“Crucially, in arresting tumour growth, the new compounds do not damage the cells’ DNA, which is a critical difference between this new class of compounds and standard cancer therapies.”
The research, spanning over a decade, involves a collaboration with the Monash Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences (MIPS) and the Cancer Therapeutics CRC (CTx).
Critical findings
The researchers, who have worked together for more than 30 years, made the crucial discovery of the key functions of the MYST family of proteins and how they can be used towards anti-cancer therapies.
MYST proteins play a critical role in controlling the activity of our genes, which ensure our bodies work correctly.
When these proteins malfunction, there can be harmful consequences to our body – including uncontrolled growth of cells. The unregulated growth can lead to the development of cancer.
Working with the Cancer Therapeutics CRC (CTx), researchers from the Monash Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences (MIPS), CSIRO and St Vincent’s Institute of Medical Research, the researchers investigated ways to inhibit MYST proteins to treat cancer. A large chemical compound screen led to the development of novel inhibitors of the MYST proteins. This was followed by a collaboration with researchers from the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre to expand the potential cancer spectrum that may benefit from MYST inhibitor treatment. Nearly a quarter of a million different compounds were screened over several years to uncover this finding.
Compounds based on the early-stage discoveries of Professor Voss and Associate Professor Thomas progressed into clinical trials in late 2020.
New weapon to fight cancer
Associate Professor Thomas said this novel class of drugs has the potential to be an entirely new strategy towards fighting cancer.
“Our research has already shown great promise in halting cancer progression in models of blood and liver cancers. This is a significant step forward in combating the global health challenge of cancer,”
“We are grateful for this award and thank the team of 50 researchers who worked on this project with us. We hope our work highlights the importance of long-term investment in translational research to improve health outcomes for people impacted by cancer.”
The research attracted global media attention after it was published in Nature – the most esteemed scientific research publication – in 2018. They researchers have also been awarded the 2021 Australian Academy of Technology and Engineering (ATSE) Clunies Ross Knowledge Commercialisation Award, jointly with Professor Jonathan Baell (MIPS), and the 2021 Victoria Prize for Science and Innovation.
END
Eureka win for researchers behind new anti-cancer strategy
2023-08-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cattle farming expansion and unchecked climate change would expose more than 1 billion cows to heat stress
2023-08-24
More than 1 billion cows around the world will experience heat stress by the end of the century if carbon emissions are high and environmental protection is low, according to new research published today in IOP Publishing’s journal Environmental Research Letters.
This would mean cattle farming would face potentially lethal heat stress in much of the world, including Central America, tropical South America, Equatorial Africa, and South and Southeast Asia. The research also found that rapidly reducing greenhouse gas emissions, as well as keeping cattle production close to current levels, would reduce these impacts by at least 50% in Asia, 63% in South America, and ...
Bees from the time of the pharaohs found mummified on the Southwest Coast of Portugal
2023-08-24
A new study reports the discovery of hundreds of mummified bees inside their cocoons. These cocoons, produced almost three thousand years ago, were discovered in a new paleontological site discovered on the coast of Odemira, in Portugal.
About 2975 years ago, Pharaoh Siamun reigned in Lower Egypt; in China the Zhou Dynasty elapsed; Solomon was to succeed David on the throne of Israel; in the territory that is now Portugal, the tribes were heading towards the end of the Bronze Age. In particular, on the southwest coast of Portugal, where is now Odemira, something strange and rare ...
Study IDs secret of stealthy invader essential to ruinous rice disease
2023-08-24
The virulence of a rice-wrecking fungus — and deployment of ninja-like proteins that help it escape detection by muffling an immune system’s alarm bells — relies on genetic decoding quirks that could prove central to stopping it, says research from the University of Nebraska–Lincoln.
A Nebraska team helmed by Richard Wilson hopes that identifying an essential but formerly unknown stage in the fungal takeover of rice cells can accelerate the treatment or prevention of rice blast disease, which ruins up to 30% of global yields each year.
“The response I’ve gotten from people in my field is that they’re very excited, ...
Mutations in blood stem cells can exacerbate colon cancer
2023-08-24
Researchers at the University of Florida College of Medicine have discovered how common age-related changes in the blood system can make certain colon cancers grow faster. The study, to be published August 24 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), also suggests how these effects might be therapeutically targeted to reduce tumor growth and improve patient survival.
As we age, the hematopoietic stem cells that reside in the bone marrow and give rise to all of the body’s different blood cells gradually acquire mutations in their ...
The ‘treadmill conveyor belt’ ensuring proper cell division
2023-08-24
Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) have discovered how proteins work in tandem to regulate ‘treadmilling’, a mechanism used by the network of microtubules inside cells to ensure proper cell division. The findings are published today in the Journal of Cell Biology.
Microtubules are long tubes made of proteins that serve as infrastructure to connect different regions inside of a cell. Microtubules are also critical for cell division, where they are key components of the spindle, the structure which attaches itself to chromosomes and pulls them apart into each new cell.
For the spindle to function properly, cells rely on microtubules to ‘treadmill’. ...
Significant progress in cell separation technology made by Griffith University team
2023-08-24
Early detection allows for timely intervention in many diseases before they progress to a severe stage, often at a lower treatment cost. This is particularly crucial in the case of cancer, as the stage of cancer development at the time of initial diagnosis significantly influences the patient's prognosis and survival rate. Therefore, regular medical check-ups can ensure better survival and quality of life. However, the multitude of medical examination items makes the experience both loved and loathed. With various ...
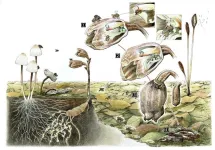
Fungi-eating plants and flies team up for reproduction
2023-08-24
Fungi-eating orchids were found for the first time to offer their flowers to fungi-eating fruit flies in exchange for pollination, which is the first evidence for nursery pollination in orchids. This unique new plant-animal relationship hints at an evolutionary transition towards mutualistic symbiosis.
Orchids are well known to trick their pollinators into visiting the flowers by imitating food sources, breeding grounds or even mates without actually offering anything in return. The fungi-eating, non-photosynthetic orchid genus Gastrodia is no different: To attract fruit flies (Drosophila spp.), the plants usually emits a smell like their common diet of fermented fruits ...
Preterm babies given certain fatty acids have better vision
2023-08-24
Preterm babies given a supplement with a combination of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids have better visual function by the age of two and a half. This has been shown by a study at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden.
The study, published in The Lancet Regional Health Europe, covers 178 extremely preterm babies at the neonatal units of the university hospitals in Gothenburg, Lund, and Stockholm between 2016 and 2019. Extremely preterm babies are those born before the 28th week of pregnancy.
Around half of the children were given preventive oral nutritional supplements containing the omega-6 fatty acid AA (arachidonic acid) and the omega-3 fatty acid DHA (docosahexaenoic ...
Manchester research to boost bioprinting technology to address critical health challenges in space
2023-08-24
New research by The University of Manchester will enhance the power of bioprinting technology, opening doors to transform advances in medicine and addressing critical health challenges faced by astronauts during space missions.
Bioprinting involves using specialised 3D printers to print living cells creating new skin, bone, tissue or organs for transplantation.
The technique has the potential to revolutionise medicine, and specifically in the realm of space travel, bioprinting could have a significant impact.
Astronauts on extended space missions have ...
Social media does not cause depression in children and young people
2023-08-24
“The prevalence of anxiety and depression has increased. As has the use of social media. Many people therefore believe that there has to be a correlation,” says Silje Steinsbekk, a professor at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU) Department of Psychology.
But that is not the case if we are to believe the results of the study “Social media behaviours and symptoms of anxiety and depression. A four-wave cohort study from age 10-16 years”.
Trondheim Early Secure Study
In the Trondheim Early Secure Study research project, researchers followed 800 children in Trondheim ...