(Press-News.org) Reefs, whether natural or man-made, are hotspots of marine biodiversity. But especially in soft-bottomed seas, reefs have now become scarce because many hard substrates have been removed due to overfishing of shellfish, dredging, trawling, and deep-sea mining. How can we restore this lost biodiversity, as encouraged by the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration (2021-2030) and the EU Biodiversity Strategy?
Now, researchers have shown that culled fruit trees sunk into the sea are a cheap and effective way to recreate reefs and boost the local diversity and abundance of marine life. The study, published in Frontiers in Marine Science, was done in the Wadden Sea, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and the largest tidal flats system in the world.
“Here we show that native marine biodiversity can be restored in a highly degraded ecosystem like the Dutch Wadden Sea by using trees as reefs,” said Jon Dickson, the study´s lead author and a PhD candidate at the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research.
“Before humans domesticated the landscape with agriculture, logging, and river controls, trees fell into rivers in large numbers and were washed out to sea. We know that such sunken wood has been present in marine ecosystems since the Jurassic, providing a home, shelter, and food for marine animals.”
Culled pear trees
In April 2022, Dickson et al. constructed 32 pyramid-like structures from 192 felled pear trees past their economic lifespan, and transported these by ship to open waters between the Dutch barrier islands Texel and Vlieland. There, the ‘tree-reefs’ were rooted in concrete feet and sunk to the soft sea bottom at four different locations, approximately three to four meters deep.
Four months later, they were briefly raised onto a ship, to allow the researchers to count the number of different species of sessile organisms on them, for example shellfish, algae, or polyps. They were replaced on the sea bottom and allowed to accumulate more biodiversity for a further two months. Then, three fish traps were lowered around each reef block, as well as nearby control sites and retrieved 24 hours later. All fish and crustaceans in the traps were counted and measured, with their species identified, before being released unharmed.
‘Profusion´ of marine animals
“Within six months, the tree-reefs were covered in a profusion of sessile animals and algae, and home to more fish than surrounding control areas,” said Dickson.
In total, the researchers found 15 species of sessile organisms: predominantly barnacles and hydroid polyps, while bryozoa, sea grapes, sea lettuce, and sea stars were also found. Each of these taxa tended to specialize in a different range of heights measured from the sea bottom.
Within tree-reef sites, six species of fish (such as whiting-pout, common goby, and European eel) and four of crustaceans were caught, compared to only two species of fish and five of crustaceans within control sites, approximately 200 meters away. The abundance was likewise greater within the tree-reef sites: for example, 5.1 times more individuals of the dominant species five-bearded rockling were caught there than in control sites.
Rapid colonization
“Current findings highlight that initial colonization of natural tree-reefs is rapid and suggest that recovery of communities associated with woody substrates may be possible by active restoration,” concluded the authors.
“Since we have done our experiment only in one sea, we don’t yet know how tree-reefs would perform off the coast of other continents. Also, how long will they function as reefs as they biodegrade? What species will live in, on, and around them in the longer term? These are questions we need to answer,” said Dickson.
END
Reefs made from culled trees can help kickstart sea life in threatened waters
Culled fruit trees sunk into the Wadden Sea boost local diversity and abundance of marine life
2023-08-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Paper cups are just as toxic as plastic cups
2023-08-25
Replacing single use plastic cups with paper ones is problematic. Researchers at the University of Gothenburg show that a paper cup that ends up in nature can also cause damage as they also contain toxic chemicals.
Reports of plastics pollution contaminating all parts of the Earth and in all living things has accelerated a shift to alternative materials. The coffee latte you take with you from the kiosk on the corner now comes in paper cups, sometimes even with paper lids. But that cup can also harm living ...
Dance as a performative art form enhanced identity negotiation and strengthened group identity in people with Parkinson’s disease
2023-08-25
A recent study by the University of Eastern Finland and Balettakademien Stockholm found that performing in a dance company and being involved in its activities play a significant role in the identity and disease-related identity negotiation in people with Parkinson’s disease. Performing in the dance company and sharing the process of performing with others created a strong group identity for the dancers with Parkinson’s disease. The dancers’ experiences of watching and being watched provided them with novel ways of expressing themselves and being seen without their identity being associated with Parkinson’s disease.
Earlier ...
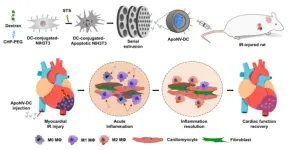
Myocardial infarction, the number one cause of sudden death, may be treated by modulating the immune response.
2023-08-25
Myocardial infarction, the number one cause of sudden death in adults and the number two cause of death in Korea, is a deadly disease with an initial mortality rate of 30%, and about 5-10% of patients die even if they are transported to a medical center for treatment. The number of myocardial infarction patients in Korea has been increasing steeply, from 99,647 in 2017 to 126,342 in 2021, an increase of 26.8% in five years. Until now, drug administration, percutaneous angioplasty, and arterial bypass surgery have been known as treatments, but ...
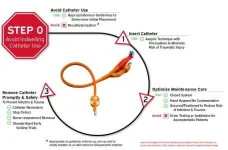
Alternatives to indwelling urinary catheters help patients avoid infections and urethral trauma
2023-08-25
ARLINGTON, Va. (August 25, 2023) — Avoiding the unnecessary use of indwelling catheters and promptly removing catheters that are no longer needed are the first steps in preventing catheter-associated urinary tract infections in acute care hospitals, according to new recommendations developed by five medical societies and published today in the journal Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.
“Urinary catheters can be associated with infection and also with non-infectious harms like trauma and obstruction,” said Payal Patel, M.D., an infectious disease physician at Intermountain Health and ...
UCLA researchers say embedding study recruitment in pre-appointment check-in may significantly boost participation
2023-08-25
FINDINGS
UCLA researchers find that they can electronically recruit patients for biomedical research at rates up to 40 times higher than the traditional method of patient portal messages by embedding study recruitment into the pre-appointment preCheck-in page.
BACKGROUND
While patient portal messages are increasingly used to recruit patients for research studies, this method typically results in study enrollment rates of 1-8%. In addition, this method of study recruitment has historically led to ...
New ‘promising medicines’ fund may incentivise commercialisation of high price drugs with weak evidence on clinical benefits
2023-08-25
A new fund to fast-track patient access to potentially valuable new medicines may incentivise the pharmaceutical industry to develop high priced drugs for rare diseases with weak evidence on clinical benefits.
Health economics and policy academics from the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM), writing in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, warn that if the NHS England Innovative Medicines Fund (IMF) is not implemented appropriately, it risks disincentivising the generation of essential evidence and could shift the financial burden from the pharmaceutical industry to the public finances.
The IMF operates on similar terms to ...
Certain gut conditions may be early warning signs of Parkinson’s disease
2023-08-25
Certain gut problems, such as constipation, difficulty swallowing, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), may be early warning signs of the neurological condition Parkinson’s disease, suggests research published online in the journal Gut.
Gastrointestinal symptoms are thought to precede the development of cerebrovascular disease, such as stroke or a brain aneurysm, or Alzheimer’s disease, and it has been suggested (Braak’s hypothesis) that gut conditions may precede the development of Parkinson’s disease too.
To ...
Poor lifestyle of over 60s linked to heightened risk of nursing home care
2023-08-25
Over 60s with the unhealthiest lifestyles are significantly more likely to require admission to a nursing home than their peers with the healthiest lifestyles, suggest the findings of a large population study published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
Physical inactivity, smoking, poor diet and sleep disorders between the ages of 60 and 64 seemed to be particularly influential: they were associated with a more than doubling in the risk of admission, the findings show.
Modifiable lifestyle risk factors are associated with the development and progression of several long term conditions, ...
Beverage Plant Research indexed in CABI
2023-08-25
We are delighted to announce that the Beverage Plant Research articles are now indexed in CABI specialized databases. This important milestone ensures that articles published in Beverage Plant Research are easily found when searching for beverage plant literature and it enables this journal authors to keep track of how often their article has been cited by others. According to the correspondence made by CABI, the Beverage Plant Research will be indexed from Volume 1, 2021.
About Beverage Plant Research
Beverage Plant Research (e-ISSN: ...
Paper drinking straws may be harmful and may not be better for the environment than plastic versions, researchers warn
2023-08-25
“Eco-friendly” paper drinking straws contain long-lasting and potentially toxic chemicals, a new study has concluded.
In the first analysis of its kind in Europe, and only the second in the world, Belgian researchers tested 39 brands of straws for the group of synthetic chemicals known as poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
PFAS were found in the majority of the straws tested and were most common in those made from paper and bamboo, the study, published ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Reefs made from culled trees can help kickstart sea life in threatened watersCulled fruit trees sunk into the Wadden Sea boost local diversity and abundance of marine life