(Press-News.org) ST. LOUIS — Erectile dysfunction (ED) is more common in older individuals with long-term Type 2 diabetes. However, emerging research at Saint Louis University School of Medicine has found that ED indicates undiagnosed prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in young men under 40.
Although the prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes declined in the United States from 1988 to 2020, 2.5% of the population has persistent undiagnosed diabetes. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate 8.5 million adults have undiagnosed diabetes, and a quarter of these cases are among young persons 18 to 44.
In a recent study published in Preventive Medicine, Jane Tucker, M.D., associate professor of family and community medicine at SLU, and Jeffrey Scherrer, Ph.D., professor of family and community medicine at SLU and a member of the Saint Louis University AHEAD Institute, examined data to look at the connection between type 2 diabetes and ED.
Researchers designed the study to determine the risk for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes among young men with and without new ED diagnoses and the time between a new ED diagnosis and the onset of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. This retrospective study reviewed the electronic health data of 1,915,468 patients from 2008-22. The study found that ED patients have a 34% increased risk for prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. Additionally, 75% of patients developed prediabetes or type 2 diabetes within a year of ED diagnosis.
“This indicates a remarkable ability to predict the potential onset of illness and treat it early with lifestyle or medication,” Tucker said.
Funds to maintain the virtual data warehouse came from the Saint Louis University Research Institute, comprising de-identified patient data from more than 5 million SSM Health patients. Researchers at SLU’s AHEAD Institute maintained the data resource and supported the study through analytics and data management. Saint Louis University is a Health Care Systems Research Network (HCSRN) member. HCSRN and its health-system members provide an exponential increase in opportunities for grant funding and collaboration on various research topics such as aging, heart disease, and mental health.
Other authors include Joanne Salas, MPH, of the Department of Family and Community Medicine at Saint Louis University, Harry S. Truman Veterans Administration Medical Center, Columbia, Mo., and the Advanced HEAlth Data (AHEAD) Research Institute at SLU; Scott Secrest, MPH, of the Department of Family and Community Medicine at Saint Louis University.
About AHEAD Institute
The Advanced HEAlth Data (AHEAD) Research Institute at Saint Louis University is a comprehensive center for data-driven innovation and research to improve the health of individuals and populations. The institute brings together researchers from various fields and disciplines to help improve patient and population health, advance the quality of health care and decrease health care costs. The new institute will utilize and develop data resources, novel analytic methods, predictive modeling, machine learning, and integrated wearable health devices and collaborate with national research networks.
About Saint Louis University School of Medicine
Established in 1836, Saint Louis University School of Medicine has the distinction of awarding the first medical degree west of the Mississippi River. The school educates physicians and biomedical scientists, conducts medical research, and provides health care on a local, national and international level. Research at the school seeks new cures and treatments in five key areas: cancer, liver disease, heart/lung disease, aging and brain disease, and infectious diseases.
END
SLU research: Erectile dysfunction linked to undiagnosed prediabetes, type 2 diabetes in young men
2023-08-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Children with SEND deserve authentic inclusion in the foreign languages classroom, report warns
2023-08-25
Pupils with special educational needs and disabilities should be given equal opportunities to learn languages, a new report argues.
Anecdotal evidence suggests that children with SEND are often removed from language lessons, because the subject is perceived as “difficult”, an assumption that is further exacerbated by trends with GCSE subject choices. Instead of withdrawing children with additional needs from the foreign languages classroom, opportunities should be provided for them to thrive within it.
Evidence shows learning new languages can be possible and hugely beneficial for many children with ...
New guideline details dental pain management strategies for pediatric patients
2023-08-25
CHICAGO, Aug. 25, 2023 – Acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen are recommended as first-line treatments for managing short-term dental pain in children under age 12, according to a new clinical practice guideline developed by the American Dental Association Science & Research Institute (ADASRI), the University of Pittsburgh School of Dental Medicine and the Center for Integrative Global Oral Health at the University of Pennsylvania School of Dental Medicine. The guideline has been endorsed by the American Dental Association.
A guideline panel determined that, when used as directed, acetaminophen alone, ...
In Type 1 diabetes, verapamil prevents decline of IGF-1 and promotes beta-cell IGF-1 signaling
2023-08-25
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – In 2012, University of Alabama at Birmingham researcher Anath Shalev, M.D., reported that a decades-old blood pressure medication called verapamil completely reversed diabetes in animal models. In 2018, the team had translated these findings into a randomized, controlled, clinical trial, demonstrating significantly improved beta cell function for one year in human subjects with recent onset Type 1 diabetes. By last year, in a small follow-up study, Shalev and colleagues had found that adult Type 1 diabetes patients taking oral verapamil required less daily insulin ...
How being in space impairs astronauts’ immune system
2023-08-25
A new study led by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden has examined how T cells of the immune system are affected by weightlessness. The results, which are published in the journal Science Advances, could explain why astronauts’ T cells become less active and less effective at fighting infection.
The next steps in the exploration of space are human missions to the moon and to Mars. Space is an extremely hostile environment that poses threats to human health. One such threat is changes to the immune system that occur in astronauts while in space and ...
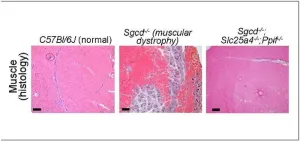
Mitochondria pore emerges as potential key to managing muscular dystrophies
2023-08-25
Ever since the Jerry Lewis telethons began in the 1960s, millions of people have become familiar with an otherwise rare disease called muscular dystrophy (MD).
The medical world has learned much over the ensuing years, including that more than 30 closely related disorders exist that can produce the gradual muscle degeneration that steals a child’s ability to walk and eventually disrupts other organ functions. An estimated 250,000 people in the U.S. are living with a muscular dystrophy. While many are living longer lives thanks to improved treatments, no cure has been found.
Now an eye-opening study ...
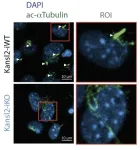
Unlocking the secrets of cell antennas
2023-08-25
Cilia are thin, eyelash-like extensions on the surface of cells. They perform a wide variety of functions, acting as mechanosensors or chemosensors, and play a crucial role in many signaling pathways. In the last few decades, the organelle has undergone a remarkable, but at the same time sinister, career transformation. It evolved from an organelle whose relevance was unclear to becoming a central player in the pathogenesis of a large group of diseases. These so-called ciliopathies are associated with a wide range of symptoms, including hearing loss, visual impairment, obesity, kidney disease, and mental disability. Different gene mutations impair cilia formation, ...
How origami might inform disease diagnoses
2023-08-25
Researchers at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering looked to origami to create new sensors that could someday be employed to detect deformations in organs and also for use in wearables and soft robotics.
Their paper, “High-Stretchability and Low-Hysteresis Strain Sensors Using Origami-Inspired 3D Mesostructures,” featured in Science Advances explains how USC researchers Hangbo Zhao, Xinghao Huang, Liangshu Liu, Yung Hsin Lin, Rui Feng, Yiyang Shen, and Yuanning Chang developed “stretchable strain sensors,” ...
Weight loss medication benefits patients with heart failure and obesity
2023-08-25
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 25 Aug 2023: Semaglutide improves heart failure-related symptoms and physical function and results in greater weight loss compared with placebo in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and obesity, according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session today at ESC Congress 2023.1
Approximately half of patients with heart failure in the community have HFpEF.2 Most patients with HFpEF are overweight or obese, and growing evidence suggests that obesity and excess adiposity are not simply comorbidities, ...
Oral anticoagulation is not effective in patients with atrial high-rate episodes
2023-08-25
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 25 Aug 2023: Blood thinners (anticoagulants) cause bleeding without preventing stroke in patients with atrial high rate episodes (AHRE), but without electrocardiogram (ECG)-diagnosed atrial fibrillation, according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session today at ESC Congress 2023 and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.1
Anticoagulants prevent strokes in patients with atrial fibrillation but are not effective in those without atrial fibrillation, for example in patients with ...
Colchicine fails to reduce primary outcomes in COP-AF trial but encouraging signals found
2023-08-25
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 25 Aug 2023: Colchicine does not significantly reduce perioperative atrial fibrillation (AF) or myocardial injury after non-cardiac surgery (MINS) in patients undergoing major non-cardiac thoracic surgery, according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session today at ESC Congress 2023.1
Perioperative AF occurs in approximately 10% of patients after major thoracic surgery, while MINS has an incidence of about 20% in the same patient population.2 Patients with perioperative AF and MINS have a poor prognosis.3,4 High levels ...