(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, August 29, 2023 – With their intricate arrangements and dynamic functionalities, proteins perform a plethora of biological tasks by employing unique arrangements of simple building blocks where geometry is key. Translating this nearly limitless library of arrangements into their respective functions could let researchers design custom proteins for specific uses.
In Journal of Applied Physics, from AIP Publishing, Markus Buehler of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology combined attention neural networks, often referred to as transformers, with graph neural networks to better understand and design proteins. The approach couples the strengths of geometric deep learning with those of language models not only to predict existing protein properties but also to envision new proteins that nature has not yet devised.
“With this new method, we can utilize all that nature has invented as a knowledge basis by modeling the underlying principles,” Buehler said. “The model recombines these natural building blocks to achieve new functions and solve these types of tasks.”
Owing to their complex structures, ability to multitask, and tendency to change shape when dissolved, proteins have been notoriously difficult to model. Machine learning has demonstrated the ability to translate the nanoscale forces governing protein behavior into working frameworks describing their function. However, going the other way — turning a desired function into a protein structure — remains a challenge.
To overcome this challenge, Buehler’s model turns numbers, descriptions, tasks, and other elements into symbols for his neural networks to use.
He first trained his model to predict the sequencing, solubility, and amino acid building blocks of different proteins from their functions. He then taught it to get creative and generate brand new structures after receiving initial parameters for a new protein’s function.
The approach allowed him to create solid versions of antimicrobial proteins that previously had to be dissolved in water. In another example, his team took a naturally occurring silk protein and evolved it into various new forms, including giving it a helix shape for more elasticity or a pleated structure for additional toughness.
The model performed many of the central tasks of designing new proteins, but Buehler said the approach can incorporate even more inputs for more tasks, potentially making it even more powerful.
“A big surprise element was that the model performed exceptionally well even though it was developed to be able to solve multiple tasks. This is likely because the model learns more by considering diverse tasks,” he said. “This change means that rather than creating specialized models for specific tasks, researchers can now think broadly in terms of multitask and multimodal models.”
The broad nature of this approach means this model can be applied to many areas outside protein design.
“While our current focus is proteins, this method has vast potential in materials science,” Buehler said. “We're especially keen on exploring material failure behaviors, aiming to design materials with specific failure patterns.”
###
The article “Generative pretrained autoregressive transformer graph neural network applied to the analysis and discovery of novel proteins” is authored by Markus Buehler. It will appear in Journal of Applied Physics on Aug. 29, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0157367). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0157367.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
The Journal of Applied Physics is an influential international journal publishing significant new experimental and theoretical results in all areas of applied physics. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/jap.
###
END
Neural network helps design brand new proteins
A flexible, language-based approach proves surprisingly effective at solving intractable problems in materials science.
2023-08-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
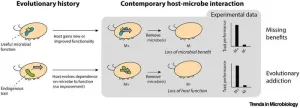
Some hosts have an “evolutionary addiction” to their microbiome
2023-08-29
We’ve long known that hosts malfunction without their microbiome—whether they are missing key microbial species or are completely microbe free. This malfunctioning is usually explained by the need for microbes to perform unique and beneficial functions, but evolutionary ecologist Tobin Hammer of the University of California, Irvine, is questioning that narrative.
In a peer-reviewed opinion article publishing August 29 in the journal Trends in Microbiology, Hammer argues that, in some cases, microbes might not actually be helping their hosts; instead, microbe-free hosts might malfunction because they have evolved an addiction to their microbes. ...
A lightweight wearable device helps users navigate with a tap on the wrist
2023-08-29
Scientists at Rice University in Houston, Texas have developed a fabric-based wearable device that “taps” a user’s wrist with pressurized air, silently helping them navigate to their destination. The study, published August 29 in the journal Device, demonstrated that users correctly interpreted which direction the device was telling them to go an average of 87% of the time. Since the wearable embeds most of its control system within the fabric itself, using air instead of electronics, it can be built lighter and more compact than existing designs.
“We envision this device will be used by individuals who need or desire information to be transmitted ...
Long-term maternal and child outcomes following postnatal SSRI treatment
2023-08-29
About The Study: The results of this study of 61,000 mother-child dyads suggest that postnatal selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) treatment was associated with a reduced risk of postnatal depression–associated maternal mental health problems and child externalizing behaviors across early childhood years. These findings suggest that postnatal SSRI treatment may bring benefits in the long term to women with postnatal depression and their offspring.
Authors: Chaoyu Liu, M.D., Ph.D., of King’s College in London, is the corresponding author.
To access the ...
Cannabis use disorder and reasons for use in a state where recreational cannabis use is legal
2023-08-29
About The Study: In this study of primary care patients in a state with legal recreational cannabis use, cannabis use disorder (CUD) was common among patients who used cannabis. Moderate to severe CUD was more prevalent among patients who reported any nonmedical use. These results underscore the importance of assessing patient cannabis use and CUD symptoms in medical settings.
Authors: Gwen T. Lapham, Ph.D., M.P.H., M.S.W., of the Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
#MedEd: How doctors use social media to advance medicine
2023-08-29
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 11:00 A.M. EDT ON TUESDAY, AUGUST 29, 2023
Social media’s effects on propagating misinformation among the lay public are widely debated, but a new paper from JAMA suggests physicians using social media are revolutionizing medical education.
La Jolla, Calif. (August 29, 2023) — Ever wonder what your doctor is doing on social media? A new study published in JAMA led by John W. Ayers, Ph.D., from the Qualcomm Institute within the University of California San Diego, finds some physicians are harnessing the reach ...
Underutilized antidepressant treatment for postnatal depression associated with improved child outcomes at age five
2023-08-29
New research led by the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London has found that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) treatment for postnatal depression is associated with improvements in child behaviour up to five years after childbirth.
Up to 15% of women experience postnatal depression which has been shown to be associated with poor outcomes for mothers’ and their children. Researchers at King’s IoPPN, in collaboration with the University of Oslo, analysed data from ...
Broken by bison, aspen saplings having a tough time in northern Yellowstone
2023-08-29
CORVALLIS, Ore. – In northern Yellowstone National Park, saplings of quaking aspen, an ecologically important tree in the American West, are being broken by a historically large bison herd, affecting the comeback of aspen from decades of over-browsing by elk.
Findings of the research led by Luke Painter of Oregon State University were published today in Ecology and Evolution.
The study comes five years after Painter, who teaches ecology and conservation in the OSU College of Agricultural Sciences, published a paper in Ecosphere showing that wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone had been a catalyst for aspen recovery both outside and ...
Partners from more than 100 countries collaborate as LOINC® issues 1,945 new concepts in semiannual release
2023-08-29
INDIANAPOLIS -- LOINC® from Regenstrief Institute is issuing its semiannual content update with 1,945 new concepts to help health systems, laboratories and other health organizations exchange medical data. The release contains newly created content based on requests submitted by stakeholders from more than 100 countries.
LOINC version 2.75 is available for download from the LOINC website and via the LOINC Terminology Service using HL7® FHIR®. The updated version includes new, edited and newly mapped concepts ...
New study will examine impact of lifestyle physical activity on cognition for older adults
2023-08-29
Jason Yang has been awarded nearly $400,000 from the National Institute on Aging to explore the role of lifestyle physical activity (light movements, walking) in cognition among insufficiently active older adults with higher risks for Alzheimer’s or related dementias. The exercise science assistant professor will use the two-year R21 grant to help determine if frequent and regular engagement in lifestyle physical activity over time may benefit cognitive function for this population.
A ...
More sleep could reduce impulsive behavior in children
2023-08-29
Sleep is a critical part of a child’s overall health, but it can also be an important factor in the way they behave.
According to a new study from the Youth Development Institute at University of Georgia, getting enough sleep can help children combat the effects of stressful environments.
“Stressful environments are shown to make adolescents seek immediate rewards rather than delayed rewards, but there are also adolescents who are in stressful environments who are not impulsive,” said lead author Linhao Zhang, a fourth-year doctoral student in UGA’s College of Family and Consumer Sciences. “We looked at what explains that link and what makes some people ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Celebrity dolphin of Venice doesn’t need special protection – except from humans
Tulane study reveals key differences in long-term brain effects of COVID-19 and flu
The long standing commercialization challenge of lithium batteries, often called the dream battery, has been solved.
New method to remove toxic PFAS chemicals from water
The nanozymes hypothesis of the origin of life (on Earth) proposed
Microalgae-derived biochar enables fast, low-cost detection of hydrogen peroxide
Researchers highlight promise of biochar composites for sustainable 3D printing
Machine learning helps design low-cost biochar to fight phosphorus pollution in lakes
Urine tests confirm alcohol consumption in wild African chimpanzees
Barshop Institute to receive up to $38 million from ARPA-H, anchoring UT San Antonio as a national leader in aging and healthy longevity science
Anion-cation synergistic additives solve the "performance triangle" problem in zinc-iodine batteries
Ancient diets reveal surprising survival strategies in prehistoric Poland
Pre-pregnancy parental overweight/obesity linked to next generation’s heightened fatty liver disease risk
Obstructive sleep apnoea may cost UK + US economies billions in lost productivity
Guidelines set new playbook for pediatric clinical trial reporting
Adolescent cannabis use may follow the same pattern as alcohol use
Lifespan-extending treatments increase variation in age at time of death
From ancient myths to ‘Indo-manga’: Artists in the Global South are reframing the comic
Putting some ‘muscle’ into material design
House fires release harmful compounds into the air
Novel structural insights into Phytophthora effectors challenge long-held assumptions in plant pathology
Q&A: Researchers discuss potential solutions for the feedback loop affecting scientific publishing
A new ecological model highlights how fluctuating environments push microbes to work together
Chapman University researcher warns of structural risks at Grand Renaissance Dam putting property and lives in danger
Courtship is complicated, even in fruit flies
Columbia announces ARPA-H contract to advance science of healthy aging
New NYUAD study reveals hidden stress facing coral reef fish in the Arabian Gulf
36 months later: Distance learning in the wake of COVID-19
Blaming beavers for flood damage is bad policy and bad science, Concordia research shows
The new ‘forever’ contaminant? SFU study raises alarm on marine fiberglass pollution
[Press-News.org] Neural network helps design brand new proteinsA flexible, language-based approach proves surprisingly effective at solving intractable problems in materials science.