Vision for future micro-optical technology based on metamaterials
2023-08-30
(Press-News.org)
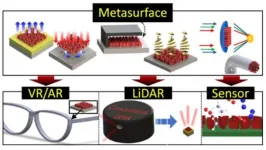
Metasurfaces, also known as invisibility cloak technology, are an artificial material adept at manipulating. With metasurfaces allowing for lenses to be reduced to one 10,000th the size of conventional lenses, they are generating considerable interest as optical components allowing miniaturization of optical systems for the next generation of virtual and augmented reality as well as LiDAR. If metasurfaces become commercially viable, overcoming the challenges of complex manufacturing processes and high production costs, Korea could gain a significant technological edge in the field of nano-optics.
A collaborative research team led by Professor Junsuk Rho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and the Department of Chemical Engineering with PhD candidates Younghwan Yang, Junhwa Seong, Minseok Choi, and Junkyeong Park, (co-lead authors) from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), and Dr. Gyoseon Jeon, Dr. Kyong-il Lee, and Dr. Dong Hyun Yoon from the Research Institute of Industrial Science and Technology (RIST) has published a paper summarizing research trends in a near-future micro-optical platform based on metasurfaces in Light: Science and Applications. They also propose future research directions and methods for commercialization in the academic journal.
Historically, metasurface research has concentrated on the full manipulation of light’s characteristics, resulting in a diverse array of optical devices such as metalenses, metaholograms, and beam diffraction devices. Nevertheless, recent studies have shifted their focus toward integrating metasurfaces with other optical components.
In their paper, the research team proposes a study of and applications for integrated metasurfaces. These integrated metasurfaces are optical components that can be combined with various standard optical components such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and liquid crystal display (LCD). For commercialization of metasurfaces, the research team suggested that future research in this field should focus on how to integrate metasurface into commonly used devices, making them applicable in everyday life.
Furthermore, the research team emphasizes the importance of collaboration between industry and academia, underscoring the impact that metasurface research can have on the future optical device industry and national competitiveness. They stressed that national-level support and cooperation are essential for the development of innovative optical platforms.
Professor Junsuk Rho explained, “Integrated metasurfaces complement existing electronic technologies and represent another innovative solution for a variety of applications.” He added, “I hope there will be sustained efforts, research, and national support that will lead to even more innovative outcomes.”
The research was sponsored by a program of POSCO’s Industry-Academic Integrated Research Center, the STEAM Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Doctoral Student Grant Program of the Ministry of Education, Samsung Science and Technology Center, and Chung Mong-Koo Foundation.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-30
An online course designed to curb negative thinking has had strong results in helping people reduce the time they spend ruminating and worrying, a new study from UNSW Sydney has shown.
And researchers say the online course, which will soon be hosted on the Australian Government funded online clinic This Way Up and is free with a prescription from a clinician, was found to significantly improve the mental health of the people who participated in the study. The trial was part of a collaboration between UNSW, the Black Dog Institute and The Clinical Research Unit for Anxiety and Depression at St ...
2023-08-30
Professionals working with children and young people will be offered training in brain science in an Australia-first initiative between The University of Queensland (UQ) and the Australian Research Alliance for Children and Youth (ARACY) through the Thriving Queensland Kids Partnership (TQKP).
Thriving Kids Brain Builders is a neuroscience translation initiative being developed with UQ’s Queensland Brain Institute (QBI) for people working across the health, education, social and community services, justice and housing sectors.
QBI ...
2023-08-30
Prostate cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer in the world, but not only does it put the lives of those diagnosed at risk, but can also severely impact patient quality of life due to side-effects of treatment.
One such side-effect commonly reported by patients is sexual dysfunction – however, a new long-term clinical trial led by Edith Cowan University (ECU) and presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Breakthrough Meeting in Japan, has revealed there is a therapy which may help combat this ...
2023-08-30
How long can trees tolerate drought before the forest dies?
Researchers from UC Davis can now predict which forests could survive despite future drought. Their new method links precipitation to tree growth, and it can help people decide where to put their resources as climate change affects patterns of snow and rainfall that impact the health of forests.
“If a forest is doing OK, but in the future we know it’s likely to get only half the average rainfall it used to get, we can calculate the likelihood ...
2023-08-30
As part of an innovative prison reform program, the Oregon State Penitentiary created a healing garden on its grounds to provide some respite from the concrete and resemble the outside world. One incarcerated man who had spent most of the past two decades in solitary confinement described going to the garden as, “the first time I walked on grass in 20 years.”
“Many of us have found beauty in weeds and flowers growing through the cracks in the pavement,” he told UC San Francisco researchers, who helped institute and then evaluated the reforms. “There is both beauty and inspiration in knowing that we, ...
2023-08-30
Quantifying Counterfactual Military History probes whether historic battles and military interventions could have turned out quite differently
Oxford, U.K., 30 August 2023 – Statistical methods can evaluate whether pivotal military events, like the Battle of Jutland, American involvement in the Vietnam war or the nuclear arms race, could’ve turned out otherwise, according to a new book.
Military historical narratives and statistical modelling bring fresh perspectives to the fore in ...
2023-08-29
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Recently, when customers began complaining that their vehicles with driver-assistance technologies were “phantom braking” or slamming on the brakes without any visible obstacles present, researchers at Michigan State University wanted to learn more about this phenomenon — why it happens and how to stop it.
“Frequent phantom braking incidents can erode confidence in autonomous driving technologies,” said Qiben Yan, an assistant professor in the College of Engineering. “If riders perceive the technology as unpredictable or unreliable, they’ll be less likely to embrace it.”
Autonomous vehicles have a vision system, ...
2023-08-29
Late preterm infants, or infants born between 34 and 36-6/7 weeks gestation, are the majority of infants born preterm, and are at greater risk for academic delays compared to full term infants.
Certain factors, including a low level of maternal education, prenatal tobacco use, twins/multiple gestation and male sex increased the risk for deficits in math and reading by kindergarten for late preterm infants, a new study finds.
However, sensitive parenting and preschool enrollment are two possible ways to counter the risk of being born late preterm, and to promote academic resilience.
“Our findings highlight an opportunity for pediatric providers to offer prevention strategies ...
2023-08-29
A multidisciplinary team lead by University of Texas at Arlington mathematics Assistant Professor Souvik Roy is on a mission to improve medical imaging using a new technique called quantitative photoacoustic tomography (QPAT).A multidisciplinary team lead by University of Texas at Arlington mathematics Assistant Professor Souvik Roy is on a mission to improve medical imaging using a new technique called quantitative photoacoustic tomography (QPAT).
QPAT is an imaging modality that combines ultrasound, which is an imaging technique that uses sound waves to image features inside ...
2023-08-29
Astronomers have uncovered a link between Neptune's shifting cloud abundance and the 11-year solar cycle, in which the waxing and waning of the Sun's entangled magnetic fields drives solar activity.
This discovery is based on three decades of Neptune observations captured by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and the W. M. Keck Observatory in Hawaii, as well as data from the Lick Observatory in California.
The link between Neptune and solar activity is surprising to planetary scientists because Neptune is our solar system's farthest major planet and receives sunlight with about 0.1% ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Vision for future micro-optical technology based on metamaterials