(Press-News.org) "The unprecedented societal interruptions during the Covid-19 pandemic of 2020 and onward took their toll on economic activity. Lockdowns disrupted supply chains and caused economic losses with implications for private households," lead author Robin Middelanis from PIK explains. "Global stress like this reduces the economic capacity to cope with additional shocks from weather extremes that put even more pressure on already stressed societies.” For an individual climate disaster, impacts from local production losses can be flexibly reduced to a certain extent by the support of unaffected production sites in the economic network. Compensation mechanisms like this become more difficult when the world economy is stressed as a whole. The costs for households increase as products run short and become more expensive.
For their study published in the journal Environmental Research Letters, the researchers analyzed two scenarios, framed as a "stressed" economy and a counterfactual "unstressed" economy with full economic capacity. Under both scenarios, they simulated indirect economic impacts from direct local economic shocks caused by climate extremes like heat stress, river floods and tropical cyclones. For this, the interaction of more than 7,000 individual producing sectors and regional consumers connected through over 1.8 million trade links was computed on a daily time scale for the years 2020-2021. The study focuses on the resulting indirect price effects on private households for the three largest economies, the United States, China and the European Union.
"It is as easy as it is dangerous to underestimate the economic impacts of increasing weather extremes. As they will intensify under global warming they will coincide with non-climate-related economic crises and that is a threat," stresses Anders Levermann, head of the Research Department Complexity Science at PIK. "Our study shows that mitigation of and adaptation to climate risks not only imply the protection of vulnerable regions. Moreover, increasing the resilience of trade relations to cope with shocks originating in other regions is of vital importance to our societies."
END
Climate extremes hit stressed economies even harder
2023-08-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Engaging in administrative payment tasks may correlate with treatment delays and nonadherence in cancer care
2023-08-30
Bottom Line: Engaging in administrative tasks to estimate costs or pay for care among a cohort of cancer patients and survivors was associated with an 18% increase in cost-related treatment delays or nonadherence.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Author: Meredith Doherty, PhD, LCSW, an assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania School of Social Policy & Practice (SP2)
Background: Navigating the U.S. health care system ...
Alcohol makes you more likely to approach attractive people but doesn’t make others seem better looking: Study
2023-08-30
PISCATAWAY, NJ — It’s “liquid courage,” not necessarily “beer goggles”: New research indicates that consuming alcohol makes you more likely to approach people you already find attractive but does not make others appear more attractive, according to a report in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
The conventional wisdom of alcohol’s effects is that intoxication makes others seem better looking. But, according to the new study, this phenomenon has not been studied systematically. Earlier research typically ...
Lead service lines in New York City disproportionately impact Hispanic/Latino communities and children already at risk of lead exposure
2023-08-30
Results from a study just released by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health show major inequities in the location of lead service lines across New York City. Communities with large numbers of Hispanic/Latino residents and those with children who are already highly vulnerable to lead exposure from numerous sources are disproportionately impacted by water service lines that may contain lead. The study findings are published online in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives.
There is no safe level of lead exposure for children. Even at lower levels of exposure, lead is associated with impaired cognitive function, attention-related behavioral problems, and diminished academic ...
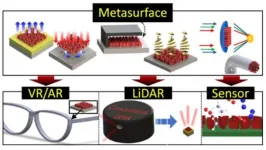
Vision for future micro-optical technology based on metamaterials
2023-08-30
Metasurfaces, also known as invisibility cloak technology, are an artificial material adept at manipulating. With metasurfaces allowing for lenses to be reduced to one 10,000th the size of conventional lenses, they are generating considerable interest as optical components allowing miniaturization of optical systems for the next generation of virtual and augmented reality as well as LiDAR. If metasurfaces become commercially viable, overcoming the challenges of complex manufacturing processes and high production costs, Korea could gain a significant technological edge ...
No worries: online course to help you stop ruminating
2023-08-30
An online course designed to curb negative thinking has had strong results in helping people reduce the time they spend ruminating and worrying, a new study from UNSW Sydney has shown.
And researchers say the online course, which will soon be hosted on the Australian Government funded online clinic This Way Up and is free with a prescription from a clinician, was found to significantly improve the mental health of the people who participated in the study. The trial was part of a collaboration between UNSW, the Black Dog Institute and The Clinical Research Unit for Anxiety and Depression at St ...
Boosting neuroscience training to help children flourish
2023-08-30
Professionals working with children and young people will be offered training in brain science in an Australia-first initiative between The University of Queensland (UQ) and the Australian Research Alliance for Children and Youth (ARACY) through the Thriving Queensland Kids Partnership (TQKP).
Thriving Kids Brain Builders is a neuroscience translation initiative being developed with UQ’s Queensland Brain Institute (QBI) for people working across the health, education, social and community services, justice and housing sectors.
QBI ...
Exercise could help one of prostate cancer treatment’s most-common and devastating side effects
2023-08-30
Prostate cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer in the world, but not only does it put the lives of those diagnosed at risk, but can also severely impact patient quality of life due to side-effects of treatment.
One such side-effect commonly reported by patients is sexual dysfunction – however, a new long-term clinical trial led by Edith Cowan University (ECU) and presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Breakthrough Meeting in Japan, has revealed there is a therapy which may help combat this ...
Can this forest survive? Predicting forest death or recovery after drought
2023-08-30
How long can trees tolerate drought before the forest dies?
Researchers from UC Davis can now predict which forests could survive despite future drought. Their new method links precipitation to tree growth, and it can help people decide where to put their resources as climate change affects patterns of snow and rainfall that impact the health of forests.
“If a forest is doing OK, but in the future we know it’s likely to get only half the average rainfall it used to get, we can calculate the likelihood ...
How Norway is helping to restore humanity inside U.S. prisons
2023-08-30
As part of an innovative prison reform program, the Oregon State Penitentiary created a healing garden on its grounds to provide some respite from the concrete and resemble the outside world. One incarcerated man who had spent most of the past two decades in solitary confinement described going to the garden as, “the first time I walked on grass in 20 years.”
“Many of us have found beauty in weeds and flowers growing through the cracks in the pavement,” he told UC San Francisco researchers, who helped institute and then evaluated the reforms. “There is both beauty and inspiration in knowing that we, ...
Statistics can help us figure out how historic battles could have turned out differently, according to experts
2023-08-30
Quantifying Counterfactual Military History probes whether historic battles and military interventions could have turned out quite differently
Oxford, U.K., 30 August 2023 – Statistical methods can evaluate whether pivotal military events, like the Battle of Jutland, American involvement in the Vietnam war or the nuclear arms race, could’ve turned out otherwise, according to a new book.
Military historical narratives and statistical modelling bring fresh perspectives to the fore in ...