(Press-News.org) Shaggy-haired, tusked pigs roam free in the woods of Germany and Austria. Although these game animals look fine, some contain radioactive cesium at levels that render their meat unsafe to eat. Previously, scientists hypothesized that the contamination stemmed from the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear power plant accident. But now, researchers in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology report that nuclear weapon fallout from 60 to 80 years ago also contributes significantly to the wild boars’ persistent radioactivity.
Radioactive cesium, a byproduct of nuclear weapons explosions and nuclear energy production, poses risks to public health when it enters the environment. And the environment across Europe got a large pulse of radioactive cesium contamination following the Chernobyl power plant accident 37 years ago. Most of that radioactivity originated from cesium-137, but a much longer-lived form, called cesium-135, can also be produced during nuclear fission. Over time, cesium-137 has declined in most game animals, but wild boars’ radioactivity levels haven’t changed substantially. Their meat continues to exceed regulatory limits for consumption, in some places leading to less hunting and consequently contributing to the overpopulation of the animals in Europe. Because the radioactive cesium levels haven’t changed as expected, Georg Steinhauser, Bin Feng and colleagues wanted to investigate the amount and origin of that contamination in wild boars from Germany.
The researchers worked with hunters to collect wild boar meat from across Southern Germany and then measured the samples’ cesium-137 levels with a gamma-ray detector. To determine the origin of the radioactivity, the team compared the amount of cesium-135 to cesium-137 with a sophisticated mass spectrometer. Previous studies showed that this ratio clearly indicates sources: A high ratio points to nuclear weapons explosions, whereas a low ratio implicates nuclear reactors.
The team observed that 88% of the 48 meat samples exceeded German regulatory limits for radioactive cesium in food. For the samples with elevated levels, the researchers calculated the ratios of cesium-135 to cesium-137, and found that nuclear weapons testing supplied between 10 and 68% of the contamination. And in some samples, the amount of cesium from weapons alone exceeded regulatory limits. The researchers propose that the mid-20th century weapons tests were an underappreciated source of radioactive cesium to German soil, which was also unevenly impacted by the Chernobyl accident. Contamination from both sources have been taken up by the wild boars’ food, such as underground truffles, contributing to their persistent radioactivity. The researchers say that future nuclear accidents or explosions could worsen these animals’ contamination, potentially impacting food safety for decades, as this study shows.
The authors acknowledge funding from the Bavarian Academy for Hunting and Nature and an Alexander von Humboldt Foundation Postdoctoral Fellowship.
The paper’s abstract will be available on Aug. 30 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.est.3c03565
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
Nuclear weapons tests are unappreciated source of radioactivity in German wild boars
2023-08-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ESO telescopes help unravel pulsar puzzle
2023-08-30
With a remarkable observational campaign that involved 12 telescopes both on the ground and in space, including three European Southern Observatory (ESO) facilities, astronomers have uncovered the strange behaviour of a pulsar, a super-fast-spinning dead star. This mysterious object is known to switch between two brightness modes almost constantly, something that until now has been an enigma. But astronomers have now found that sudden ejections of matter from the pulsar over very short periods are responsible for the peculiar switches.
“We have witnessed extraordinary cosmic events where enormous amounts of matter, similar to cosmic cannonballs, are launched into ...
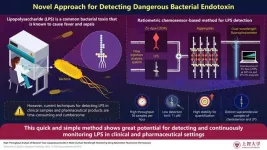
Novel chemosensor-based method for rapid detection of bacterial toxin
2023-08-30
The COVID-19 pandemic made it very clear that we need better methods to quickly screen for dangerous pathogens and substances. One such compound that regularly flies under the radar is lipopolysaccharide (LPS), largely known as "endotoxins." This molecule, which is found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, can be very harmful to humans. It can trigger a major immune response, producing fever and inflammation. In the worst cases, it can cause organ failure due to sepsis.
Surprisingly, for such a ubiquitously present toxin, there are very few ways to effectively detect the presence of LPS. The gold standard for its detection is the limulus amebocyte ...
How a mere 12% of Americans eat half the nation’s beef, creating significant health and environmental impacts
2023-08-30
A new study has found that 12% of Americans are responsible for eating half of all beef consumed on a given day, a finding that may help consumer groups and government agencies craft educational messaging around the negative health and environmental impacts of beef consumption.
Those 12% – most likely to be men or people between the ages of 50 and 65 – eat what researchers called a disproportionate amount of beef on a given day, a distinction based on the latest Dietary Guidelines for Americans, which suggest 4 ounces per day of meat, poultry, and eggs combined for those consuming 2200 ...
New research establishes enduring connection between racial segregation, childhood blood lead levels
2023-08-30
Living in a racially segregated neighborhood puts Black children at a higher risk of having elevated blood lead levels, and this association has persisted over more than two decades, according to new research from the Children’s Environmental Health Initiative, which is led by University of Illinois Chicago Chancellor Marie Lynn Miranda.
The study, published in Pediatrics, analyzed data from the early 1990s and from 2015 from blood lead level tests of more than 320,000 children younger than 7 in North Carolina. Researchers ...
Pandemic pushed half-million kids into grandparents’ homes
2023-08-30
PULLMAN, Wash. – Grandparents appeared to serve as an important private safety net when COVID-19 first hit the U.S., according to a study led by a Washington State University researcher.
The pandemic’s arrival in 2020 coincided with a surge of nearly 510,000 children living in “doubled-up” households, co-residing with other adults in addition to their parents or parents’ partners. While these living arrangements had already been increasing before COVID-19, this was an additional increase beyond what would be expected based on previous trends ...
Stress and insomnia linked to irregular heart rhythms after menopause
2023-08-30
Research Highlights:
A study of more than 83,000 questionnaires by women ages 50-79, found more than 25% developed irregular heart rhythms, known as atrial fibrillation, which may increase their risk for stroke and heart failure.
Stressful life events and insomnia were strongly linked to the development of atrial fibrillation, highlighting the need for mental well-being evaluations to be included with physical health examinations.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, Aug. 30, 2023
DALLAS, Aug. 30, 2023 — After menopause an estimated 1 in 4 women may develop irregular heart rhythms — known as atrial fibrillation – ...
New principles for patient data use balance research benefits, individual privacy
2023-08-30
Statement highlights:
This statement emphasizes that policies for patient data sharing should be interpreted and applied respectfully toward patients and research participants, equitable in impact both in terms of risks and potential benefits, and beneficial across broad and demographically diverse communities in the United States.
The statement outlines six new principles focused on encouraging the generalizability of research advances, good stewardship across the translational spectrum, transparency, education and involvement of patients, access and privacy protections.
Embargoed until 4:00 ...
Blood cell insights offer potential boost to lung cancer therapies
2023-08-30
Fresh discoveries about a type of immune cells could give lung cancer patients a more accurate prognosis and better identify who will benefit from immunotherapies.
Researchers found that the location in and around tumours of cytotoxic T cells, which play a key role in fighting cancer, may help predict patient survival and indicate whether or not treatments will work.
The findings could help to pave the way for improved immunotherapies - powerful but expensive life-extending treatments which currently fail in 80 per cent of cases - allowing them to work more effectively in more patients, researchers say.
Experts ...
Climate extremes hit stressed economies even harder
2023-08-30
"The unprecedented societal interruptions during the Covid-19 pandemic of 2020 and onward took their toll on economic activity. Lockdowns disrupted supply chains and caused economic losses with implications for private households," lead author Robin Middelanis from PIK explains. "Global stress like this reduces the economic capacity to cope with additional shocks from weather extremes that put even more pressure on already stressed societies.” For an individual climate disaster, impacts from local production losses can be flexibly reduced to a certain extent by the support ...
Engaging in administrative payment tasks may correlate with treatment delays and nonadherence in cancer care
2023-08-30
Bottom Line: Engaging in administrative tasks to estimate costs or pay for care among a cohort of cancer patients and survivors was associated with an 18% increase in cost-related treatment delays or nonadherence.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Author: Meredith Doherty, PhD, LCSW, an assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania School of Social Policy & Practice (SP2)
Background: Navigating the U.S. health care system ...