Antibody shows promise for preventing organ rejection after transplantation
In a study using primates, the monoclonal antibody was successful in promoting graft survival after kidney and islet transplantations
2023-08-30
(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.C. – A man-made antibody successfully prevented organ rejection when tested in primates that had undergone a kidney transplant, Duke Health researchers report.
The finding clears the way for the new monoclonal antibody to move forward in human clinical trials. Results of the study appear online Aug. 30 in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
“Current medications to prevent organ rejection are good overall, but they have a lot of side effects,” said lead author Imran J. Anwar, M.D., a surgical research fellow in Duke’s Department of Surgery. “These therapies suppress the immune system, putting patients at risk of infections and organ damage, and many cause non-immune complications such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
“The push over the last 30 to 40 years has been to develop new, less toxic drugs,” Anwar said. “We are hopeful this antibody moves us closer to that goal.”
Anwar and colleagues, including co-senior author Allan Kirk, M.D., Ph.D., chair of the Department of Surgery, focused on a monoclonal antibody identified as AT-1501. It was engineered to minimize the risk of blood clots, which had become problematic for an earlier version of this therapy.
In studies using primates that had undergone kidney transplantation, AT-1501 prevented rejection without the need for additional immunosuppressive drugs or promoting blood clots, confirming its immunosuppressive potential.
In animals that had undergone islet transplantation, AT-1501 alone did not lead to uniform rejection control, but it was effective in combination with existing immunosuppressive agents. The combination therapies in islet transplantation led to uniform islet graft survival without weight loss or infections that can typically arise. The islet transplants were performed by Norma Kenyon, Ph.D., co-senior author and professor at the University of Miami.
“These data support AT-1501 as a safe and effective agent to promote both islet and kidney transplant survival and function and allow us to advance into clinical trials right away,” Kirk said. “This less toxic approach has been pursued for over 20 years, and I think we are finally at a turning point. This could be a great advance for people in need of organ transplants.”
In addition to Kirk and Anwar, study authors include Dora M. Berman, Isabel DeLaura, Qimeng Gao, Melissa A. Willman, Allison Miller, Alan Gill, Cindy Gill, Steve Perrin, Camillo Ricordi, Philip Ruiz, Mingqing Song, Joseph M Ladowski, and Norma S. Kenyon.
The study received funding support from the National Institutes of Health (U19-AI051731), the Diabetes Research Institute Foundation, and Anelixis Therapeutics, now Eledon Pharmaceuticals, which is developing AT-1501 for kidney and islet cell transplant.
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-08-30
DURHAM, N.C. – Researchers have developed a blood test that detects Parkinson’s disease, potentially establishing a way to help diagnose the condition before nervous system damage worsens.
A new blood-based diagnostic test would be a major advancement for Parkinson’s disease, which afflicts 10 million people worldwide and is the second-most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer’s. Led by a team of Duke Health neuroscientists, the study appears Aug. 30 in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
“Currently, Parkinson’s disease is diagnosed largely based on clinical symptoms after significant neurological damage has ...
2023-08-30
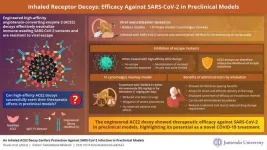
The surface protein of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), known as the spike protein, is critical for infecting host cells. The spike protein facilitates the infection process by binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors on the surface of airway epithelial cells, initiating the virus entry into the cells. By engineering an ACE2 receptor to increase the affinity to the spike protein, researchers demonstrated a novel method to neutralize the virus effectively. The engineered ACE2 (3N39v4-Fc) acts as a decoy by binding to the viral spike protein, thus preventing the binding of viruses to the ACE2 receptor on the cell surface. ...
2023-08-30
New Curtin research into injuries sustained by trail users has found mountain biking is not the dangerous, injury-plagued sport reserved for thrill-seekers that it is often perceived to be and that the health benefits outweigh the risks.
Researchers analysed data from dozens of studies across the world, including Australia, encompassing 220,935 injured mountain bikers and 17,757 injured hikers. The study aimed to pinpoint the injury types and affected body areas in order to gain insights into the medical treatment of such cases.
Lead author PhD candidate Paul Braybrook, from Curtin’s School of Nursing, said mountain bikers were primarily injured on their upper limbs, ...
2023-08-30
The same neurons that help bats navigate through space may also help them navigate collective social environments, finds a new study published today in the journal Nature.
Many mammals — including bats and humans — are believed to navigate with the help of a brain structure called the hippocampus, which encodes a mental “map” of familiar surroundings. For example, as you walk around your neighborhood or commute to work, individual “place” neurons in the hippocampus fire to indicate where you are.
In the new study, researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, used wireless neural ...
2023-08-30
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. and WINNIPEG, Manitoba – IHT Group, a division of Decisive Dividend Corp. (TSXV: DE) based in Winnipeg, Manitoba, is bringing patented cooling pad technology for hogs to the North American market in spring 2024.
The pads are 2-foot-by-4-foot aluminum tread plates on top of copper pipes that circulate water. Sensors in the pads determine if the hog is too hot and circulate new water to keep the pad cool. The technology was designed by researchers in Purdue University’s Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering and Department of Animal Sciences.
Heat harms hogs
Record heat across North America ...
2023-08-30
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — When an immunocompromised person’s system begins to recover and produce more white blood cells, it’s usually a good thing – unless they develop a potentially deadly inflammatory condition. New research from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign has found that the pulmonary distress often associated with the condition is caused not by damage to the lungs, but by newly populated T-cells infiltrating the brain.
Knowing this mechanism of action can help researchers and ...
2023-08-30
Venice, Italy – The International Society of Microbiota (ISM) is pleased to announce the upcoming symposium on probiotics and microbiota supplements. The symposium will take place on October 17, 2023, in Venice, Italy, one day prior to the 10th World Congress on Targeting Microbiota 2023.
About ISM 2023 Symposium:
The symposium will focus on the strain specificity of probiotics and microbiota supplements and their clinical applications for disease management. It will also elaborate on the use and mode of action of postbiotics and metabolites like the SCFA butyrate.
Speakers will present the latest research on the use of probiotics to treat a variety ...
2023-08-30
[Boston, MA, USA—August 30, 2023] Each year, the American Meteorological Society recognizes outstanding individuals and organizations in the weather, water, and climate community through its Awards and Honors program. The organization is proud to announce its 2024 recipients, who will receive their award or honor at the 104th AMS Annual Meeting in Baltimore, Maryland, 28 January–1 February, 2024.
“Working across a wide range of sciences and services, the members of our community are vital to upholding safety and quality of life in the United States and across ...
2023-08-30
While self-driving vehicles (SDVs) are being hailed as a solution for safer, more efficient roads, new research suggests British Columbians are not quite ready to embrace self-driving cars wholeheartedly – and will need a period of gradual transition before adoption.
The study, conducted by the Research on Active Transportation Lab (REACT) at the University of British Columbia, reveals mixed perceptions of automated vehicles, particularly their effects on pedestrian comfort and safety.
Do self-driving cars feel safe?
Four out of 10 participants (41 per cent) thought that pedestrians faced reduced safety and comfort levels ...
2023-08-30
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments include a novel computational tool to detect single base pair DNA changes in single-cell sequencing data, a potential target to treat hypertension caused by drugs commonly used in organ transplants, further insights into the steps involved in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Antibody shows promise for preventing organ rejection after transplantation
In a study using primates, the monoclonal antibody was successful in promoting graft survival after kidney and islet transplantations