(Press-News.org) Thursday, 31 August 2023: The largest genetic study of its kind, coordinated by the International League Against Epilepsy, including scientists from FutureNeuro at RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, has discovered specific changes in our DNA that increase the risk of developing epilepsy.
The research, published today in Nature Genetics, greatly advances our knowledge of why epilepsy develops and may inform the development of new treatments for the condition.
Epilepsy, a common brain disorder of which there are many different types, is known to have genetic component and to sometimes run in families. Here, researchers compared the DNA from diverse groups of almost 30,000 people with epilepsy to the DNA of 52,500 people without epilepsy. The differences highlighted areas of our DNA that might be involved in the development of epilepsy.
The researchers identified 26 distinct areas in our DNA that appear to be involved in epilepsy. This included 19 which are specific to a particular form of epilepsy called ‘genetic generalized epilepsy’ (GGE). They were also able to point to 29 genes that are probably contributing to epilepsy within these DNA regions.
The scientists found that the genetic picture was quite different when comparing distinct types of epilepsy, in particular, when ‘focal’ and ‘generalized’ epilepsies were compared. The results also suggested that proteins that carry electrical impulse across the gaps between neurons in our brain make up some of the risk for generalized forms of epilepsy.
“Gaining a better understanding of the genetic underpinnings of epilepsy is key to developing new therapeutic options and consequently a better quality of life for the over 50 million people globally living with epilepsy,” said Professor Gianpiero Cavalleri, Professor of Human Genetics at RCSI School of Pharmacy and Biomolecular Science and Deputy Director of the SFI FutureNeuro Research Centre.
“The discoveries we report on here could only be achieved through international collaboration, on a global scale. We are proud of how the global community of scientists working to better understand the genetics of the epilepsies have pooled resources and collaborated effectively, for the benefit of people impacted the condition” commented Professor Cavalleri.
The researchers also showed that many of the current medications for epilepsy work by targeting the same epilepsy risk genes that were highlighted in this study. However, based on their data, the researchers were able to propose some potentially effective alternative drugs. These will need to be clinically tested for use in epilepsy as they are normally used for other conditions, but they are known to target some of the other epilepsy risk genes uncovered.
“This identification of epilepsy associated genetic changes will allow us to improve diagnosis and classification of different epilepsy subtypes. This in turn, will guide clinicians in selecting the most beneficial treatment strategies, minimising seizures” said Professor Colin Doherty, Consultant Neurologist, St James’s Hospital, Co-author and Clinical Investigator at the SFI FutureNeuro Centre.
Over 150 researchers, based across Europe, Australia, Asia, South America and North America, carried out the research. They worked together as part of the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) Consortium on Complex Epilepsies. The ILAE Consortium was formed by researchers in 2010, recognising that the complexity of genetic and environmental factors underlying epilepsy would require research across massive datasets, and therefore unprecedented collaboration on an international scale.
“Undertaking such a comprehensive study is a remarkable achievement that RCSI and Futureneuro are proud to have played a leading role in. The challenge now is to translate the findings of this research to improve the lives of people with epilepsy” concluded Professor Cavalleri.
“With this study, we have bookmarked parts of our genome that should be the major focus of future epilepsy research. It will form the basis for further work looking at the molecular pathways involved in seizure generation, neuronal dysfunction and altered brain activity” said Professor Samuel Berkovic, University of Melbourne.
"This is a major milestone for the ILAE Consortium on Complex Epilepsies, demonstrating what can be achieved when scientists openly collaborate and share data from across the world. The outputs are wide-reaching and applicable to epilepsy patients globally.” said Professor Helen Cross, President of the International League Against Epilepsy.
Science Foundation Ireland (SFI) supported the work through their funding of the Futureneuro Research Centre.
ENDS
For further information:
Laura Anderson, Communications Officer, RCSI
087 199 0399/ lauraanderson@rcsi.ie
About RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences
RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences is ranked first in the world for its contribution to UN Sustainable Development Goal 3, Good Health and Well-being, in the Times Higher Education (THE) University Impact Rankings 2023.
Exclusively focused on education and research to drive improvements in human health worldwide, RCSI is an international not-for-profit university, headquartered in Dublin. It is among the top 250 universities worldwide in the World University Rankings (2023). RCSI has been awarded Athena Swan Bronze accreditation for positive gender practice in higher education.
Founded in 1784 as the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland (RCSI) with national responsibility for training surgeons in Ireland, today RCSI is an innovative, world-leading international health sciences university and research institution offering education and training at undergraduate, postgraduate and professional level.
Visit the RCSI MyHealth Expert Directory to find the details of our experts across a range of healthcare issues and concerns. Recognising their responsibility to share their knowledge and discoveries to empower people with information that leads them to better health, these clinicians and researchers are willing to engage with the media in their area of expertise.
END
Largest genetic study of epilepsy to date provides new insights on why epilepsy develops and potential treatments
2023-08-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Intracellular recycling: the key to surviving potent anti-cancer drugs
2023-08-31
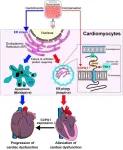
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University(TMDU) determine how cardiomyocytes protect themselves against anti-cancer medication
Tokyo, Japan – A cell contains many specialized subunits, called organelles, that carry out important tasks such as energy generation, protein synthesis, and calcium outflux. But what happens when something goes wrong with one of the organelles?
In a study recently published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology: CardioOncology, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University(TMDU) have ...
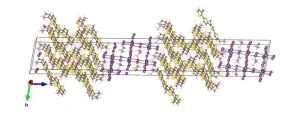
Growing triple-decker hybrid crystals for lasers
2023-08-31
By controlling the arrangement of multiple inorganic and organic layers within crystals using a novel technique, researchers at Duke University and Purdue University have shown they can control the energy levels of electrons and holes (positive charge carriers) within a class of materials called perovskites. This tuning influences the materials’ optoelectronic properties and their ability to emit light of specific energies, demonstrated by their ability to function as a source of lasers.
Appearing online August 31 in the journal Nature Chemistry, the research is the result of a close collaboration between several ...
Positive framing of genomics met with scepticism in some communities
2023-08-31
August 31, 2023 - New research published today in Human Genetics and Genomics Advances reveals the difference between ‘what we say’ and ‘what people hear’ when engaging underrepresented communities around genomics and healthcare.
Genomics datasets, which underpin the ability to interpret all genetic tests, are known to consist of DNA from predominately white, Northern European populations. As genomics becomes an increasingly important part of everyday healthcare*, barriers to diverse participation must be overcome so that everyone can benefit from genomic medicine, not just the privileged few.
The research ...
People who are in good shape take fewer mental-health related medication
2023-08-31
“We find that people who are in better shape fill fewer prescriptions for anxiety and depression medications,” says Linda Ernstsen, the senior author of the article and an associate professor from the Department of Public Health and Nursing at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU).
The research group based its work on the Trøndelag Health Study (HUNT). Since 1984, 250,000 Trøndelag residents have voluntarily contributed their health data to this comprehensive ...
Breathe! The shape-shifting ball that supports mental health
2023-08-31
A soft ball that ‘personifies’ breath, expanding and contracting in synchronicity with a person’s inhalations and exhalations, has been invented by a PhD student at the University of Bath in the UK. The ball is designed to support mental health, giving users a tangible representation of their breath to keep them focused and to help them regulate their emotions.
Alexz Farrall, the student in the Department of Computer Science who invented the device, said: "By giving breath physical form, the ball enhances self-awareness and engagement, fostering positive mental health outcomes."
Generally, ...
Out with the old, in with the new: Agile mentorship to support future scientists
2023-08-31
INDIANAPOLIS – Mentorship has existed throughout history. Socrates mentored Plato, who, in turn, mentored Aristotle. Humphry Davy, the chemist who was the first to isolate potassium, sodium and at least five other elements, mentored Michael Faraday, inventor of the world’s first electric generator. Sigmund Freud mentored Carl Jung. Science teacher Elizabeth Mommaerts mentored Sally Ride. Maya Angelou mentored Oprah Winfrey. The list of knowledge bearers and knowledge seekers who have connected meaningfully goes ...
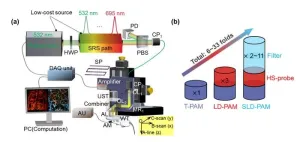
CityU researchers develop ultra-sensitive photoacoustic microscopy for wide biomedical application potential
2023-08-31
Optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy is an up-and-coming biomedical imaging technique for studying a broad range of diseases, such as cancer, diabetes and stroke. But its insufficient sensitivity has been a longstanding obstacle for its wider application. Recently, a research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) developed a multi-spectral, super-low-dose photoacoustic microscopy system with a significant improvement in the system sensitivity limit, enabling new biomedical applications and clinical translation in the future.
Photoacoustic ...
Henry Ford Health Hospitals earn full reaccreditation from National Accreditation Program for Breast Centers
2023-08-31
DETROIT – All five of Henry Ford Health’s acute care hospitals have earned a full three-year reaccreditation by the National Accreditation Program for Breast Centers (NAPBC), a quality program administered by the American College of Surgeons. With Henry Ford Hospital Detroit, Henry Ford Jackson Hospital, Henry Ford Macomb Hospital, Henry Ford West Bloomfield Hospital and Henry Ford Wyandotte Hospital earning full reaccreditation, Henry Ford has the highest number of Commission on Cancer and NAPBC-accredited hospitals of any health system in Michigan.
“The NAPBC accreditation is reflective of our unwavering commitment ...
Is digital media use a risk factor for psychosis in young adults?
2023-08-31
On average, young adults in Canada spend several hours on their smartphones every day. Many jump from TikTok to Netflix to Instagram, putting their phone down only to pick up a video game controller. A growing body of research is looking into the potential dangers of digital media overuse, as well as potential benefits of moderate digital media use, from a mental health standpoint.
A recent McGill University study of 425 Quebecers between the ages of 18 and 25 has found that young adults who have more frequent psychotic experiences also tend to spend more time using digital media. Interestingly, the study, which surveyed the participants ...
Why men, wealthy people and maritime residents are more likely to develop skin cancer
2023-08-31
A new study led by McGill University examines why people living in Atlantic regions are more at-risk for developing melanoma than other Canadians, providing lessons on skin cancer prevention for the whole country.
Rates of melanoma, a deadly form of skin cancer, have been rising globally, including in Canada. Current estimates indicate that up to 1 in 3 Canadians will develop some form of skin cancer during their lifetime. While some Atlantic provinces such as Prince Edward Island (PEI) and Nova Scotia have the highest incidence rate of melanoma in the country, neighbouring provinces like New Brunswick ...