(Press-News.org) *Note- this is an early release from the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) meeting in Hamburg, October 2-6. Please credit the meeting if you use this story*
New research to be presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 October) shows that use of low dose (100mg daily) aspirin among older adults aged 65 years and older is associated with a 15% lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The authors, led by Professor Sophia Zoungas, School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia, say the results show that anti-inflammatory agents such as aspirin warrant further study in the prevention of diabetes.
The effect of aspirin on incident type 2 diabetes among older adults remains uncertain. This study investigated the randomised treatment effect of low dose aspirin on incident diabetes and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels among older adults. The authors did a follow-up study of the ASPREE trial - a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of aspirin, the principal results of which were published in NEJM in 2018. The original study showed that aspirin conferred a 38% increased risk of major haemorrhage in older adults without any reduction in incidence of cardiovascular disease.
The study enrolled community-dwelling individuals aged 65 years or over, and free of cardiovascular disease, independence-limiting physical disability and dementia. Participants were randomised 1:1 to 100 mg daily aspirin or placebo. Incident diabetes was defined as self-report of diabetes, commencement of glucose lowering medication, and/or a fasting plasma glucose (FBP) level of 7.0 mmol/L or higher at annual follow-up visits. Patients with diabetes at the start of the study were excluded. Computer and statistical modelling assessed the effect of aspirin on incident diabetes and FPG levels respectively.
A total of 16,209 participants were included in the analysis (8,086 randomised to aspirin and 8,123 to placebo). Over a median follow-up of 4.7 years, 995 incident diabetes cases were recorded (aspirin: 459, placebo: 536). Compared with placebo, the aspirin group had a 15% reduction in incident diabetes and a slower rate of increase in FPG (difference in annual FPG change: -0.006 mmol/L).
The authors say: “Aspirin treatment reduced incident diabetes and slowed the increase in fasting plasma glucose over time among initially healthy older adults. Given the increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes among older adults, the potential for anti-inflammatory agents like aspirin to prevent type 2 diabetes or improve glucose levels needs further study.”
However, Professor Zoungas adds: “The earlier published trial findings from ASPREE in 2018 showed aspirin did not prolong healthy independent living, but was associated with a significantly increased risk of bleeding, primarily in the gastrointestinal tract. Major prescribing guidelines now recommend older adults take daily aspirin only when there is a medical reason to do so, such as after a heart attack.”
“Although these new findings are of interest, they do not change the clinical advice about aspirin use in older people at this time.”
END
Study shows that low-dose aspirin associated with a 15% lower risk of developing diabetes in people aged over 65 years
However due to risk of bleeding in elderly, major prescribing guidelines now recommend older adults take daily aspirin only when there is a medical reason to do so, such as after a heart attack
2023-09-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New grant to optimize gut microbes, boost health benefits of broccoli
2023-08-31
URBANA, Ill. — Love it or hate it, broccoli is chock-full of health-promoting chemicals linked to heart health, cancer prevention, immune function, weight management, and more. However, some people are less efficient than others at unlocking those chemical benefits. A research team at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign suggests gut microbe communities may be responsible for the variation. With a new grant from the USDA’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture, the team plans to identify which microbes maximize the benefits of broccoli and other brassica ...
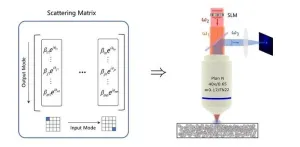
Illuminating new horizons: Navigating nonlinear scattering with precision
2023-08-31
In the intricate world of light, a journey through inhomogeneous media often leads to distortions in space, time, spectrum, and polarization. These distortions, detrimental to applications like optical manipulation, imaging, and communication, have long posed a challenge. Enter the art of wavefront shaping (WS) — a potent tool for correcting these wave maladies in linear optics. But that's not all. Nonlinearity adds a twist, finding purpose in fields from biological sensing to phototherapy. Now, picture combining these forces — ...
Digging deeper into how vaccines work against parasitic disease
2023-08-31
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists have established the effectiveness of vaccines they developed to prevent the disfiguring skin disease leishmaniasis in animal studies, and Phase 1 human trial planning is in motion for the most promising candidate.
But in new work, the research team has determined how these vaccine candidates, created using mutated disease-causing parasites, prompt molecular-level changes in host cells that have specific roles in helping generate the immune response.
Despite using the same CRISPR ...
Housing heroes: New program to support veterans experiencing homelessness
2023-08-31
Since 2009, the number of veterans experiencing homelessness across the United States has shrunk by more than 50%, according to a 2022 Department of Housing report.
With the support of a $150,000 grant from the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), the University of Missouri School of Law Veterans Clinic is aiming to continue this trend here at home with a new program designed to further empower veterans in taking steps out of homelessness.
The Veterans Outreach Program will help attorneys connect with veterans experiencing homelessness with the goal of offering them the legal assistance ...
Mapping the coronavirus spike protein could provide insight into vaccine development
2023-08-31
Although the COVID-19 pandemic was the first time most of humanity learned of the now infamous disease, the family of coronaviruses was first identified in the mid-1960s. In a new study, molecular biologist Steven Van Doren, a scientist in the University of Missouri College of Agriculture, Food and Natural Resources, has uncovered unexpected actions of a key player in how the coronavirus infects its target — a discovery that could guide further vaccine development.
Funded by a National Science Foundation (NSF) grant, Van Doren and his team studied the fusion peptide, an important feature of the spike protein that serves to bind the virus with ...
Dectin-1 stimulation promotes distinct inflammatory signature in HIV and aging
2023-08-31
“To our knowledge, our study is the first to evaluate the specific function of Dectin-1 in the setting of aging and HIV-infection.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 31, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 16, entitled, “Dectin-1 stimulation promotes a distinct inflammatory signature in the setting of HIV-infection and aging.”
Dectin-1 is an innate immune receptor that recognizes and binds β-1, 3/1, 6 glucans on fungi. In this new study, researchers Archit Kumar, Jiawei Wang, Allen Esterly, Chris ...
Excess ceramide and disrupted iron metabolism in neuronal mitochondria found to be the cause for MEPAN syndrome
2023-08-31
A recent study published in Nature Metabolism has revealed the pathogenic mechanism underlying a rare pediatric neurodegenerative disorder known as mitochondrial enoyl reductase protein-associated neurodegeneration (MEPAN) syndrome. The study was led by Dr. Hugo J. Bellen, distinguished service professor at Baylor College of Medicine, and Chair of Neurogenetics at the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children’s Hospital (Duncan NRI), and Dr. Debdeep Dutta, a postdoctoral fellow in the Bellen lab. The Duncan NRI team found that in patients and animal models of this disorder, a large number of neurons ...
A new approach to stop cancer growth?
2023-08-31
CLEVELAND– Case Western Reserve University biochemical researchers have identified a new function of a key protein that leads to cancer–a finding they believe could lead to more effective treatments for a range of cancers and other diseases.
The protein is LSD1 (lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A), which functions as a type of traffic cop inside human cells. It controls gene activity during embryonic development and regulating gene expression throughout life.
Scientists have also identified in recent years that the overexpression of LSD1—in this instance, producing too many proteins—can ...
Study: ‘Suicidal’ mechanism discovered in ion channel receptors enables the sensing of heat and pain
2023-08-31
BUFFALO, N.Y. – The ability to accurately detect heat and pain is critical to human survival, but scientists have struggled to understand on a molecular level exactly how our bodies sense these potential risks.
Now, University at Buffalo researchers have unraveled the complex biological phenomena that drive these critical functions. Their research, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on Aug. 28, has uncovered a previously unknown and completely unexpected “suicidal” reaction in ion channel receptors that explains the complicated mechanisms that underlie sensitivity to temperature and pain.
The ...
Scientists unpick how lung cells induce immune response to influenza
2023-08-31
Researchers from Trinity College Dublin have discovered some new and surprising ways that viral RNA and influenza virus are detected by human lung cells, which has potential implications for treating people affected by such viruses.
Influenza viruses remain a major threat to human health and can cause severe symptoms in young, elderly, and immuno-compromised populations, leading to annual epidemics which endanger between 3 and 5 million people of severe illness and cause 290,000 to 650,000 deaths worldwide.
These viruses primarily target respiratory epithelial cells ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Study shows that low-dose aspirin associated with a 15% lower risk of developing diabetes in people aged over 65 yearsHowever due to risk of bleeding in elderly, major prescribing guidelines now recommend older adults take daily aspirin only when there is a medical reason to do so, such as after a heart attack