(Press-News.org) EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE AT 2 P.M. ET FRIDAY, SEPT. 1, 2023
Photos
ANN ARBOR—A new University of Michigan-led study finds that farmers in India have adapted to warming temperatures by intensifying the withdrawal of groundwater used for irrigation. If the trend continues, the rate of groundwater loss could triple by 2080, further threatening India's food and water security.
Reduced water availability in India due to groundwater depletion and climate change could threaten the livelihoods of more than one-third of the country's 1.4 billion residents and has global implications. India recently overtook China to become the world's most populous nation and is the second-largest global producer of common cereal grains including rice and wheat.
"We find that farmers are already increasing irrigation use in response to warming temperatures, an adaptation strategy that has not been accounted for in previous projections of groundwater depletion in India," said study senior author Meha Jain, assistant professor at U-M's School for Environment and Sustainability. "This is of concern, given that India is the world's largest consumer of groundwater and is a critical resource for the regional and global food supply."
The lead author is Nishan Bhattarai of the Department of Geography and Environmental Sustainability at the University of Oklahoma, formerly a postdoctoral researcher in Jain's U-M lab.
The study, scheduled for online publication Sept. 1 in the journal Science Advances, analyzed historical data on groundwater levels, climate and crop water stress to look for recent changes in withdrawal rates due to warming. The researchers also used temperature and precipitation projections from 10 climate models to estimate future rates of groundwater loss across India.
Previous studies have focused on the individual effects of climate change and groundwater depletion on crop production in India. Those studies did not account for farmer decision-making, including how farmers may adapt to changing climate through changes in irrigation decisions.
The new study takes into account the fact that warmer temperatures may increase water demand from stressed crops, which in turn may lead to increased irrigation by farmers.
"Using our model estimates, we project that under a business-as-usual scenario, warming temperatures may triple groundwater depletion rates in the future and expand groundwater depletion hotspots to include south and central India," Bhattarai said.
"Without policies and interventions to conserve groundwater, we find that warming temperatures will likely amplify India's already existing groundwater depletion problem, further challenging India's food and water security in the face of climate change."
Previous studies found that climate change could decrease the yield of staple Indian crops by up to 20% by mid-century. At the same time, the country's groundwater is being depleted at an alarming rate, primarily because of water withdrawal for irrigation.
For the newly published study, the researchers developed a dataset that contains groundwater depths from thousands of wells across India, high-resolution satellite observations that measured crop water stress, and temperature and precipitation records.
Most climate models call for increased temperature, increased monsoon (June through September) precipitation and decreased winter precipitation in India over the coming decades. The U-M-led research team found that warming temperatures coupled with declining winter precipitation more than offset added groundwater recharge from increased monsoon precipitation, resulting in accelerated groundwater declines.
Across various climate-change scenarios, their estimates of groundwater-level declines between 2041 and 2080 were more than three times current depletion rates, on average.
In addition to Jain and Bhattarai, authors of the Science Advances study are David Lobell of Stanford University, Balwinder Singh of the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center in India and the Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development in Western Australia, Ram Fishman of Tel Aviv University, William Kustas of the U.S. Department of Agriculture and Yadu Pokhrel of Michigan State University.
The research was funded by a NASA Land-Cover Land-Use Change Grant and a NASA new investigator program award to Jain. It was supported in part by the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Agricultural Research Service.
Study: Warming temperatures exacerbate groundwater depletion rates in India (available when embargo lifts)
END
Groundwater depletion rates in India could triple in coming decades as climate warms, study shows
2023-09-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Toxic molds, fossil fuels, antibiotics linked to chemical intolerance: Survey
2023-09-01
SAN ANTONIO (Sept. 1, 2023) — What initiates chemical intolerance (CI)? In a newly released survey of thousands of U.S. adults, respondents most frequently cited exposures to biological sources, such as mold and algae “blooms,” and/or fossil fuels, their combustion products and synthetic chemical derivatives such as pesticides, plastics and persistent organic pollutants.
It's an issue in the news, as toxic mold spawned by the moisture left behind by flood waters from Hurricane ...
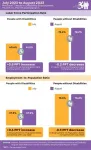
nTIDE August 2023 Jobs Report: Record-breaking employment trend continues for people with disabilities
2023-09-01
East Hanover, NJ – September 1, 2023 – Labor Day weekend brings more good news for people with disabilities, with record-breaking highs for labor force participation and employment-to-population ratio, according to today’s National Trends in Disability Employment – semi-monthly update (nTIDE), issued by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD). In comparison, both indicators declined slightly for people without disabilities.
Month-to-Month nTIDE Numbers (comparing July 2023 to August 2023)
Based on data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) Jobs Report released ...
Air pollution has decreased across the US, but new Yale research finds health burdens remain unequal among racial groups
2023-09-01
New Haven, Conn. — Health benefits that have resulted from reductions in fine particulate air pollution aren’t distributed equally among populations in the U.S., a new Yale-led study finds. Racial and ethnic minorities — and Black people in particular — still experience disproportionately high rates of cardiovascular disease-related deaths caused by exposure to fine particulate matter, according to the research.
The findings were published Aug. 31 in Nature Human Behavior.
Fine particulate matter, also known as PM2.5, consists of particles or droplets smaller than 2.5 micrometers in diameter, or ...
Precarious employment conditions can increase risk of early death
2023-09-01
People without a secure job contract can reduce their risk of premature death by 20 per cent if they gain permanent employment, a study from Karolinska Institutet published in The Journal of Epidemiology and Community reports. According to the researchers, the results indicate that job security on the Swedish labour market needs to improve.
Precarious employment is a term that is used to describe jobs with short contracts (e.g. temping), low wages and a lack of influence and rights, all of which lead to a working life without predictability and security.
In the present study, the researchers have examined how this affects the risk of death.
“This is ...
Alaska scientists heading to Greenland for glacier research, museum project
2023-09-01
University of Alaska Fairbanks scientists will make several trips to Greenland over two years to study how meltwater and the ocean affect glacial ice loss.
The four-year research project, funded by a $565,000 National Science Foundation grant, will create a traveling museum exhibit about the drivers of Arctic climate change. The exhibit will appear first at the University of Alaska Museum of the North, likely in 2026.
Ice loss from the polar ice sheets is the largest anticipated contributor to global mean-sea-level rise in the coming century. Scientists need to better understand glacier behavior to improve predictions of sea-level rise.
At the study’s conclusion, ...
Native American patients were sicker and more likely to die during the COVID-19 pandemic, UNM researchers find
2023-09-01
When the COVID-19 pandemic swept into New Mexico in the spring of 2020, seriously ill patients from all over the state were brought to The University of New Mexico Hospital in Albuquerque, where many wound up in intensive care, breathing with the help of ventilators.
Early on, researchers from the UNM Center for Global Health launched a study of hospitalized patients to gauge the severity of symptoms from the infection, gathering data on 475 patients from April 2020 through December 2021.
In paper published this week in PNAS Nexus, ...
New research explains “Atlantification” of the Arctic Ocean
2023-09-01
New research by an international team of scientists explains what’s behind a stalled trend in Arctic Ocean sea ice loss since 2007. The findings indicate that stronger declines in sea ice will occur when an atmospheric feature known as the Arctic dipole reverses itself in its recurring cycle.
The many environmental responses to the Arctic dipole are described in a paper published online today in the journal Science. This analysis helps explain how North Atlantic water influences Arctic Ocean climate. Scientists call it Atlantification.
The research is led by professor Igor Polyakov of the University of Alaska Fairbanks College of ...
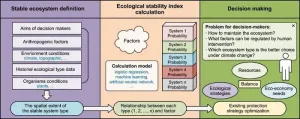
Landscape-based methodology reveals ecological stability in the Qingzang plateau
2023-09-01
In a groundbreaking study published in Volume 17 of the journal Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences introduced a landscape-oriented framework to assess ecological stability in China's Qingzang Plateau (QP). The QP demonstrated a medium-high stability level with minimal changes in recent years. Ecological stability involves understanding changes in ecosystem components over time, with two major concepts explored: systems close to equilibrium and non-equilibrium behavior. Despite lacking a consensus on the definition of "ecological stability", stability indices ...
Research explores why daughters in Chinese families of son preference fail to break from sustained exploitation
2023-09-01
New research from Lancaster University Management School (LUMS) unveils the extent of sustained exploitation within many Chinese families that have a clear preference for sons over daughters – and why daughters can stay ‘trapped’ in this situation throughout their lives.
The new study explores Chinese families that have a strong preference for sons, where daughters are expected to make substantial financial or labour contributions to their parents before and after marriage– often to subsidise the schooling and living ...
Adding immune modulator to targeted therapy does not improve survival in difficult-to-treat thyroid cancer
2023-09-01
Results of a multicenter phase II clinical trial led by the University of Chicago Medicine Comprehensive Cancer Center show that adding an immunomodulatory agent to treatment with the targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) cediranib did not make a difference in outcomes for treating patients with an advanced form of thyroid cancer that develops from thyroid follicular cells called differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC).
The findings were published in Annals of Oncology on May 13, 2023.
Most patients with DTC receive successful treatment. But a small group develops cancer that recurs or spreads to other parts of the body, making it hard to treat with traditional methods like ...