(Press-News.org) Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 04 September 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. New ACP paper addresses ethical issues in determining death; recommends clarification to the Uniform Determination of Death Act
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-1361
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
The American College of Physicians (ACP) has issued a new paper addressing current controversies about the standards for determining death, supporting a clarification to the Uniform Determination of Death Act (UDDA) but otherwise reaffirming the current UDDA and the ethical principles that are its foundation. The paper is published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Highly publicized legal cases have challenged the standards used to determine brain death and clinical questions have arisen about the use of the word “irreversible” when death is declared, sparking re-examination of the UDDA. The Uniform Law Commission appointed a committee that has been debating whether to revise the 1981 UDDA, the legal standard in the United States. Competing revisions have been proposed, including everything from eliminating brain death altogether to stipulating that brain death means only the loss of certain specified functions. Also of concern is the extent to which issues of organ transplantation and organ availability seem to be influencing efforts to modify the UDDA. While revisiting the more than 40-year-old UDDA is clearly indicated, ACP urges caution – and recommends that only a clarification revision is needed.
The paper also includes a glossary of important concepts and their definitions to further clarify these complex issues. Developed by ACP’s Ethics, Professionalism and Human Rights Committee, ACP believes physicians should advocate for policies and practices on the determination of death that are consistent with the medical profession’s fundamental commitment to individual patients and to the public and supports:
Revising the Uniform Determination of Death Act to replace the word “irreversible” with “permanent” in clarifying the permanent cessation of circulatory and respiratory functions, but retaining the word irreversible in describing brain death (the “irreversible cessation of all functions of the entire brain…”).
Maintaining circulatory and whole brain (neurologic) standards for determining death as separate, independent standards, consistent with current medical practice and with respect for established standards as well as for those cultures and religious traditions that accept only the circulatory determination of death.
Retaining the whole brain standard for determining death according to neurologic criteria and opposing “higher brain” function standards.
Aligning medical tests used for determining death with legal standards, not the other way around, asserting that medical criteria or tests should not be specified in the UDDA as they do not define death but rather, indicate whether death has occurred.
Acknowledging that determination of death is a distinct issue from organ transplantation, and that the criteria for determining death should not be governed by the need to procure organs for transplantation.
Calling for additional education for physicians, other clinicians, and the public about how death is determined and improving communication about the determination of death and dying process.
Media contacts: For an embargoed PDF, please contact Angela Collom at acollom@acponline.org. To speak with someone from ACP, please contact Andrew Hachadorian at ahachadorian@acponline.org.
----------------------------
2. Pharmacy Discount Card Programs Like Amazon Prime and GoodRx Gold Could Save Patients Millions Of Dollars In Out-of-Pocket Costs For Commonly Prescribed Generic Medications
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-0644
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
A nationally representative study found that at least one out of five prescriptions for commonly prescribed generic medications were cheaper through Amazon Prime or GoodRx Gold discount cards compared to actual out-of-pocket (OOP) payments made by patients. The authors also highlight the disproportionately higher frequency of OOP payments exceeding discount card pricing for various vulnerable subgroups like the uninsured and those in the no coverage (deductible) phase. The findings are published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Researchers from University of Toledo Colege of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences compared OOP payments obtained from 2020 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) to 2023 counterfactual discount card pricing (Amazon Prime and GoodRx Gold) for 20 commonly prescribed generic medications. They estimated the proportion and extent of OOP payments exceeding Amazon and GoodRx discount card pricing benchmarks (referred to as “excess OOP payment”). Results indicate that OOP payments made by patients exceeded Amazon and GoodRx prices for about 20% and 43% of prescriptions evaluated, respectively. Proportion of excess OOP payment was 40% and 79% for prescriptions assumed to be in the no coverage (deductible) phase, respectively. Lastly, the estimated cumulative OOP cost-savings, assuming patients obtained their medications using Amazon and GoodRx discount cards, amount to approximately $969 million and $1.83 billion, respectively. The authors caution that while some discount card programs may provide out-of-pocket cost relief for select generic medications, their dependence on pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) for claims adjudication and access to pharmacy networks hinder long-term solutions. They say addressing OOP costs effectively requires policy reforms supporting the adoption of value-based insurance designs for a lasting and comprehensive strategy.
Media contacts: For an embargoed PDF, please contact Angela Collom at acollom@acponline.org. To speak with the corresponding author Pranav M. Patel, PharmD, MS, please email Tyrel Linkhorn at tyrel.linkhorn@utoledo.edu
----------------------------
3. Low-cost generic drug programs have large gaps in coverage for core evidence-based CVD medications
Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company Demonstrated Most Comprehensive Coverage
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-0287
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
A cross-sectional study of 19 low-cost generic programs (LCGPs) found that their medication coverage for six cardiovascular diseases (CVD) varied significantly between programs. Of all analyzed programs, Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company demonstrated the most comprehensive coverage for all diseases included in the study. The findings are published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States, and CVD medicines form the foundation of disease state management. However, rising prescription costs and insurance restrictions have imposed barriers to medication availability, leading to health disparities, poor patient adherence,
and poor health outcomes. To reduce cost and improve medication availability, many pharmacies have developed LCGPs to help low-income or uninsured patients gain greater access to affordable medicines. Although LCGPs all share the same purpose of improving medication availability and affordability, their formularies may vary widely.
Researchers from Western University of Health Sciences conducted a cross-sectional study of 19 LCGPs and evaluated the proportion of programs that offered evidence-based CVD medicines within a clinical framework for 6 cardiovascular diseases, including atrial fibrillation, heart failure, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, post–acute coronary syndrome secondary prevention, and stable angina. The authors found that the availability of CVD medication varied by program, drug, and condition. They report that LCGPs affiliated with H-E-B, Kroger, Walmart, and Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drug Company had the most breadth and choice of coverage. They also note that almost all LCGPs offered angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, b -blockers, thiazides, and moderate-intensity statins, but availability was low for higher-cost or lower-use generics. The authors suggest that LCGPs should identify existing limitations in their coverage and continuously revise their formularies to improve the comprehensiveness of CVD medication coverage.
Media contacts: For an embargoed PDF, please contact Angela Collom at acollom@acponline.org. To speak with the corresponding author Cynthia A. Jackevicius, BScPhm, PharmD, MSc, please contact cjackevicius@westernu.edu.
--------------------------------
4. Atypical antipsychotics not safer than haloperidol for older adults with postoperative delirium
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M22-3021
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
A study of more than 17,000 older adults prescribed an antipsychotic medication after major surgery found that atypical antipsychotics are not less harmful than haloperidol. The findings are published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Postoperative delirium is the most common complication after major surgery in older adults. It is associated with longer hospital stays, institutional discharge, decline in function, mortality, and increased healthcare costs. Nonpharmacologic interventions are recommended for initial treatment of delirium, but antipsychotics are still often used to manage behavioral symptoms. Previous research found that the use of haloperidol has declined, and atypical antipsychotic use has increased over time. Such trends reflect clinicians’ perception that atypical antipsychotics are less harmful than haloperidol.
Researchers from Hebrew SeniorLife, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School studied 17,115 patients aged 65 years and older without psychiatric disorders who were prescribed an oral antipsychotic drug after major surgery to compare the risk for in-hospital adverse events. The authors found that among four antipsychotics, there was no statistically significant difference in the risk for in-hospital death among patients treated with haloperidol, olanzapine, quetiapine, and risperidone. The risk for nonfatal clinical events ranged from 2.0% to 2.6% for a cardiac arrhythmia event, 4.2% to 4.6% for pneumonia, and 0.6% to 1.2% for stroke or transient ischemic attack, with no statistically significant differences by treatment group. The authors recommend reducing antipsychotic use altogether as there is no safer antipsychotic drug option and focusing concerted clinical and health policy efforts and investment in nonpharmacologic interventions for delirium prevention and management.
Media contacts: For an embargoed PDF, please contact Angela Collom at acollom@acponline.org. To speak with the corresponding author Dae Hyun Kim, MD, ScD, please contact Michael Chmura at MichaelChmura@hsl.harvard.edu.
--------------------------------
Also in this issue:
Insulins and the Evolving Landscape of U.S. Prescription Drug Pricing
Mariana P. Socal, MD, PhD; and Ge Bai, PhD, CPA
Ideas and Opinions
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-1105
END
Pharmacy discount card programs like Amazon Prime and GoodRx gold could save patients millions of dollars in out-of-pocket costs for commonly prescribed generic medications
2023-09-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Farms that create habitat key to food security and biodiversity
2023-09-04
It seems intuitive that forests would provide better habitat for forest-dwelling wildlife than farms. Yet, in one of the longest-running studies of tropical wildlife populations in the world, Stanford researchers found that over 18 years, smaller farms with varying crop types – interspersed with patches or ribbons of forest – sustain many forest-dependent bird populations in Costa Rica, even as populations decline in forests.
In a paper published Sept. 4 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Nicholas Hendershot and colleagues ...
The art of wandering in vertebrates: new mapping of neurons involved in locomotion
2023-09-04
For those fortunate enough to walk normally, wandering is such an expected behavior that we hardly consider that it involves complex, partly involuntary processes. “Animals move to explore their environment in search of food, interaction with others, or simply out of curiosity. But the perception of danger or a painful stimulus can also activate an automatic flight reflex”, Martin Carbo-Tano, a post-doctoral fellow at Paris Brain Institute, explains. In both cases, movement initiation relies on the activation of so-called reticulospinal control neurons, which form an intertwined network in ...
Most species are rare. But not very rare
2023-09-04
Halle/Saale, Fort Lauderdale. More than 100 years of observations in nature have revealed a universal pattern of species abundances: Most species are rare but not very rare, and only a few species are very common. These so-called global species abundance distributions have become fully unveiled for some well-monitored species groups, such as birds. For other species groups, such as insects, however, the veil remains partially unlifted. These are the findings of an international team of researchers led by the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv), the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg ...
Extreme El Niño weather saw South America’s forest carbon sink switch off
2023-09-04
Extreme El Niño weather saw South America’s forest carbon sink switch off
Hot and dry conditions resulted in increased tree death
Evidence that most forest areas withstand periods of severe drought
Greatest impact in forests with drier climates
Tropical forests in South America lose their ability to absorb carbon from the atmosphere when conditions become exceptionally hot and dry, according to new research.
For a long time, tropical forests have acted as a carbon sink, taking more ...
Blowing snow contributes to Arctic warming
2023-09-04
When it comes to global warming trends, the Arctic is a troubling outlier. The Arctic warms nearly four times faster than the global average, and aerosols play an important role in that warming. Scientists have long known that pollutants from other regions can accumulate in the Arctic atmosphere where they alter atmospheric chemistry, absorb sunlight, and affect local weather patterns, leading to localized warming that melts ice and snow. Sea salt particles dominate aerosol mass concentration, but their production mechanisms and impact on Arctic climate have remained unclear.
Atmospheric scientists led by Jian Wang, director of the Center for Aerosol ...
Innovative solutions for chemical challenges: Harnessing the potential of machine learning
2023-09-04
In a review published in Engineering, scientists explore the burgeoning field of machine learning (ML) and its applications in chemistry. Titled “Machine Learning for Chemistry: Basics and Applications,” this comprehensive review aims to bridge the gap between chemists and modern ML algorithms, providing insights into the potential of ML in revolutionizing chemical research.
Over the past decade, ML and artificial intelligence (AI) have made remarkable strides, bringing us closer to the realization of intelligent machines. The advent of deep learning methods and enhanced data storage capabilities has played a pivotal role in this progress. ML has already demonstrated success ...
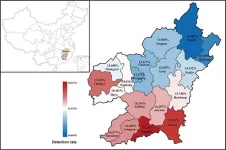
Uncovering thalassemia diversity in southern china through next-generation sequencing
2023-09-04
Around 5.2% of the global population carries abnormal hemoglobin genes [1]. Each year, 300,000 to 500,000 children are born with severe hemoglobinopathies worldwide, with approximately 80% of these cases occurring in developing countries [2]. Thalassemia is the most common hereditary hemoglobinopathy and occurs in 4.4 out of every 10,000 live births [3]. It is prevalent in Mediterranean coastal areas, Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and southern China.
A previous study indicated that Ganzhou, the southernmost city in Jiangxi province, had a thalassemia prevalence ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers develop novel tumor-targeting nanospheres with the potential to dramatically improve light-based cancer diagnosis and treatment
2023-09-04
Abu Dhabi, UAE (September 4, 2023) – In a breakthrough in cancer therapeutics, a team of researchers at the Magzoub Biophysics Lab at NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) has made a significant advance in light-based therapies – biocompatible and biodegradable tumor-targeting nanospheres that combine tumor detection and monitoring with potent, light-triggered cancer therapy to dramatically increase the efficacy of existing light-based approaches.
Non-invasive, light-based therapies, photodynamic therapy (PDT) and photothermal therapy (PTT) have the potential to be safe and effective alternatives to conventional cancer treatments, which are beset by a ...
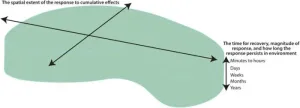
Ecosystem footprint concept and its potential applications in environmental management
2023-09-04
Traditionally, the impact of human activity on an ecosystem has lacked context when planning restorative ecosystem mitigation and management strategies. Multiple human activities over time and space, the resilience of a particular ecosystem, and the stress caused by many individual or related, overlapping activities that generate cumulative effects may affect the overall "ecosystem response footprint," or ability of an ecosystem to adapt and change to human activity.
A team of marine scientists reviewed the most recent perspectives on ecological footprints to rigorously define the term "ecosystem response footprint" as the ...
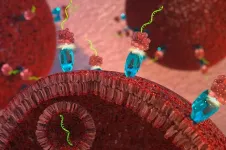
First-in-class targeted microRNA therapy slows cancer tumor growth
2023-09-04
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – A new cancer therapy developed by Purdue University researchers attacks tumors by tricking cancer cells into absorbing a snippet of RNA that naturally blocks cell division. As reported today in Oncogene, tumors treated with the new therapy did not increase in size over the course of a 21-day study, while untreated tumors tripled in size over the same time period.
Cancer can begin almost anywhere in the human body. It is characterized by cells that divide uncontrollably and that may be able to ignore signals to ...