(Press-News.org) The diagnosed severity of aortic stenosis strongly correlates with clinical outcomes, new Kaiser Permanente research shows. But the study also suggests that fine-tuning physician assessment of those patients with moderate aortic stenosis could help improve outcomes and better determine which patients might benefit from surgery.
The study found that patients diagnosed with moderate aortic stenosis have outcomes most similar to those categorized with mild aortic stenosis while only those with moderate-to-severe aortic stenosis had outcomes similar to those with severe aortic stenosis.
“Moderate aortic stenosis represents a wide spectrum of disease,” said Matthew D. Solomon, MD, PhD, a physician researcher at the Kaiser Permanente Division of Research and a cardiologist at The Permanente Medical Group. “Despite controversy in the field about the prognosis for these patients, our results show that moderate aortic stenosis patients have a different trajectory than those with severe aortic stenosis, and that they can be safely followed with close surveillance.”
The new study included nearly 547,000 Kaiser Permanente Northern California patients who had an echocardiogram between 2008 and 2018 to determine if they had aortic stenosis. Close to 50,000 patients were identified as having mild, mild-to-moderate, moderate, moderate-severe, or severe aortic stenosis. The research team analyzed associations between the physician assessments and the patients’ clinical outcomes — hospitalization for heart problems, surgery to replace the aortic valve, or death.
The study was funded by The Permanente Medical Group Delivery Science and Applied Research Program.
END
Large Kaiser Permanente study could lead to better management for patients with aortic stenosis
2023-09-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Landmark NIH grant awarded to School of Nursing and Health Studies
2023-09-05
The University of Miami School of Nursing and Health Studies (SONHS) has been awarded an unprecedented $23.57 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to join the Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO) Program.
The interdisciplinary grant, the largest award to date in the Coral Gables Campus’ history, is funding an ambitious project spearheaded by Hudson Santos, RN, PhD, FABMR, FAAN, the lead Principal Investigator and Vice Dean for Research Affairs, with Professor Michael Paidas, MD, chair of the University of Miami Miller School of Medicines Department of Obstetrics, ...
Study reveals disparities within NHS leadership
2023-09-05
New research shows that Allied Health Professions (AHPs) are significantly underrepresented in senior leadership roles despite being the third largest workforce in the NHS.
Ranging from paramedics to podiatrists, the AHPs encompass various healthcare disciplines, constituting a workforce of 185,000 within the NHS.
However AHPs have historically been underrepresented in strategic leadership positions, often occupied by medical professionals. To address this, NHS England advocated for the establishment of a Chief AHP role in every Trust to harness the untapped potential of this workforce and increase diversity in leadership ...
Eating a vegan diet could reduce grocery bill 16%, a savings of more than $500 a year, finds new research
2023-09-05
WASHINGTON, D.C.—Food costs decrease 16% on a low-fat vegan diet, a savings of more than $500 a year, compared to a diet that includes meat, dairy, and other animal products, according to a new analysis from the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine published in JAMA Network Open.
“We knew that a vegan diet significantly reduces your risk of conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and obesity—and now we have proof that opting for beans instead of beef will also lead to significant savings on your grocery bill,” says study co-author Hana Kahleova, ...
Positive body image linked to better life satisfaction
2023-09-05
Having more positive body image is strongly associated with better psychological wellbeing and life satisfaction, according to a new study led by Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) in England.
Published in the journal Body Image, the research is one of the largest studies ever conducted on the topic of body image, involving 56,968 participants in 65 nations.
The research was focused on ‘body appreciation’, defined as “accepting, holding favourable opinions toward, and respecting the body, while also rejecting media-promoted appearance ...
AADOCR announces MIND the Future Class of 2023-2024
2023-09-05
Alexandria, VA -- The American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (AADOCR) is pleased to announce the program participants (mentees) for the fourth cohort of the AADOCR Mentoring an Inclusive Network for a Diverse Workforce of the Future (AADOCR MIND the Future):
Shaun Abrams
NIH/NIDCR, Bethesda, MD
Craniofacial development, anomalies, stem cell biology
Jean Calvo
University of California, San Francisco
Pediatric dentistry, dental education, patient safety, individuals with special needs
Louise M. Dornelas-Figueira
University of Florida, Gainesville
Oral ...
Disparities in who dwells behind crumbling US levees
2023-09-05
American Geophysical Union
5 September 2023
Release 23-33
For Immediate Release
This press release is available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/disparities-in-who-dwells-behind-us-levees/
Key points:
Tens of millions of people live in areas protected by at least one levee in the United States
Nationally, members of historically disadvantaged or underserved groups are more likely to be overrepresented in communities living behind levees
People of Hispanic descent are most likely to be overrepresented behind levees, with ~40% overrepresentation ...
Chris Allen named chief financial officer of Keck Medicine of USC
2023-09-05
LOS ANGELES — Keck Medicine of USC has named Chris Allen chief financial officer (CFO), effective Aug. 31. He previously served as interim CFO of Keck Medicine and CFO of Keck Medical Center of USC.
In this role, Allen will continue to oversee Keck Medicine’s strategic financial plans, financial and governmental reporting, budgeting, funds flow, revenue cycle and material management. He will also lead the assessment, planning, implementation and evaluation of the health system’s financial ...
Mason researchers studying zoonotic transmission pathways
2023-09-05
Taylor M. Anderson, Assistant Professor, Geography and Geoinformation Science, and Amira Roess, Professor, Global Health and Epidemiology, are studying zoonotic transmission pathways.
Specifically, the researchers received funding for the project: "Investigating zoonotic transmission pathways to better understand and predict the spread of SARS-CoV-2 in urban and suburban landscapes: a case study of the white-tailed deer."
They aim to investigate unknown transmission pathways at the human-wildlife interface in urban ...
Resistant starch supplement reduces liver triglycerides in people with fatty liver disease
2023-09-05
Resistant starch is a nondigestible fiber that ferments in the large intestine, and consumption of it has previously been shown to have a positive effect on metabolism in animal studies. Now, a 4-month randomized controlled trial in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) indicates that daily intake of resistant starch can alter gut bacteria composition and lower liver triglycerides and liver enzymes associated with liver injury and inflammation. This research appears in the journal Cell Metabolism on September 5.
NAFLD, caused by a buildup of fat in the liver, affects about 30% of the population worldwide. It can lead ...
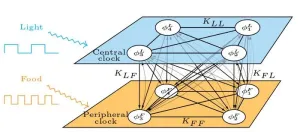
Synchronizing your internal clocks may help mitigate jet lag, effects of aging
2023-09-05
WASHINGTON, Sept. 5, 2023 -- Traveling to faraway places is a great way to seek out new experiences, but jet lag can be an unpleasant side effect. Adjusting to a new time zone is often accompanied by fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and a host of other problems that can turn an otherwise exciting adventure into a miserable trip.
Jet lag is caused by a difference between the circadian system — the body’s internal clock — and the surrounding environment. Around the turn of the century, scientists began to recognize that the body has multiple internal clocks, calibrated in different ways, and that jet lag-like symptoms can result when these ...