(Press-News.org) Having more positive body image is strongly associated with better psychological wellbeing and life satisfaction, according to a new study led by Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) in England.
Published in the journal Body Image, the research is one of the largest studies ever conducted on the topic of body image, involving 56,968 participants in 65 nations.
The research was focused on ‘body appreciation’, defined as “accepting, holding favourable opinions toward, and respecting the body, while also rejecting media-promoted appearance ideals as the only form of human beauty”.
Previous research has shown that high levels of body appreciation are linked to a range of positive wellbeing traits such as improved self-esteem and healthy eating habits, and negatively associated with issues such as depression and anxiety. However, few studies have assessed body appreciation across nations.
Led by researchers from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), a consortium of scientists asked participants in 65 nations to complete the Body Appreciation Scale-2 (BAS-2), which contains 10 items, including ‘I respect my body’ and ‘I appreciate the different and unique characteristics of my body’.
The study found that across nations, greater body appreciation was significantly associated with higher psychological wellbeing, as assessed using a measure of life satisfaction. The researchers also found that body appreciation was higher in participants who were single (compared with being married or in a committed relationship) and those living in rural areas.
The study also found large differences in body appreciation scores across the 65 survey nations. The lowest scores were recorded by Australia, followed by India and then the United Kingdom. At the other end of the scale, Malta scored highest.
Viren Swami, Professor of Social Psychology at Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) and lead author of the study, said: “This is one of the largest studies on body image ever carried out, brought about by a collaborative research effort involving over 250 scientists across the world. Our finding that greater body appreciation is associated with better psychological wellbeing highlights the importance of developing ways to promote more positive body image globally.
“Also, people who live in urban areas may feel stronger pressure to conform to body ideals promoted by Western society, and it is also notable that people from countries considered culturally different to the United States appeared to have broadly greater body appreciation. People in rural areas may also benefit from being in nature, which past research has also shown to be linked with positive body image.
“This research also highlights what can be achieved when scientists from across the world come together to achieve a common goal.”
END
Positive body image linked to better life satisfaction
Largest study of its kind also finds people in rural areas appreciate their bodies more
2023-09-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AADOCR announces MIND the Future Class of 2023-2024
2023-09-05
Alexandria, VA -- The American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (AADOCR) is pleased to announce the program participants (mentees) for the fourth cohort of the AADOCR Mentoring an Inclusive Network for a Diverse Workforce of the Future (AADOCR MIND the Future):
Shaun Abrams
NIH/NIDCR, Bethesda, MD
Craniofacial development, anomalies, stem cell biology
Jean Calvo
University of California, San Francisco
Pediatric dentistry, dental education, patient safety, individuals with special needs
Louise M. Dornelas-Figueira
University of Florida, Gainesville
Oral ...
Disparities in who dwells behind crumbling US levees
2023-09-05
American Geophysical Union
5 September 2023
Release 23-33
For Immediate Release
This press release is available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/disparities-in-who-dwells-behind-us-levees/
Key points:
Tens of millions of people live in areas protected by at least one levee in the United States
Nationally, members of historically disadvantaged or underserved groups are more likely to be overrepresented in communities living behind levees
People of Hispanic descent are most likely to be overrepresented behind levees, with ~40% overrepresentation ...
Chris Allen named chief financial officer of Keck Medicine of USC
2023-09-05
LOS ANGELES — Keck Medicine of USC has named Chris Allen chief financial officer (CFO), effective Aug. 31. He previously served as interim CFO of Keck Medicine and CFO of Keck Medical Center of USC.
In this role, Allen will continue to oversee Keck Medicine’s strategic financial plans, financial and governmental reporting, budgeting, funds flow, revenue cycle and material management. He will also lead the assessment, planning, implementation and evaluation of the health system’s financial ...
Mason researchers studying zoonotic transmission pathways
2023-09-05
Taylor M. Anderson, Assistant Professor, Geography and Geoinformation Science, and Amira Roess, Professor, Global Health and Epidemiology, are studying zoonotic transmission pathways.
Specifically, the researchers received funding for the project: "Investigating zoonotic transmission pathways to better understand and predict the spread of SARS-CoV-2 in urban and suburban landscapes: a case study of the white-tailed deer."
They aim to investigate unknown transmission pathways at the human-wildlife interface in urban ...
Resistant starch supplement reduces liver triglycerides in people with fatty liver disease
2023-09-05
Resistant starch is a nondigestible fiber that ferments in the large intestine, and consumption of it has previously been shown to have a positive effect on metabolism in animal studies. Now, a 4-month randomized controlled trial in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) indicates that daily intake of resistant starch can alter gut bacteria composition and lower liver triglycerides and liver enzymes associated with liver injury and inflammation. This research appears in the journal Cell Metabolism on September 5.
NAFLD, caused by a buildup of fat in the liver, affects about 30% of the population worldwide. It can lead ...
Synchronizing your internal clocks may help mitigate jet lag, effects of aging
2023-09-05
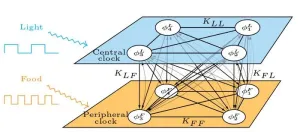
WASHINGTON, Sept. 5, 2023 -- Traveling to faraway places is a great way to seek out new experiences, but jet lag can be an unpleasant side effect. Adjusting to a new time zone is often accompanied by fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and a host of other problems that can turn an otherwise exciting adventure into a miserable trip.
Jet lag is caused by a difference between the circadian system — the body’s internal clock — and the surrounding environment. Around the turn of the century, scientists began to recognize that the body has multiple internal clocks, calibrated in different ways, and that jet lag-like symptoms can result when these ...
Trends in preterm infant mortality by race, socioeconomic status
2023-09-05
About The Study: This study found that between 1995 and 2020, U.S. preterm infant mortality improved among all categories of prematurity. Inequalities in preterm infant mortality based on maternal race and ethnicity have remained constant while socioeconomic disparities have widened over time.
Authors: Tim Venkatesan, M.A. (Cantab), M.B., B.Chir., D.T.M.&H., of the UCL Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health in London, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.3487)
Editor’s ...
Emergency department pediatric readiness and disparities in mortality based on race and ethnicity
2023-09-05
About The Study: In this study of 633,000 children treated in 586 emergency departments across 11 states, mortality of Black children was greater than that of white children at all quartile levels of readiness among those with acute medical emergencies but not traumatic injuries. Increased readiness was associated with decreased mortality overall, and it decreased most for Black children with acute medical emergencies.
Authors: Peter C. Jenkins, M.D., M.Sc., of the Indiana University School of Medicine in Indianapolis, is the corresponding ...
Cardiac arrest survival at EMS agencies in catchment areas with primarily Black and Hispanic populations
2023-09-05
About The Study: Risk-standardized survival rates for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest were 1.9% lower at emergency medical service (EMS) agencies working in Black and Hispanic catchment areas than in white catchment areas in this study including 764 EMS agencies. This difference was not explained by EMS response times, rates of EMS termination of resuscitation, or first responder rates of initiating cardiopulmonary resuscitation or applying an automated external defibrillator. These findings suggest there is a need for further assessment of these discrepancies.
Authors: Paul S. Chan, M.D., M.Sc., Saint Luke’s Hospital ...
Eye-tracking–based measurement of social visual engagement compared with expert clinical diagnosis of autism
2023-09-05
About The Study: In a study of children ages 16 to 30 months assessed for autism in six specialty clinics, eye-tracking–based measurement of social visual engagement was predictive of autism diagnoses by clinical experts. Further evaluation of this test’s role in early diagnosis and assessment of autism in routine specialty clinic practice is warranted.
Authors: Warren Jones, Ph.D., of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.13295)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
[Press-News.org] Positive body image linked to better life satisfactionLargest study of its kind also finds people in rural areas appreciate their bodies more