Chinese paleontologists find new fossil link in bird evolution
2023-09-06
(Press-News.org)
Birds descended from theropod dinosaurs by the Late Jurassic, but our understanding of the earliest evolution of the Avialae, the clade comprising all modern birds but not Deinonychus or Troodon, has been hampered by a limited diversity of fossils from the Jurassic.
As of now, no definitive avialans have been reported except from the Middle–Late Jurassic Yanliao Biota in northeast China (166–159 million years ago; Ma) and the slightly younger German Solnhofen Limestones, which preserve Archaeopteryx. Consequently, there is a gap of about 30 million years before the oldest known record of Cretaceous birds. However, the Jurassic avialans are key to deciphering the evolutionary origin of the characteristic avialan body plan. More importantly, they are key to reconciling the phylogenetic controversy about the origin of birds.
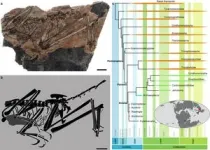
A joint research team from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing and the Fujian Institute of Geological Survey (FIGS) described and analyzed a new 150-million-year-old avialan theropod from Zhenghe County, Fujian Province.
The findings were published in Nature on Sept. 6.
The new species, named Fujianvenator prodigiosus, exhibits a bizarre assembly of morphologies that are shared with other avialans, troodontids, and dromaeosaurids, showing the impact of evolutionary mosaicism in early bird evolution.
"Our comparative analyses show that marked changes in body plan occurred along the early avialan line, which is largely driven by the forelimb, eventually giving rise to the typical bird limb proportion," said Dr. WANG Min from IVPP, lead and corresponding author of the study. "However, Fujianvenator is an odd species that diverged from this main trajectory and evolved bizarre hindlimb architecture."
The surprisingly elongate lower leg and other morphologies, in combination with other geological observations, suggest that Fujianvenator lived in a swamp-like environment and was a high-speed runner or a long-legged wader, representing a previously unknown ecology for early avialans.
"Besides Fujianvenator, we have found abundant other vertebrates, including teleosts, testudines and choristoderes," said XU Liming from FIGS, lead author of the study.
During the Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous, southeastern China underwent intensive tectonic activities due to subduction of the paleo-Pacific plate, resulting in widespread magmatism and coeval fault-depression basins, where Fujianvenator was found. This geological background is essentially the same as in the Late Jurassic in north and northeastern China, where the older Yanliao Biota is preserved.
"The extraordinary diversity, unique vertebrate composition, and paleoenvironment strongly indicate that this locality documents a terrestrial fauna, which we named the Zhenghe Fauna," said Dr. ZHOU Zhonghe from IVPP, co-author of the study. In-situ radioisotopic dating and stratigraphic surveys constrain the Zhenghe Fauna to the period from 150–148 Ma. Therefore, Fujianvenator documents one of the stratigraphically youngest and geographically southernmost members of the Jurassic avialans.
The discovery of the Zhenghe Fauna opens a new window into the Late Jurassic terrestrial ecosystem of the planet, and the joint research team from IVPP and FIGS plan to continue their exploration of Zhenghe and nearby areas.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-09-06
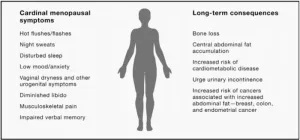
Although about half of people go through menopause, less than 15% of them receive effective treatment for their symptoms. Treatment options for people experiencing irritating or severe menopause symptoms are often under researched, and some have questionable efficacy, or cause harmful side effects. In a comprehensive review publishing in the journal Cell on September 6, a team of world-renowned menopause experts summarizes what we know about menopause, calls for more research into the timeline and treatment of menopause, ...
2023-09-06
Ottawa, ON, September 5, 2023 – Annual rates of emergency department visits for cannabis-involved traffic injury increased by 475 percent over 13 years, according to a new study from The Ottawa Hospital, Bruyère Research Institute, and ICES.
The study examined cannabis-involvement in emergency department (ED) visits for traffic injuries between 2010 and 2021 and looked for changes after the legalization of cannabis in October 2018 and following the commercialization of the legal market (expanded cannabis products and retail stores), which overlapped with the ...
2023-09-06
Neuroscience is in great upheaval. The two major families of cells that make up the brain, neurons and glial cells, secretly hid a hybrid cell, halfway between these two categories. For as long as Neuroscience has existed, it has been recognized that the brain works primarily thanks to the neurons and their ability to rapidly elaborate and transmit information through their networks. To support them in this task, glial cells perform a series of structural, energetic and immune functions, as well as stabilize physiological constants. Some of these glial cells, known as astrocytes, ...
2023-09-06
By improving hospital care pathways, researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center successfully reduced inpatient opioid use by 50% after pancreatic cancer surgery and cut the median opioid prescription volumes at discharge to zero. This approach, described in a study published today in JAMA Surgery, could help reduce the risk of long-term opioid dependence in patients.
In this cohort study, which involved 832 patients undergoing pancreatic resection surgery, the researchers investigated how making incremental modifications to post-surgery procedures affected the amounts of opioids used by inpatients and at the point of discharge. In less ...
2023-09-06
Analysis led by Brigham researchers showed an increase in out-of-state abortion travelers to Massachusetts from other states including Texas, Louisiana, Florida, and Georgia after Dobbs.
Use of non-profit funding by charitable organizations for abortion care more than doubled among out-of-state travelers
A rigorous analysis by researchers confirms a rise in out-of-state travelers coming to Massachusetts to seek abortion care. In a new study by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member ...
2023-09-06
About The Study: Researchers identified decreases of in situ and invasive melanoma diagnoses during 2020, which may reflect decreased skin cancer screening examinations or access to dermatologic care during the pandemic, both of which may lead to reduced melanoma diagnoses. This study adds to the current literature by highlighting that the relative increase in thick melanomas in 2020 was primarily associated with a marked decrease in thin melanomas, rather than an absolute increase in thicker melanomas.
Authors: Rebecca I. Hartman, M.D., M.P.H., of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
2023-09-06
About The Study: This study found large increases in cannabis involvement in emergency department visits for traffic injury over time in Ontario, Canada, which may have accelerated following nonmedical cannabis commercialization. Although the frequency of visits was rare, they may reflect broader changes in cannabis-impaired driving. Greater prevention efforts, including targeted education and policy measures, in regions with legal cannabis are indicated.
Authors: Daniel T. Myran, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Ottawa in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.31551)
Editor’s ...
2023-09-06
Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), astronomers have detected the magnetic field of a galaxy so far away that its light has taken more than 11 billion years to reach us: we see it as it was when the Universe was just 2.5 billion years old. The result provides astronomers with vital clues about how the magnetic fields of galaxies like our own Milky Way came to be.
Lots of astronomical bodies in the Universe have magnetic fields, whether it be planets, stars or galaxies. “Many people ...
2023-09-06
Oscillating chemical systems are present at nearly every popular chemistry exhibition – especially the ones that display striking colour changes. But so far there are very few practical uses for these types of reactions beyond timekeeping. In nature, on the other hand, many important life processes such as cell division and circadian rhythms involve oscillations. Scientists at the University of Groningen have now developed an oscillating system that contains a catalyst, and exhibits periodic catalytic activity: this synthetic chemical oscillator can do more than just keep time. A description of this ...
2023-09-06
LA JOLLA, CA—Scripps Research chemists have extended a powerful molecule-building method—called C-H activation—to the broad class of chemicals known as alcohols.
The synthetic chemistry feat, reported in Nature on September 6, 2023, follows the development of C-H activation techniques for the three other major classes of organic molecule—amines, acids and ketones—that are used to construct pharmaceuticals. It gives chemists a versatile new toolkit for making drugs and other valuable compounds now using the alcohol chemical class; moreover, its ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Chinese paleontologists find new fossil link in bird evolution