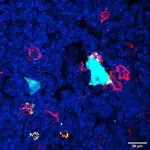
(Press-News.org) RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- It came as a surprise to Professor David Lo and his graduate student Diana Del Castillo when they were recently consulted by researchers in Israel for their expertise on specialized cells called Microfold cells, or M cells, which are mostly known for their presence in the intestinal epithelium. The Israeli group had identified similar cells in the thymus, an organ located just above the heart that makes lymphocytes — white blood cells that play an important role in the immune system and protect the body against infection.
Lo, a distinguished professor of biomedical sciences in the UC Riverside School of Medicine, and Del Castillo, who are co-authors on the research paper published in Nature, confirmed the newly discovered cells in the thymus are just like M cells. Acting like gatekeepers, M cells are specialized antigen-delivery cells for the immune system in organs like the intestine and lung. They play a key role during the development of the body’s immune system.
The researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel, led by Jakub Abramson, initiated the mouse study on the thymic epithelium before contacting Lo, whose research interests include understanding how M cells in the gut and airways work to build our immune system.
“I have been working on these cells for several years, so when the Israeli team contacted me, I was intrigued,” Lo said. “I learned this group had been doing studies on the cellular architecture of stromal cells — cells that make up certain types of connective tissue — in the thymus and, using a new advanced method, had discovered a population of cells much like the M cells we see in the gut and airways. In my own research, I had simply never thought to look for M cells in the thymus.”
Fortuitously for the Israeli scientists, Del Castillo, under Lo’s guidance, had been studying mucosal tissues — tissues that line some of the body’s canals and organs — in mice in the lab and was able to answer several questions, such as where in the thymus the newly discovered cells are located and what they are doing there.
“These particular M cells are limited to a specific region in the thymus and have unique associations with different cell types and functions,” Del Castillo said. “Questions these cells have already prompted include how similar are they to M cells elsewhere in the body and what is different about where they have been found.”
Lo explained that for many years the thymus has been a tissue of interest to immunologists because most of the immune system’s development is centered and dependent on the thymus.
“It’s still an ongoing deep puzzle that continues to attract interest,” he said. “The thymus offers clues to how the immune system got its start. This complicated organ, with so many different stromal cell types and interactions, is responsible for producing lymphocytes that protect us from infection.”
According to Lo, the newly discovered M cells are extremely similar to the M cells seen in the gut and airways.
“But the thymic M cells have different developmental origins, which is an interesting puzzle in itself,” he said. “After they develop, they look very much like the ones we have been studying in the gut. As we know, M cells capture viruses and bugs that enter the airways and hand them off to the immune system, which then responds to the infectious agents. Are the M cells doing the same thing in the thymus in terms of organization and function? That’s what we would like to know.”
Del Castillo, who is working toward her doctoral degree in biomedical sciences, used genetically engineered mice to tackle the questions from the Israeli researchers.
“We found the new cells were scattered in the medullary region of the thymus,” she said. “This has interesting implications in terms of the role and compartmentalization of the thymus, such as how these cells may function to regulate lymphocyte training within this organ.”
Lo and Del Castillo were surprised to find that many steps involved in shaping an immune response in various parts of the body seem to be echoed in the thymus.
“It is fascinating to see that many of these early cell interactions and development we have studied closely in the peripheral immune system take place in the thymus,” Lo said. “We had not anticipated to see these interactions here. It’s like watching a short video in the thymus about what is happening big-scale out in the periphery.”
The thymus also ensures that lymphocytes do not accidentally attack our own tissues; the thymic medulla is where these decisions are made, the UCR scientists said.
“The newly discovered M cells are part of this decision-making process,” Del Castillo said. “The production of antibodies in the peripheral immune system to fight off infectious organisms involves several steps and many cells interacting with each other. What is fascinating is that some of these interactions are recapitulated in the early stages of the development of the thymic M cells.”
According to Lo, the thymic M cells could be seen as being trained to function later, when needed, in the periphery in such a way that they are ready to communicate and interact with other cells.
“The thymus is complicated because it creates a whole functional immune system and repertoire, and we know many component parts play a role in its performance,” he said. “We didn’t expect M cells to even show up in the thymus. This is, therefore, a satisfying discovery because it is so clearly connected to similar processes happening in the gut and airways, which is where 60-70% of our infectious agents enter our bodies.”
The research paper, Lo’s tenth publication in Nature, is titled “Thymic mimetic cells function beyond self-tolerance.”
The University of California, Riverside is a doctoral research university, a living laboratory for groundbreaking exploration of issues critical to Inland Southern California, the state and communities around the world. Reflecting California's diverse culture, UCR's enrollment is more than 26,000 students. The campus opened a medical school in 2013 and has reached the heart of the Coachella Valley by way of the UCR Palm Desert Center. The campus has an annual impact of more than $2.7 billion on the U.S. economy. To learn more, visit www.ucr.edu.
END
Study reports discovery of new cell type in thymus
UC Riverside biomedical scientists say the cells are like M cells in the gut and airways
2023-09-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Devices offers long-distance, low-power underwater communication
2023-09-06
MIT researchers have demonstrated the first system for ultra-low-power underwater networking and communication, which can transmit signals across kilometer-scale distances.
This technique, which the researchers began developing several years ago, uses about one-millionth the power that existing underwater communication methods use. By expanding their battery-free system’s communication range, the researchers have made the technology more feasible for applications such as aquaculture, coastal hurricane prediction, and climate change modeling.
“What started as a very exciting ...
Beauty salon–based intervention increases trust of PrEP among Black cisgender women
2023-09-06
September 6, 2023 — Among African American and other Black cisgender women, a beauty salon–based intervention improved knowledge and awareness of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) against HIV and increased trust in it, according to a pilot study published in the September issue of The Journal of the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care (JANAC), the official journal of the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care. JANAC is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
However, most study participants did not self-identify as requiring PrEP or having risk factors for HIV. "Like ...
Pumping like the heart
2023-09-06
Pumping liquids may seem like a solved problem but optimizing the process is still an area of active research. Any pumping application—from industrial scales to heating systems at home—would benefit from a reduction in energy demands. Researchers at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) now showed how pulsed pumping can reduce both friction from and energy consumption of pumping. For this, they took inspiration from a pumping system intimately familiar to everyone: the human heart.
According to an international study, nearly twenty percent of global electric power are used for pumping liquids around—ranging from industrial applications ...
Chinese paleontologists find new fossil link in bird evolution
2023-09-06
Birds descended from theropod dinosaurs by the Late Jurassic, but our understanding of the earliest evolution of the Avialae, the clade comprising all modern birds but not Deinonychus or Troodon, has been hampered by a limited diversity of fossils from the Jurassic.
As of now, no definitive avialans have been reported except from the Middle–Late Jurassic Yanliao Biota in northeast China (166–159 million years ago; Ma) and the slightly younger German Solnhofen Limestones, which preserve Archaeopteryx. Consequently, there is a gap of about 30 million years before the oldest ...
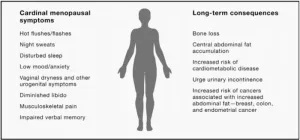
Review of over 70 years of menopause science highlights research gaps and calls for individualized treatment
2023-09-06
Although about half of people go through menopause, less than 15% of them receive effective treatment for their symptoms. Treatment options for people experiencing irritating or severe menopause symptoms are often under researched, and some have questionable efficacy, or cause harmful side effects. In a comprehensive review publishing in the journal Cell on September 6, a team of world-renowned menopause experts summarizes what we know about menopause, calls for more research into the timeline and treatment of menopause, ...
Commercialization of cannabis linked to increased traffic injuries
2023-09-06
Ottawa, ON, September 5, 2023 – Annual rates of emergency department visits for cannabis-involved traffic injury increased by 475 percent over 13 years, according to a new study from The Ottawa Hospital, Bruyère Research Institute, and ICES.
The study examined cannabis-involvement in emergency department (ED) visits for traffic injuries between 2010 and 2021 and looked for changes after the legalization of cannabis in October 2018 and following the commercialization of the legal market (expanded cannabis products and retail stores), which overlapped with the ...
The discovery of a new kind of cell shakes up neuroscience
2023-09-06
Neuroscience is in great upheaval. The two major families of cells that make up the brain, neurons and glial cells, secretly hid a hybrid cell, halfway between these two categories. For as long as Neuroscience has existed, it has been recognized that the brain works primarily thanks to the neurons and their ability to rapidly elaborate and transmit information through their networks. To support them in this task, glial cells perform a series of structural, energetic and immune functions, as well as stabilize physiological constants. Some of these glial cells, known as astrocytes, ...
Enhanced recovery program successfully reduced opioid use after pancreatic cancer surgery
2023-09-06
By improving hospital care pathways, researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center successfully reduced inpatient opioid use by 50% after pancreatic cancer surgery and cut the median opioid prescription volumes at discharge to zero. This approach, described in a study published today in JAMA Surgery, could help reduce the risk of long-term opioid dependence in patients.
In this cohort study, which involved 832 patients undergoing pancreatic resection surgery, the researchers investigated how making incremental modifications to post-surgery procedures affected the amounts of opioids used by inpatients and at the point of discharge. In less ...
Study finds increase in travelers to Massachusetts seeking abortion care post-Dobbs
2023-09-06
Analysis led by Brigham researchers showed an increase in out-of-state abortion travelers to Massachusetts from other states including Texas, Louisiana, Florida, and Georgia after Dobbs.
Use of non-profit funding by charitable organizations for abortion care more than doubled among out-of-state travelers
A rigorous analysis by researchers confirms a rise in out-of-state travelers coming to Massachusetts to seek abortion care. In a new study by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member ...
Incidence of in situ and invasive cutaneous melanomas during the pandemic
2023-09-06
About The Study: Researchers identified decreases of in situ and invasive melanoma diagnoses during 2020, which may reflect decreased skin cancer screening examinations or access to dermatologic care during the pandemic, both of which may lead to reduced melanoma diagnoses. This study adds to the current literature by highlighting that the relative increase in thick melanomas in 2020 was primarily associated with a marked decrease in thin melanomas, rather than an absolute increase in thicker melanomas.
Authors: Rebecca I. Hartman, M.D., M.P.H., of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
[Press-News.org] Study reports discovery of new cell type in thymusUC Riverside biomedical scientists say the cells are like M cells in the gut and airways