(Press-News.org) With the help of a new grant from the National Institute of Health for more than $2.6 million, Assistant Professor Timothy Huang, Ph.D., will continue his research on the role of the brain’s immune cells on the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease affects more than 47 million people worldwide, with 10 million new cases of dementia diagnosed each year. This number will continue to grow as the world population ages. Newly approved FDA treatments for Alzheimer’s remove beta-amyloid, a protein that accumulates into plaques, from the brain. However, these drugs are not a cure, and they don’t reverse the loss of memory and impaired cognition associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
“The key to finding effective ways to prevent and treat Alzheimer’s is digging deeper into the molecular aspects related to pathology and determining which changes may cause Alzheimer’s and which are a result of the disease,” says Huang. “This award will help us learn more about the link between genetic variants of TREM2—a key protein found in the brain’s immune cells—and the risk of developing Alzheimer’s.”
Huang’s research will focus on the puzzling observation that a rare genetic variant of TREM2 potentially reduces levels of beta-amyloid but is nonetheless associated with an increased risk of disease in some individuals. His team will investigate the possibility that the genetic variant produces its deleterious effects on tau—a toxic protein that accumulates inside the brain’s synapses and compromises the transmission of signals from one neuron to another.
“Results from this study will allow us to better understand how an Alzheimer’s disease risk factor can reduce beta-amyloid levels, which are thought to be protective, yet increase the risk of disease onset,” says Huang. “Since new treatments are focused on reducing amyloid levels, understanding how TREM2 genetic variants can reduce beta-amyloid yet confer increased risk of disease may give us further insight into improved or complementary drug treatments in the future.”
The grant, awarded by the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health, is “Molecular pathobiology of soluble TREM2 in Alzheimer's disease,” Award number: RF1 AG056130-06.
END
Timothy Huang awarded $2.6M to solve Alzheimer’s disease puzzle
2023-09-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Culture-friendly therapies for treating anxiety and depression in Japanese youth
2023-09-07
Cognitive-behavioral therapies (CBT) have become increasingly popular over the past few decades. This psychological treatment, used to treat problems ranging from marital issues, eating disorders, anxiety disorders and depression, has been adopted by clinicians around the world. However, the implementation of CBT still lags outside the Western countries where it was first developed.
In a new review article, researchers examined the most popular CBT programs for young people in Japan, a country that ...
Faulkner to be honored by American Heart Association
2023-09-07
AUGUSTA, Ga. (Sept. 7, 2023) – Jessica Faulkner, PhD, a physiologist whose research is focused on sex differences in cardiovascular disease at the Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, is the recipient of the Harry Goldblatt Award for New Investigators from the American Heart Association’s 2023 Hypertension Council. She will be honored at the Hypertension Scientific Sessions in Boston this week.
This prestigious award is named for the pathologist who established the first animal model of hypertension in 1934 and recognizes an early career independent investigator working in hypertension or cardiovascular research who has significantly contributed ...
New test shows promise for detecting hard-to-find cervical cancers
2023-09-07
September 7, 2023—(BRONX, NY)—In findings with potentially important implications for cervical cancer screening, scientists at the National Cancer Institute (NCI)-designated Montefiore Einstein Cancer Center (MECC) have developed a test for detecting a type of cervical cancer that Pap tests often miss. The findings published online today in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute (JNCI).
“Our novel test appears sensitive for detecting cervical adenocarcinoma [ADC]—which now accounts for up to 25% of cervical cancer cases—as well as its precursor ...
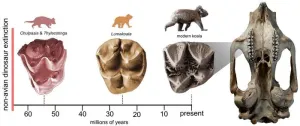
New koala relative fills a branch of Australia’s unique marsupial story
2023-09-07
Koalas are endangered in much of Australia now but in in the past there were multiple species living across the continent. The discovery of an ancient relative of the koala helps fill a 30 million year gap in the amazing evolution of Australia’s marsupials, according to a new study by Australian and British scientists published in Scientific Reports.
The study was led by Flinders University PhD student Arthur Crichton, who found fossil teeth of the new species at the Pwerte Marnte Marnte fossil site south of Alice ...
Eye-tracking technology helps give a voice to older people living with dementia
2023-09-07
More than 50% of Australians living in residential aged care facilities have a dementia diagnosis, with aged care services around the world preparing for the number of older people aged 65 years and above to double in the next 30 years.
For the first time, experts at the Caring Futures Institute at South Australia’s Flinders University are using innovative eye-tracking technology to ensure that the voices of all older people are heard to drive positive and effective change in keeping with the Royal Commission into Aged Care Quality and Safety’s call to re-assess the quality of aged care in Australia.
The Flinders University ...
Capturing carbon in savannas: New research examines role of grasses for controlling climate change
2023-09-07
In recent years, the escalating impact of global warming has prompted efforts to reverse troubling trends, often by planting trees to capture and remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it. New research from a team led by Young Zhou, from the Quinney College of Natural Resources and the Ecology Center, shows that, in addition to trees, humble grasses also play an essential role in capturing carbon — more important than previously thought.
A recent initiative set its sights on capturing carbon in tropical savannas, an ecosystem characterized by shared space of trees and grasses. The project initiated ...
Street medicine filling a major gap by providing behavioral health care for people who are homeless
2023-09-07
Mental health and substance use disorders are prevalent among people experiencing homelessness, yet access to care for these health issues is challenging for people living on the streets. Now, a new survey conducted by a team of researchers from USC Street Medicine found that, in California, street medicine programs are helping to fill this gap, delivering critical, high-level mental health and substance use treatments to the state’s unsheltered population.
The survey, published in Community Mental Health Journal, shows that street medicine has the potential to serve as the basis for a strategy to expand access to behavioral health care for people who ...
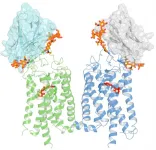
UC Irvine researchers discover a nanobody which may lead to treatment for Retinitis Pigmentosa
2023-09-07
A team of scientists from the University of California, Irvine, believe they have discovered a special antibody which may lead to a treatment for Retinitis Pigmentosa, a condition that causes loss of central vision, as well as night and color vision.
The study, Structural basis for the allosteric modulation of rhodopsin by nanobody binding to its extracellular domain, was published in Nature Communications. Authors of the study were Arum Wu, PhD, David Salom, PhD, John D. Hong, Aleksander Tworak, PhD, Philip D. Kiser, PharmD, PhD, and Krzysztof Palczewski, PhD, in the Department ...
Use of common painkillers alongside hormonal contraception linked to heightened risk of blood clots
2023-09-07
Women who use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory painkillers alongside hormonal contraception appear to be at a small increased risk of blood clots known as venous thromboembolism (VTE), finds a large Danish study published by The BMJ today.
The risk was greater in women using combined oral contraceptives containing third or fourth generation progestins, but smaller in women using progestin-only tablets, implants and coils, alongside the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) ibuprofen, diclofenac, and naproxen.
The researchers stress ...
High intake of several emulsifier E numbers linked to increased cardiovascular disease risk
2023-09-07
High intake of several emulsifiers (part of the ‘E numbers’ group of food additives), widely used in industrially processed foods to improve texture and extend shelf-life, is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), suggests a study published by The BMJ today.
Given that these food additives are used ubiquitously in thousands of widely consumed ultra-processed food products, these findings have important public health implications, say the researchers.
Emulsifiers are often added to processed and packaged foods such as pastries, cakes, ice cream, ...