(Press-News.org) Analysis of data from more than 1 million Danish inpatients identifies nearly 4,000 drug pairings that are associated with more frequent dosage adjustments when prescribed together—potentially hinting at previously undiscovered drug interactions. Søren Brunak of the University of Copenhagen, Denmark, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Digital Health.
In some cases, especially among elderly populations, a person may be prescribed several different medications at once in order to treat one or multiple health conditions—a phenomenon known as polypharmacy. Polypharmacy is associated with increased health risks due to the potential for harmful interactions between different drugs. Polypharmacy research has typically focused on the number and type of drugs a patient receives. However, the dosage of each drug may also influence interactions and health outcomes.
To deepen understanding of polypharmacy in the context of drug dosage, Leal, Haue, Brunak and colleagues analyzed data from the electronic health records of more than 1 million patients admitted as inpatients in Danish hospitals from 2008 to 2016. They used a statistical approach known as Bayesian inference to identify drug pairings associated with more frequent adjustments to the dosage of the drugs.
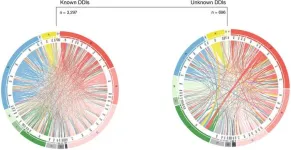
Out of 77,249 total drug pairings, 3,993 were associated with more frequent dosage adjustments when given together. Further analysis showed that, of the pairs associated with more frequent dosage adjustments, 2,412 were also associated with hospital readmission, mortality, or longer hospital stays, and 308 were associated with worsened kidney function.
Many of the drug pairs associated with dosage adjustments have already been linked by previous research to potential harmful drug interactions. However, 694 have not, and while this study does not prove any cause-effect relationships, the authors suggest that some of these drug pairings may involve previously undiscovered interactions. These are often given to fewer patients and therefore harder to detect in small scale studies – contrary to the 185 million treatment episodes used in this study. Future research will be needed to explore that possibility.
Overall, these findings help deepen understanding of links between drug dosage and polypharmacy, and could help guide future evaluation of drug interactions and efforts to reduce the risks of polypharmacy for patients.
############
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Digital Health: https://journals.plos.org/digitalhealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pdig.0000336
Citation: Leal Rodríguez C, Haue AD, Mazzoni G, Eriksson R, Hernansanz Biel J, Cantwell L, et al. (2023) Drug dosage modifications in 24 million in-patient prescriptions covering eight years: A Danish population-wide study of polypharmacy. PLOS Digit Health 2(9): e0000336. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pdig.0000336
Author Countries: Denmark.
Funding: This work was supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation (grants NNF17OC0027594, NNF14CC0001 and NNF18SA0034956) and the Danish Innovation Fund (grant 5153-00002B).
END
Dosage tweaks may hint at undiscovered interactions between medications
Study identifies thousands of medication pairings associated with more frequent dosage adjustments
2023-09-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How bright-light treatment improves sleep in stressed mice
2023-09-07
Chronic stress is associated with sleep disturbance. In their new study, Lu Huang and colleagues identify the neural pathway behind this behavior, and at the same time, explain how bright-light treatment is able to counter it. The research was conducted in mice at Jinan University in China and published September 7th in the open access journal PLOS Biology.
Bright-light treatment is known to improve sleep in those with sleep disorders, but how it works – and whether it works in cases of stress-induced sleep disturbances – was unknown. The researchers hypothesized that a part of the brain called the lateral habenula is deeply involved in this phenomenon because ...
Lack of evidence hampers progress on corporate-led ecosystem restoration
2023-09-07
A ‘near total’ lack of transparency is making it impossible to assess the quality of corporate-led ecosystem restoration projects, according to a Lancaster University-led study published today in Science.
Efforts to rebuild degraded environments are vital for achieving global biodiversity targets. The United Nations has launched a Decade on Ecosystem Restoration, and in recent years businesses around the world have collectively pledged to plant billions of trees, hundreds of thousands of corals and tens of ...
Implantable device enables earlier detection of kidney transplant failure in rats
2023-09-07
An implantable sensor provided advanced warning of kidney transplant failure in rats as much as several weeks earlier than commonly used biomarkers of kidney function, researchers report. The device, tested in a rat model of kidney transplantation, provides real-time continuous monitoring of organ temperature and thermal conductivity, detecting inflammatory processes associated with graft rejection. Although lifesaving for patients with end-stage kidney disease, long-term kidney transplantation survival remains a major challenge. Graft failure ...
2022 Hunga-Tonga eruption triggered fast and destructive submarine volcanic flows
2023-09-07
In 2022, the eruption of the submerged Hunga Tonga–Hunga Ha apai volcano triggered a fast-moving and destructive underwater debris flow that severed telecommunication cables and reshaped the surrounding seafloor. The findings – representing some of the first fieldwork to document what happens when large volumes of erupted volcanic material are delivered directly into the ocean – provide new insights into the behavior and hazards of submerged volcanoes. Explosive volcanic eruptions on land create pyroclastic flows of hot ash and rock that, when they reach the ocean, can trigger damaging ...
Are large corporations upholding their conservation promises?
2023-09-07
Large transnational corporations (TNCs) are positioning themselves as environmental leaders, carrying out environmental restoration projects that go beyond their legal obligations. However, some corporations oversell their efforts. In this Policy Forum, Timothy Lamont and colleagues present an evaluation of sustainability reports of 100 of the world’s largest businesses, revealing the extent to which TNCs are claiming to contribute to, but failing to report on, ecosystem restoration. “Increased rigor, consistency, transparency, and accountability are needed to ensure that corporate-led restoration delivers quantifiable, ...
Nudging food delivery customers to skip the fork drastically cuts plastic waste, study shows
2023-09-07
In 2021, more than 400 million metric tons of plastic waste were produced worldwide, and it is predicted that the world’s plastic waste growth will continue to outpace the efforts to reduce plastic pollution in the coming decades. As food delivery services became increasingly popular during the COVID-19 pandemic, the surge in plastic waste generated by single-use cutlery has become a key environmental challenge for many countries. A new study finds “green nudges” that encouraged customers to skip asking for cutlery with their delivery orders were dramatically successful and could be a powerful policy tool to reduce plastic waste.
“Few policies target plastic waste ...
First device to monitor transplanted organs detects early signs of rejection
2023-09-07
A body can reject a transplanted organ at any time — even decades later
Signs of rejection must be caught early to intervene, preserve the organ
Current monitoring methods are intermittent, imperfect and sometimes invasive
New implant offers continuous monitoring by tracking the organ’s temperature
When temperatures change, an alert is sent to a smartphone or tablet in real time
EVANSTON, Ill. — Northwestern University researchers have developed the first electronic device for continuously monitoring ...
Fiber from crustaceans, insects, mushrooms promotes digestion
2023-09-07
Who can forget the stomach-churning moments when “Survivor” contestants forced down crunchy insects, among other unappetizing edibles, for a chance to win $1 million? In daring culinary challenges, the TV show’s contestants exhibited gastronomic bravery as viewers watched in discomfort.
Digesting a crunchy critter starts with the audible grinding of its rigid protective covering — the exoskeleton. Unpalatable as it may sound, the hard cover might be good for the metabolism, according to a new study, in mice, from Washington University School of Medicine ...
They fall more easily for conspiracy theories
2023-09-07
People who primarily use their own gut feeling to determine what is true and false are more likely to believe conspiracy theories. That is the conclusion of researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, who have investigated the relationship between susceptibility to misleading information and the conviction that the truth is relative.
“I think many people who emphasise a more relativistic view of what truth is mean well. They believe that it’s important that everyone should be able to make their voice heard. But these results show that such a view can actually be quite dangerous,” says PhD student ...
Almoosa Specialist Hospital is first to be certified as a Comprehensive Chest Pain Center in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
2023-09-07
DALLAS and Al Mubarraz, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, September 7, 2023 — Almoosa Specialist Hospital, in Al Ahsa, Saudi Arabia has been recognized by the American Heart Association, the world's leading nonprofit organization focused on heart and brain health for all, as a the first Comprehensive Chest Pain Center in the country. This designation signifies the hospital’s status as a critical element in the kingdom’s effort to create a system of healthcare that seeks to save lives in Saudi Arabia by closing the gaps ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] Dosage tweaks may hint at undiscovered interactions between medicationsStudy identifies thousands of medication pairings associated with more frequent dosage adjustments