(Press-News.org) Sixty-six percent of U.S. teachers who responded to a new, nationally representative RAND Corporation survey said their base salary was inadequate, compared with 39% of U.S. working adults. These teachers want a $17,000 increase in base pay, on average, to feel that their pay is adequate.
This equates roughly to a 27% pay increase, which is comparable to the estimated gap in pay between teachers and other similarly college-educated workers, also known as the “teacher pay penalty.”
In early 2023, RAND researchers surveyed public-school teachers about how salary and work hours affect intentions to leave their jobs and relate to well-being. Researchers also conducted a parallel survey of working adults to provide context for teachers’ responses.
“Most teachers feel overworked and underpaid, but we didn’t know what teachers considered to be fair pay or how the amount of their desired pay is related to cost of living and the working conditions in their schools,” said Elizabeth D. Steiner, lead author of the report and a policy researcher at RAND, a nonprofit, nonpartisan research organization. “Teachers at all levels of experience said they deserved higher pay, suggesting the importance of raising pay across the salary schedule.”
Low salary and long working hours were the top-ranked reasons why teachers said they were considering leaving their jobs as well as commonly reported job-related stressors. The researchers found that dissatisfaction with pay was strongly related to dissatisfaction with weekly hours worked.
The survey also found that, during the school year, teachers worked more hours per week, on average, than all working adults – 53 hours compared with 46. About one of every four hours teachers worked per week was uncontracted and uncompensated.
“The survey shows that pay, hours worked and working conditions are interrelated, suggesting that pay increases alone – without improvements in working hours or conditions – are unlikely to bring about large shifts in teachers’ well-being or intentions to leave the profession,” said Ashley Woo, coauthor and an assistant policy researcher at RAND.
Black teachers were also more likely than White teachers to consider leaving their jobs, potentially threatening recent gains in racial and ethnic diversity in the teacher workforce. Black teachers reported working more hours per week, receiving slightly lower base salaries, and being less satisfied than White teachers with their base salary.
The authors recommend increasing teacher pay, reducing hours worked – particularly uncontracted and uncompensated hours – and improving working conditions to boost teacher retention.
The report is based on research funded by the National Education Association and the American Federation of Teachers. The findings and conclusions are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the positions or policies of the funders.
Another author of the report, “All Work and No Pay – Teachers’ Perceptions of Their Pay and Hours Worked: Findings from the 2023 State of the American Teacher Survey,” is Sy Doan, associate policy researcher at RAND.
RAND Education and Labor, a division of RAND, is dedicated to improving education and expanding economic opportunities for all through research and analysis. Its researchers address key policy issues in U.S. and international education systems and labor markets, from pre-kindergarten to retirement planning.
END
US teachers are less satisfied with their pay than most working adults
2023-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Targeted ultrasound can change brain functions for up to an hour after intervention
2023-09-12
The targeted use of ultrasound technology can bring about significant changes in brain function that could pave the way towards treatment of conditions such as depression, addiction, or anxiety, a new study suggests.
Research by neuroscientists at the University of Plymouth explored the impacts of an emerging technique called transcranial ultrasound stimulation (TUS).
Typically, ultrasound examinations involve diffuse broad beams of ultrasound being used to create images while leaving the target tissue unaffected.
However, focusing the beams through TUS can increase the pressure in the target region and change the way ...
U.S. advocacy strategy nets a 25 percent increase in lung cancer research funding
2023-09-12
[Singapore, 10:05 a.m. SGT--September 12, 2023] - A unified and concentrated lung cancer advocacy program in the United States resulted in a 25 percent increase in funding to a U.S.-based lung cancer research program, according to a presentation given today at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2023 World Conference on Lung Cancer in Singapore.
Lung cancer remains a major health concern, with mortality rates posing a significant challenge both globally and in the United States. The U.S. Department of Defense Congressionally Directed Medical Research Program/Lung Cancer Research Program (LCRP) was established in 2009 with a funding level of $20 million, but ...
IASLC staging model for mesothelioma validated; study supports continued use of model
2023-09-12
[Singapore, 10:05 a.m. SGT--September 12, 2023] – A model developed by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer in 2009 to help better stage mesothelioma cases performed well, according to an independent analysis presented today at The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) 2023 Conference in Singapore.
Pleural mesothelioma is a rare but aggressive cancer primarily caused by asbestos exposure and presents complex challenges for effective staging and prognostication. The IASLC took a significant step in 2009 by establishing an international pleural mesothelioma database aimed at enhancing staging ...
Long-term outcomes of radiation techniques for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer presented at IASLC 2023 Conference in Singapore
2023-09-12
[Singapore, 10:05 a.m. SGT--September 12, 2023] - Intensity-modulated radiation therapy, or IMRT, should be utilized for locally advanced NSCLC to reduce the risk of severe pulmonary toxicity and radiation exposure to the heart, according to research presented today at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2023 World Conference on Lung Cancer in Singapore.
Dr. Stephen Chun, MD Anderson in Houston, Texas, presented a comprehensive analysis of the phase III trial NRG Oncology-RTOG 0617, comparing intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) with 3D-conformal ...
Reproductive factors associated with higher risk of lung cancer in women
2023-09-12
[Singapore, 10:05 a.m. SGT--September 12, 2023] - A study presented at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2023 World Conference on Lung Cancer revealed that key reproductive factors such as early menopause, shortened reproductive span, and early age at first birth are associated with elevated risks of lung cancer in women.
Researchers from Xiangya Hospital, Changsha, Hunan, China, conducted a prospective cohort study involving 273,190 participants from the UK Biobank to delve into the links between individual reproductive ...
Dark matter halos measured around ancient quasars
2023-09-12
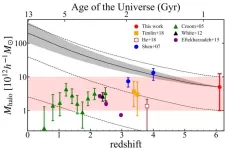
At the center of every galaxy is a supermassive black hole. Beyond a certain size, these become active, emitting huge amounts of radiation, and are then called quasars. It is thought these are activated by the presence of massive dark matter halos (DMH) surrounding the galaxy, directing matter towards the center, feeding the black hole. A team including researchers from the University of Tokyo have, for the first time, surveyed hundreds of ancient quasars and found this behavior is very consistent throughout history. This is surprising, as many large-scale processes show variation throughout the ...
Arf1 inhibitors promote the infiltration of cytotoxic T lymphocytes into tumors by affecting lipid metabolism
2023-09-12
In recent years, cancer immunotherapies, represented by immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), have been highly successful and have become an important basis for the future treatment of cancers. However, the absence of tumoral killer T cells and the complexity of tumor microenvironment can both affect the immunotherapeutic efficacy. Therefore, it is urgent to develop novel anti-tumor agents that can effectively promote effector T cell infiltration in tumors.
ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (Arf1) is a member of the Ras small GTPase family and is ...
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy provides long-term benefits to patients with locally advanced lung cancer
2023-09-12
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) should be the preferred choice when treating patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), as it reduces radiation exposure to the heart and lungs, according to researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Results from a long-term secondary analysis of the NRG Oncology-RTOG 0617 Phase III study, with a median follow-up of 5.2 years, revealed that patients receiving IMRT had a more than two-fold reduction in severe lung inflammation (pneumonitis) compared to those who received 3D-conformal radiotherapy ...
New super-fast flood model has potentially life-saving benefits
2023-09-12
Published in Nature Water, the new model has major potential benefits for emergency responses, reducing flood forecasting time from hours and days to just seconds, and enabling flood behaviour to be accurately predicted at super-fast speeds as an emergency unfolds.
University of Melbourne PHD student Niels Fraehr, alongside Professor Q J Wang, Dr Wenyan Wu and Professor Rory Nathan, from the Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology, developed the Low-Fidelity, Spatial Analysis ...
In maize, co-expression of GAT and GR79-EPSPS provides high glyphosate resistance, along with low glyphosate residues
2023-09-12
This study is led by Dr Zhihong Lang (Biotechnology Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences). To develop a new bio-breeding resource for glyphosate-resistant maize, a large transgenic maize population was generated with introducing a codon-optimized glyphosate N-acetyltransferase gene, gat, and the enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate synthase gene, gr79-epsps, into maize and a transgenic event, designated GG2, was highly resistant to glyphosate in consecutive generations of glyphosate screening. “This result is very encouraging.” Dr Lang says.
The ...