(Press-News.org) New research published today in Blood Advances reveals that since the introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines, PCV7 and PCV13, invasive pneumococcal infection (IPD) rates among children living with sickle cell disease (SCD) have declined significantly. The study explores the efficacy of existing and emerging vaccines to protect children living with SCD from life-threatening infections.
SCD is the most common inherited red blood cell disorder in the United States, affecting an estimated 100,000 people. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), SCD affects one out of every 365 Black or African American births and one out of every 16,300 Hispanic American births.
Children with SCD typically develop splenic dysfunction within their first six months to a year of life. The spleen plays a vital role in protecting the human body from infection, and children with SCD are at increased risk of developing severe, life-threatening illnesses. Those with the condition are treated with penicillin prophylaxis to reduce the risk of infection-related death.
Prior to treatment with penicillin, one in ten children per year under the age of five developed IPD, a severe infection. This accounted for 32% of all causes of death for individuals with SCD under the age of 20 in the Cooperative Study of Sickle Cell Disease. However, with antibiotic resistance on the rise over the last few decades, researchers have had to turn to new methods, such as vaccination, to protect this vulnerable population.
“In the years 2000, as pneumococci were developing antibiotic resistance, PCV7/PCV13 conjugate vaccines were introduced,” explained Thomas Adamkiewicz, M.D., MSc, a pediatric hematologist at Morehouse School of Medicine. “Since, these vaccines were developed to target bacterial serotypes not currently covered. We examined the impact of present and potential coverage of newer vaccines.”
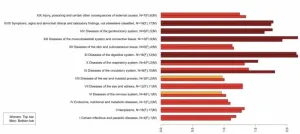
Researchers analyzed data collected over 25 years from the Georgia Emerging Infections Program, part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Active Bacterial Core Surveillance Network, which identifies all IPD occurring in metropolitan Atlanta since 1994. Investigators from the Georgia Emerging Infections Program, Children's Healthcare of Atlanta, and Emory University collaborated in this study. They identified 104 IPD episodes in 3,707 children under ten years old with HbSS and HbSC variants of SCD. After 2002, 87% percent of children with SCD received one or more doses of the PCV7 or PCV13 vaccine in their first decade of life, according to the researcher’s data. Dr. Adamkiewicz and his team found that between 1994-1999 and 2010-2018, IPD rates declined by 87% in children 0-4 years old with HbSS, the most severe form of SCD, and by 80% in those ages 5 to 9.
They also identified that among children with HbSS and IPD, case fatality rates declined from 14% to 3% after 2002, and meningitis rates declined from 16% to 8%. Scientists also observed that penicillin resistance was more prevalent among this population prior to the PCV7 vaccine’s approval.
After 2000, IPD strains with serotypes emerged that were not covered by the existing PCV7 and PVC13 vaccines caused most IPDs. The older 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) was found to be effective against pneumococcal strains with non-PCV13 serotypes, within three years after vaccination.
Investigators identified that since PCV7’s licensure, IPD rates in children with SCD ages 5 and older have decreased significantly. Further, since the approval and introduction of the PCV13 vaccine, no IPD infections related to the PCV13 strain have been recorded, despite some children with SCD not receiving their full recommended vaccine regimens. These findings suggest that herd immunity, introduced by these vaccines among the general population, is helping to protect children with SCD from infection as well.
Dr. Adamkiewicz highlights that as bacterial strains with serotypes not covered by the current vaccine are predominant, children with SCD may benefit from receiving newer recently approved vaccines such as PCV15, and PCV20, which respectively cover 16% and 51% of IPD strains not covered by PCV13. “One big question is the role of penicillin prophylaxis in children with SCD receiving new vaccines,” said Dr. Adamkiewicz. “We need far more data to make any recommendations.”
This study’s data is limited to one region of the United States, but its results might offer insights into the impact such vaccines would have on individuals with SCD in Africa – where most children with SCD reside.
While approximately two-thirds of children in the general population are reported to have received the PCV13 vaccine, mortality in children with SCD remains high, suggesting a need for wider dissemination of preventative measures, including vaccines. In 2020, in light of this need, the ASH Consortium on Newborn Screening in Africa (CONSA) -- an international network that seeks to demonstrate the benefits of newborn screening and early interventions for children with SCD in sub-Saharan Africa – was established.
While IPD remains a life-threatening risk to children with SCD, this study underscores the need for vaccines targeting broad strains of pneumococcal bacteria, and for additional research to continue advancing the prophylaxis treatments available to this population.
# # #
Blood Advances (www.bloodadvances.org) publishes more peer-reviewed hematology research than any other academic journal worldwide and is an online only, open access journal of the American Society of Hematology (ASH), the world’s largest professional society concerned with the causes and treatment of blood disorders.
Blood Advances® is a registered trademark of the American Society of Hematology.
Contact:
Kira Sampson, American Society of Hematology
ksampson@hematology.org; 202-499-1796
END
A groundbreaking discovery has been made by Professor Hyug Moo Kwon and his research team in the Department of Biological Sciences at UNIST, in collaboration with Professor Jaeseok Yang from Yonsei University. Their study sheds new light on the protein called ‘TonEBP,’ revealing its significant role in the development of lupus and lupus nephritis. This breakthrough not only enhances our understanding of these conditions, but also opens up potential avenues for future treatment options.
Lupus is an autoimmune disorder characterized by autoreactive B cells and dysregulation of various immune cells, including myeloid cells. Lupus nephritis (LN), which ...
COVID-19 mRNA vaccination protects babies and young children against COVID-19-associated emergency department/urgent care visits, according to a multistate study from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s VISION Network. The study found that children, age five and younger, who received the original COVID-19 vaccine and the updated vaccine were protected against the need for medical care for COVID in an emergency department or urgent care facility.
Emergency department/urgent care visits are considered indicators of moderate disease. The small number of hospitalizations for children ages six months to five years old limited the assessment of vaccine ...
Multimorbidity describes the state of having more than one disease. Anthony Webster sought to untangle a puzzle at the heart of multimorbidity: does having had disease make a patient more likely to have another disease, independent of broad risk factors, such as age, smoking status, or weight? Webster applied a Poisson-Binomial distribution with a Weibull model to predict the incidence of 222 common diseases for approximately 500,000 individuals within the UK Biobank cohort, taking into account their age and established risk factors, but ignoring their history of previous disease or pre-existing conditions. Webster then compared the expected number ...
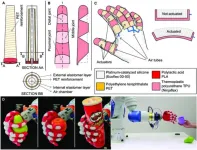
A research paper by scientists at the University of Coimbra proposed a soft robotic hand that composed of soft actuator cores and an exoskeleton, featuring a multimaterial design aided by finite element analysis to define the hand geometry and promote finger’s bendability. The new research paper, published on Aug. 8 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, presented the development, fabrication, and control of a bioinspired soft robotic hand and demonstrated finite element analysis can serve as a valuable tool to support the design and control of the hand’s fingers.
“Recent research led to impactful achievements in functional designs, modeling, ...
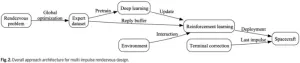
Multi-impulse orbital rendezvous is a classical spacecraft trajectory optimization problem, which has been widely studied for a long time. Numerical optimization methods, deeplearning (DL) methods, reinforcement learning (RL) methods have been proposed. However, for the numerical optimization methods, they need long computation time, and they are usually not valid for the many-impulse rendezvous case with the magnitude constraints. For the machine learning (ML) methods, the DL method needs large amounts of data, and the RL method has the weakness of low efficiency. Nevertheless, ML demonstrates more accurate predictions ...
SAN ANTONIO — September 12, 2023 —The Association of Old Crows (AOC), an international organization for the electronic warfare (EW) community, has recognized three early-career Southwest Research Institute engineers for their achievements in EW research and development. Two honorees received back-to-back Electronic Warfare Professional Outstanding Young Crow Awards. AOC named one engineer a 2023 Future 5, a designation for innovative professionals building EW careers. EW technology detects and defeats enemy signals on the electromagnetic spectrum to protect U.S. and allied forces.
Recipients of the international AOC EW Professional Outstanding Young Crow Award demonstrate outstanding ...
BATON ROUGE – The National Institutes of Health has awarded the Louisiana Clinical & Translational Science Center, or LA CaTS, a grant of nearly $1.3 million to support the efforts of in-state healthcare institutions to share health data for research purposes across a common structure.
Awarded as a single grant, the funds will be primarily split between two LA CaTS member institutions: nearly $780,000 for the Pennington Biomedical Research Center and $490,000 for Tulane University School of Medicine. Together, these two projects will strengthen the LA CaTS Center’s capacity to address health care disparities, ...
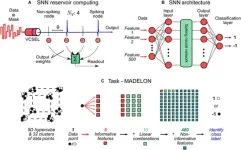
Photonic neural network systems, which are fast and energy efficient, are especially helpful for dealing with large amounts of data. To advance photonic brain-like computing technologies, a group of researchers at the University of Strathclyde combined a spike-based neural network with a semiconductor laser that exhibits spiking neuronal behaviors. Recently, they presented high-performance photonic spiking neural network operation with lower training requirements and introduced a novel training scheme for getting better results. This research was published Aug. 29 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
Neural ...
September 12th, 2023
For immediate release
Fom the bestselling author of Post-Truth and How to Talk to a Science Denier, comes On Disinformation: How to Fight for Truth and Protect Democracy
The effort to destroy facts and make America ungovernable didn't come out of nowhere. It is the culmination of seventy years of strategic denialism. In On Disinformation, Lee McIntyre shows how the war on facts began, and how ordinary citizens can fight back against the scourge of disinformation that is now threatening the very ...
Sepsis, also colloquially referred to as blood poisoning, is a serious condition. Just over 3,000 people die with a diagnosis of sepsis in Norwegian hospitals each year.
However, sepsis is not actually poisoning at all. The condition occurs when the immune system overreacts to an infection that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. The immune system attacks the organs of the body and the patient develops organ failure.
A new study of 300,000 sepsis admissions has found that the condition is more prevalent than previously thought. However, ...