(Press-News.org) Although a simple molecule, nitric oxide is an important signal substance that helps to reduce blood pressure by relaxing the blood vessels. But how it goes about doing this has long been unclear. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden now present an entirely novel principle that challenges the Nobel Prize-winning hypothesis that the substance signals in its gaseous form. Their findings are presented in the journal Nature Chemical Biology.
That the simple molecule nitric oxide or nitrogen monoxide (NO) serves as a signal substance in many important physiological processes has been known for some time. For example, the discovery of the compound’s significance was awarded the 1998 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. One of its functions is to initiate a signalling cascade that causes the smooth muscles of the vasculature to relax, thus expanding the vessels and lowering blood pressure. This is also why nitroglycerin, which releases NO, has long been a common treatment for angina.
However, the results now presented surprisingly indicate that it is not the NO molecule per se that is the active partner in the chemical interaction.
Can mean a paradigm shift
“It’s a little controversial, something of a paradigm shift in the field, in fact,” says Professor Jon Lundberg, who is the main author of the paper together with Andrei Kleschyov and Mattias Carlström, all of whom are at the Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, Karolinska Institutet.
The NO is formed in the endothelium, the tissue that constitutes the inner lining of blood vessels. For almost 40 years, the hypothesis has been that it then diffuses as a gas, spreading out randomly until it encounters an enzyme called guanylyl cyclase in the vascular smooth muscle, upon which the vessel relaxes. It is a journey over a distance of less than a millimetre, but it is a long way for a molecule.
“It’s hard to believe that it can work, since NO is so reactive and volatile that it ought to have trouble surviving that journey,” says Professor Lundberg.
Since it has also been difficult to demonstrate the presence of free NO in the cells, the actual signalling mechanism has long been a mystery.
A new signal substance
The KI group has tested the hypothesis that NO bonds with a “heme group”, a complex surrounding a single iron atom that is found in haemoglobin and that is freely available also in endothelial cells. Together they form a new and much more stable compound: NO-ferroheme.
The researchers found that NO-ferroheme significantly expands the blood vessels of mice and rats, and that in controlled experiments directly activates guanylyl cyclase, thus acting as a signal substance in the signal cascade.
“What we need to do now is establish that the endogenous NO-ferroheme that’s formed in endothelial cells really is a true signal substance and ascertain exactly how it gets synthesised in the body,” says Professor Lundberg.
Their results can provide a more detailed understanding of the chemical interaction and eventually open the way for new, improved treatments for cardiovascular disease.
The study was financed by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, Novo Nordisk, the EFSD/Lilly European Diabetes Research Programme, the Ekhaga Foundation and Karolinska Institutet. Andrei Kleschyov is the inventor of a patent related to NO-heme. Jon Lundberg and Eddie Weitzberg are co-inventors for a patent application related to the therapeutic use of inorganic nitrate. No other conflicts of interest have been reported.
Publication: “NO-ferroheme is a signaling entity in the vasculature”, Andrei L. Kleschyov, Zhengbing Zhuge, Tomas A. Schiffer, Drielle D. Guimarães, Gensheng Zhang, Marcelo F. Montenegro, Angela Tesse, Eddie Weitzberg, Mattias Carlström, Jon O. Lundberg. Nature Chemical Biology, online 14 September 2023, doi: 10.1038/s41589-023-01411-5.
END
Researchers present novel principle for nitric oxide-mediated signalling in blood vessels
2023-09-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
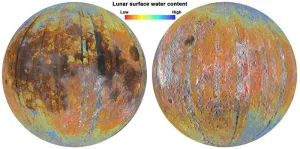
Electrons from Earth may be forming water on the Moon
2023-09-14
A team of researchers, led by a University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa planetary scientist, discovered that high energy electrons in Earth’s plasma sheet are contributing to weathering processes on the Moon's surface and, importantly, the electrons may have aided the formation of water on the lunar surface. The study was published today in Nature Astronomy.
Understanding the concentrations and distributions of water on the Moon is critical to understanding its formation and evolution, and to providing water resources for future human exploration. The new ...
New tool can reveal inequitable distribution of ‘healing’ green spaces
2023-09-14
Areas in Vancouver with the greatest need for restorative nature often have the least exposure to it, according to a new UBC study published recently in Ambio. These neighbourhoods include Strathcona, downtown Vancouver, the West End, southern Sunset and Marpole.
The researchers developed a new tool, the local restorative nature (LRN) index to assess spaces for the presence of qualities that promote mental well-being. While initially applied in Vancouver, the index can also be used in any urban landscape, according to lead author Dr. Tahia Devisscher, an assistant professor in the faculty of forestry.
We sat down with Dr. Devisscher to discuss the study findings and ...
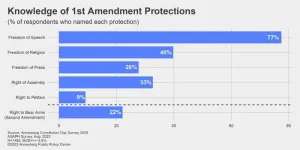
Many don’t know key facts about US Constitution, Annenberg study finds
2023-09-14
PHILADELPHIA – Many Americans do not know what rights are protected under the First Amendment and a substantial number cannot name all three branches of government, according to the 2023 Annenberg Constitution Day Civics Survey.
The Annenberg Public Policy Center’s annual, nationally representative survey finds that when U.S. adults are asked to name the specific rights guaranteed by the First Amendment to the Constitution, only one right is recalled by most of the respondents: Freedom of speech, ...
All work and no play will really make a dull life - new research reveals
2023-09-14
The study across three countries led by the Department of Psychology’s Dr Paul Hanel discovered people who prioritised achievement over enjoyment were less happy on the next day.
Whereas those who aimed for freedom said they had a 13% increase in well-being, recording better sleep quality and life satisfaction.
And participants who tried to relax and follow their hobbies recorded an average well-being boost of 8% and a 10% drop in stress and anxiety.
Dr Hanel worked with colleagues at the University of Bath on the Journal of Personality-published study.
For the first ...
New poll shows 77% of Massachusetts residents support $600 child & family tax credit
2023-09-14
Boston, MA – New polling data released late last week shows 77% of surveyed Massachusetts residents support a $600 state Child and Family Tax Credit. This polling confirms the popularity of the more generous Child and Family Tax Credit included in the House tax package, which is under consideration alongside the Senate tax bill by a bicameral conference committee.
“The overwhelming support for a $600 tax credit per child matches up with the stories I have heard from families across my district, and the experiences of working Massachusetts families that they need more financial ...
New camera offers ultrafast imaging at a fraction of the normal cost
2023-09-14
WASHINGTON — Capturing blur-free images of fast movements like falling water droplets or molecular interactions requires expensive ultrafast cameras that acquire millions of images per second. In a new paper, researchers report a camera that could offer a much less expensive way to achieve ultrafast imaging for a wide range of applications such as real-time monitoring of drug delivery or high-speed lidar systems for autonomous driving.
“Our camera uses a completely new method to achieve high-speed imaging,” said Jinyang Liang from the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS) ...
Peer-led patient navigation helps minoritized patients engage in their own mental healthcare
2023-09-14
INDIANAPOLIS – Research scientists led by Johanne Eliacin, PhD, of the U.S. Department of Veterans’ Affairs (VA) and Regenstrief Institute, have developed PARTNER-MH, an innovative, peer-led patient navigation program to support racially and ethnically minoritized veterans seeking mental healthcare, regardless of the types of mental health services needed or their mental health diagnoses.
In two peer-reviewed published papers they report significant improvements in mental health outcomes and high participant satisfaction with the program.
PARTNER-MH, developed for VA mental ...
Enhancing neonatal health: Genomic sequencing as a primary screening tool
2023-09-14
Newborn screening (NBS) is routinely performed across the world using biochemical testing methods. Recent advancements in genetic sequencing are a potential game-changer for newborn screening, swiftly assessing a comprehensive range of monogenic disorders. Yet, the effectiveness of genetic sequencing as an alternative method for NBS has not previously been studied.
To evaluate the outcomes of applying gene panel sequencing as a first-tier newborn screening test, a recent study conducted by eight NBS centers and BGI Genomics was ...
Take the money now or later? Financial scarcity doesn’t lead to poor decision making
2023-09-14
When people feel that their resources are scarce – that they don’t have enough money or time to meet their needs – they often make decisions that favor short-term gains over long-term benefits. Because of that, researchers have argued that scarcity pushes people to make myopic, impulsive decisions. But a study published by the American Psychological Association provides support for a different, less widely held view: People experiencing scarcity make reasonable decisions based on their circumstances, and only ...
Researchers make strides in harnessing low-grade heat for efficient energy conversion
2023-09-14
A team of researchers, jointly led by Professor Hyun-Wook Lee and Professor Dong-Hwa Seo from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), in collaboration with Professor Seok Woo Lee from Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, has achieved significant breakthroughs in harnessing low-grade heat sources (<100 °C) for efficient energy conversion. Their groundbreaking work focuses on developing a highly efficient Thermally Regenerative Electrochemical Cycle (TREC) system capable of converting small temperature differences into usable energy.
Conventional energy-harvesting ...