(Press-News.org) A team of researchers, jointly led by Professor Hyun-Wook Lee and Professor Dong-Hwa Seo from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), in collaboration with Professor Seok Woo Lee from Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, has achieved significant breakthroughs in harnessing low-grade heat sources (<100 °C) for efficient energy conversion. Their groundbreaking work focuses on developing a highly efficient Thermally Regenerative Electrochemical Cycle (TREC) system capable of converting small temperature differences into usable energy.
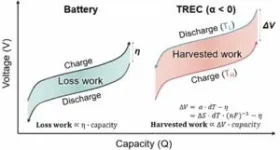
Conventional energy-harvesting systems face challenges when it comes to effectively utilizing low-grade heat sources. However, TREC systems offer an attractive solution as they integrate battery functionality with thermal-energy-harvesting capabilities. In this study, the research team delved into the role of structural vibration modes to enhance the efficacy of TREC systems.
By analyzing how changes in covalent bonding influence vibration modes—specifically affecting structural water molecules—the researchers discovered that even minute amounts of water induce strong structural vibrations within cyanide ligands’ A1g stretching mode. These vibrations substantially contribute to a larger temperature coefficient (ɑ) within a TREC system. Based on these insights, the team designed and implemented a highly efficient TREC system using a sodium-ion-based aqueous electrolyte.
“This study provides valuable insights into how structural vibration modes can enhance the energy-harvesting capabilities of TREC systems,” explained Professor Hyun-Wook Lee. “Our findings deepen our understanding of Prussian Blue analogs’ intrinsic properties regulated by these vibration modes—opening up new possibilities for improved energy conversion.”
The potential applications for TREC systems are vast, particularly in wearable technologies and other devices where small temperature differentials exist. By effectively capturing and converting low-grade heat into usable energy, TREC systems offer a promising pathway towards the development of next-generation secondary batteries.
The study findings have been published ahead of their official publication in the online version of Advanced Materials on July 3, 2023. This research has received support from the 2023 Research Fund of UNIST, Individual Basic Science & Engineering Research Program, and the National Center for Materials Research Data through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea, funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT).
Journal Reference
Ahreum Choi, You-Yeob Song, Juyoung Kim, et al., “Enhancing Efficiency of Low-Grade Heat Harvesting by Structural Vibration Entropy in Thermally Regenerative Electrochemical Cycles,” Adv. Mater., (2023).
END
Researchers make strides in harnessing low-grade heat for efficient energy conversion
The study findings have been published ahead of their official publication in the online version of Adv. Mater. on July 3, 2023
2023-09-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New $50 million institute aims to use the power of math to model, predict biological processes
2023-09-14
Building a mathematics-based understanding of biology at all scales of life — from individual cells to interactions between species — is the goal of a new $50 million institute supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation in partnership with the Simons Foundation. The two organizations are each providing $25 million to launch the National Institute for Theory and Mathematics in Biology (NITMB). The institute will bring together experts across the mathematical and biological sciences to explore research challenges related to a broad range of topics and industries, such as the environment, biomedicine and biotechnology.
The institute will be led by Northwestern University ...
Preventing ground collapse through new AI-based monitoring
2023-09-14
As severe urban overcrowding is trending worldwide many underground development projects are being carried out in metropolitan centers worldwide. South Korea has experienced problems such as aging underground facilities and inaccurate information management due to rapid urban development since the 1970s and 1980s. Accident prevention has become a major challenge since accidents in underground spaces have occurred due to various causes.
The Korean government is undertaking projects to digitize underground facilities and ground information and establish a 3D underground space information database to prevent ...
Nation’s first dual degree in medicine and AI aims to prepare the next generation of health care providers
2023-09-14
The Joe R. and Teresa Lozano Long School of Medicine at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) and the University College at The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) are officially launching the first known program in the United States to combine medicine and artificial intelligence. A Doctor of Medicine (MD) from UT Health San Antonio and a Master of Science in Artificial Intelligence (MSAI) from UTSA will form a five-year MD/MS program enabling physicians trained in San Antonio to uniquely lead in the practical use of artificial intelligence to improve diagnostic and treatment ...
Worse results and more drop-outs when teaching is in English
2023-09-14
Using English as the language of instruction in higher education has a marked negative impact on learning outcomes when it is not the students’ first language, according to a new study from KTH Royal Institute of Technology and Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden. When 2,000 Swedish students were divided up into English-language and Swedish-language versions of an introductory course in programming, those students who were taught in English obtained much worse results, and more dropped out of the course prematurely.
English is increasingly used as a global language of instruction in higher education, known as English Medium Instruction or ...
Lack of maternal care affects development, microbiome and health of wild bees
2023-09-14
TORONTO, Sept. 14, 2023 – Most wild bees are solitary, but one tiny species of carpenter bees fastidiously cares for and raises their offspring, an act that translates into huge benefits to the developing bee’s microbiome, development and health, found York University researchers.
Not unlike the positive affect human mothers can have on their offspring, the maternal care of these carpenter bees (Ceratina calcarata) staves off an overabundance of harmful fungi, bacteria, viruses and parasites in the earliest stage of development.
Without maternal care the pathogen load of these ...
Pollination by more than one bee species improves cherry harvest
2023-09-14
To obtain the biggest cherry harvest, trees should be pollinated by both honey bees and mason bees. A new study led by a researcher at the University of Gothenburg shows yet another benefit of biodiversity.
Like many other fruit trees, most sweet cherry cultivars depend on cross-pollination to produce their fruit. This means that there need to be several different cultivars of sweet cherry trees in an orchard for the bees to transport pollen from one to another.
“Sweet cherry trees are usually planted in alternate rows of different cultivars. In some cases, you can put different cultivars in the same row, but ...
New foresight report identifies urgent policy actions needed to put SDGs back on track
2023-09-14
Ahead of the UN’s SDG Summit (18-19 September), Earth4All, an international team of economists and scientists, and the Foundation for European Progressive Studies (FEPS), unveil groundbreaking research showing that policymakers can ensure the implementation of SDGs by 2050. The report ‘SDGs for All: Strategic scenarios’ equips policymakers with practical solutions designed to accelerate SDG implementation and to respond to the planetary emergency. It concludes that policymakers can step up the implementation of the SDGs by 2030 and beyond ...
The fourth wave of the US overdose crisis: fentanyl and stimulants
2023-09-14
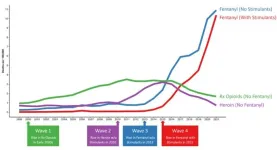
New research published in the scientific journal Addiction has found that the proportion of US overdose deaths involving both fentanyl and stimulants has increased more than 50-fold since 2010, from 0.6% (235 deaths) in 2010 to 32.3% (34,429 deaths) in 2021. By 2021, stimulants (such as cocaine and methamphetamine) had become the most common drug class found in fentanyl-involved overdoses in every US state. This rise in fentanyl/stimulant fatalities constitutes the ‘fourth wave’ in the US’s ...
Overdose deaths from fentanyl laced stimulants have risen 50-fold since 2010
2023-09-14
New UCLA-led research has found that the proportion of US overdose deaths involving both fentanyl and stimulants has increased more than 50-fold since 2010, from 0.6% (235 deaths) in 2010 to 32.3% (34,429 deaths) in 2021.
By 2021, stimulants such as cocaine and methamphetamine had become the most common drug class found in fentanyl-involved overdoses in every US state. This rise in fentanyl/stimulant fatalities constitutes the ‘fourth wave’ in the US’s long-running opioid overdose crisis –the death toll of which continues to rise precipitously.
“We’re now seeing ...
Most Ohio students who earn manufacturing-related credentials work in other industries
2023-09-14
Most students who complete manufacturing-related credentials in Ohio do not end up employed in manufacturing in the state, highlighting a challenge that faces policymakers as they push to create more U.S. manufacturing jobs, according to a new RAND Corporation report.
Among those who earned a manufacturing-related credential from a public postsecondary institute in Ohio from 2006 to 2019, fewer than 40% worked in manufacturing in the state within one year after completing their education.
Wages are not a likely contributor to the trend. Students who enter other fields after completing a manufacturing-related credential earn less than their peers who pursued ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
[Press-News.org] Researchers make strides in harnessing low-grade heat for efficient energy conversionThe study findings have been published ahead of their official publication in the online version of Adv. Mater. on July 3, 2023