(Press-News.org) CORNING, N.Y. | Corning Incorporated | September 15, 2023 - Corning Incorporated (NYSE: GLW) today announced the launch of Corning® Videodrop, an optical technology that applies the principles of interferometric microscopy to quantify the size and concentration of nanoparticles. The latest addition to the company’s growing suite of bioprocessing technology, Videodrop can analyze a solution in less than 60 seconds, and requires only a single 5-10 µl drop of sample material for testing.
The technology is capable of collecting a physical titer of viral vectors such as lentivirus, retrovirus, adenovirus, and extracellular vesicles (EVs) in the range of 80-500 nanometers. Once a sample is loaded, the processing algorithm detects and tracks nanoparticles to quantify the concentration and size distribution without the need for labeling. Videodrop can be used as an in-process control throughout the purification process.
“Videodrop is easy to use, fast, and reliable. Sample prep is also easy, being label free, and its operation is seamless thanks to its intuitive software interface,” said Chris Suarez, PhD, Sr. Manager, Scientific Applications and Support, Americas at Corning Life Sciences.
Not only can these efficiencies reduce overall costs, but Corning anticipates that this technology will support a variety of industry needs, including advancements in cell and gene therapy and vaccine production.
“We’re excited to extend our bioprocessing portfolio with our first solution that directly benefits our downstream customers,” said Janice Simler, PhD, Director of Business Operations for Bioproduction at Corning Life Sciences. “Our goal is to build out technology platforms across the whole workflow, expanding our impact as a valued partner throughout the drug development process.”
To learn more about Corning Videodrop and how it can enhance your workflow or laboratory, visit www.corning.com/Videodrop.
###
Caution Concerning Forward-Looking Statements
This press release contains "forward-looking statements" (within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995), which are based on current expectations and assumptions about Corning's financial results and business operations, that involve substantial risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially. These risks and uncertainties include: the duration and severity of the recent COVID-19 (coronavirus) outbreak, and its ultimate impact across our businesses on demand, operations and our global supply chains; the effects of acquisitions, dispositions and other similar transactions by the Company, the effect of global business, financial, economic and political conditions; tariffs and import duties; currency fluctuations between the U.S. dollar and other currencies, primarily the Japanese yen, New Taiwan dollar, euro, Chinese yuan, and South Korean won; product demand and industry capacity; competitive products and pricing; availability and costs of critical components and materials; new product development and commercialization; order activity and demand from major customers; the amount and timing of our cash flows and earnings and other conditions, which may affect our ability to pay our quarterly dividend at the planned level or to repurchase shares at planned levels; possible disruption in commercial activities due to terrorist activity, cyber-attack, armed conflict, political or financial instability, natural disasters, or major health concerns; unanticipated disruption to equipment, facilities, IT systems or operations; effect of regulatory and legal developments; ability to pace capital spending to anticipated levels of customer demand; rate of technology change; ability to enforce patents and protect intellectual property and trade secrets; adverse litigation; product and components performance issues; retention of key personnel; customer ability, most notably in the Display Technologies segment, to maintain profitable operations and obtain financing to fund their ongoing operations and manufacturing expansions and pay their receivables when due; loss of significant customers; changes in tax laws and regulations including the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017; and the potential impact of legislation, government regulations, and other government action and investigations.
For a complete listing of risks and other factors, please reference the risk factors and forward-looking statements described in our annual reports on Form 10-K and quarterly reports on Form 10-Q. Forward-looking statements speak only as of the day that they are made, and Corning undertakes no obligation to update them in light of new information or future events.
Web Disclosure
In accordance with guidance provided by the SEC regarding the use of company websites and social media channels to disclose material information, Corning Incorporated ("Corning") wishes to notify investors, media, and other interested parties that it uses its website to publish important information about the company, including information that may be deemed material to investors, or supplemental to information contained in this or other press releases. The list of websites and social media channels that the company uses may be updated on Corning's media and website from time to time. Corning encourages investors, media, and other interested parties to review the information Corning may publish through its website and social media channels as described above, in addition to the company's SEC filings, press releases, conference calls, and webcasts.
About Corning Incorporated
Corning (www.corning.com) is one of the world's leading innovators in materials science, with a 170-year track record of life-changing inventions. Corning applies its unparalleled expertise in glass science, ceramic science, and optical physics along with its deep manufacturing and engineering capabilities to develop category-defining products that transform industries and enhance people's lives. Corning succeeds through sustained investment in RD&E, a unique combination of material and process innovation, and deep, trust-based relationships with customers who are global leaders in their industries. Corning's capabilities are versatile and synergistic, which allows the company to evolve to meet changing market needs, while also helping its customers capture new opportunities in dynamic industries. Today, Corning's markets include optical communications, mobile consumer electronics, display, automotive, solar, semiconductors, and life sciences.
END
Corning® launches Videodrop, revolutionizing real-time nanoparticle detection and analysis
New optical technology aims to expedite and enhance the development of viral vectors and gene therapies
2023-09-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Groundbreaking soft valve technology enabling sensing and control integration in soft robots
2023-09-15
Soft inflatable robots have emerged as a promising paradigm for applications that require inherent safety and adaptability. However, the integration of sensing and control systems in these robots has posed significant challenges without compromising their softness, form factor, or capabilities. Addressing this obstacle, a research team jointly led by Professor Jiyun Kim (Department of New Material Engineering, UNIST) and Professor Jonbum Bae (Department of Mechanical Engineering, UNIST) has developed groundbreaking “soft valve” technology—an all-in-one solution that integrates sensors and control valves while maintaining complete softness.
Traditionally, ...
Living in a disadvantaged neighborhood affects food choices, weight gain and the microstructure of the brain
2023-09-15
You are what you eat, according to the adage. But it’s not just the body that’s impacted. According to research from UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine, living in a disadvantaged neighborhood can affect food choices, weight gain and even the microstructure of the brain.
The study, appearing in Communications Medicine, a Nature journal, finds poor quality of available foods, increased intake of calories from foods high in trans-fatty acids, and environments that do not foster physical activity, all prevalent in disadvantaged neighborhoods, disrupt the flexibility ...
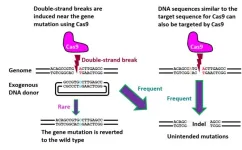
A NICER approach to genome editing
2023-09-15
Osaka, Japan – The gene editing technique CRISPR/Cas9 has allowed researchers to make precise and impactful changes to an organism’s DNA to fix mutations that cause genetic disease. However, the CRISPR/Cas9 method can also result in unintended DNA mutations that may have negative effects. Recently, researchers in Japan have developed a new gene editing technique that is as effective as CRISPR/Cas9 while significantly reducing these unintended mutations.
In a new study published in Nature ...
Learn the intricacies in solving problems related to energy transfer
2023-09-15
Volume 2 of the series on Solved Problems in Transport Phenomena is out. This unique compendium covers energy transfer at the microscopic and macroscopic levels in a format that does not overwhelm students with a large repertoire of problems. It uses clear highlights and easy-to-follow concept presentations to help students grasp the methodology in problem solving.
Solved Problems in Transport Phenomena: Energy Transfer shows the students how to tackle a problem related to heat transfer as if they were going to solve it for the first time in their lives. A balanced approach ...
A quarter of people are undoing the benefits of healthy meals by unhealthy snacking
2023-09-15
A quarter of people are undoing the benefits of healthy meals with unhealthy snacks, which increases the risk of strokes and cardiovascular disease.
The findings, published today in the European Journal of Nutrition by researchers from the School of Life Course & Population Sciences and ZOE, details the snacking habits of 854 people from the ZOE PREDICT study.
Researchers found that half of the participants do not match the healthiness of their meals to their snacks and vice versa. This difference has a negative effect on health measures, such as blood sugar and fat levels, and addressing this could be a simple diet strategy to improve ...
Polar experiments reveal seasonal cycle in Antarctic sea ice algae
2023-09-15
In the frigid waters surrounding Antarctica, an unusual seasonal cycle occurs. During winter, from March to October, the sun barely rises. As seawater freezes it rejects salts, creating pockets of extra-salty brine where microbes live in winter. In summer, the sea ice melts under constant daylight, producing warmer, fresher water at the surface.
This remote ecosystem is home to much of the Southern Ocean’s photosynthetic life. A new University of Washington study provides the first measurements of how sea-ice algae and other single-celled life adjust to these seasonal rhythms, offering clues to what might happen as ...
Clever lapwings use cover to hide in plain sight
2023-09-15
Ground-nesting birds called lapwings use the shape of their nests and surroundings to hide from predators, new research shows.
Many ground-nesting species are in decline due to changes in land management and high populations of predators, such as foxes and crows. Conservation projects can fail because too many eggs and chicks are eaten.
The new study, led by the University of Exeter, assessed the visibility of lapwing nests in terms of cover (also called “occlusion”) and camouflage using models that simulate the vision and viewing angles of various predators.
The findings showed that despite nesting in open fields, lapwings can hide their eggs ...
When it comes to starting a family, timing is everything
2023-09-15
The review, conducted jointly with researchers from Oxford University, the Royal Berkshire Hospital in Reading, and the Princess Anne Hospital in Southampton, included seven randomised controlled trials involving 2,464 women or couples who had been trying to conceive.
Each month there is a narrow window for successful conception due to the limited lifespan of the sperm and egg, which begins from around five days before ovulation (egg release) and lasts until several hours afterwards.
The period of a woman’s cycle can be identified by different methods, including urine ovulation tests (dipstick ...
Are us teenagers more likely than others to exaggerate their math abilities?
2023-09-15
A major new study has revealed that American teenagers are more likely than any other nationality to brag about their math ability.
Research using data from 40,000 15-year-olds from nine English-speaking nations internationally found those in North America were the most likely to exaggerate their mathematical knowledge, while those in Ireland and Scotland were least likely to do so.
The study, published in the peer-reviewed journal Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice, used responses from the OECD Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA), in which participants took a two-hour maths test alongside a ...
Women receiving inflated risks from genetic testing could undergo unnecessary breast surgery
2023-09-15
Women could be opting to have unnecessary surgery to avoid breast cancer, after being told they are at high risk from genetic test results which do not take family history into account.
The authors of new research led by the University of Exeter have warned that women who discover, outside of a clinical setting, that they carry a disease-causing variant in one of the BRCA genes (BRCA1 or BRCA2) may be told their risk of breast cancer is 60-80 per cent. In fact, the risk could be less than 20 per cent if they do not have a close relative with the condition.
The warning has emerged in a paper published today in the Lancet journal eClinical Medicine. Until recently, women who ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] Corning® launches Videodrop, revolutionizing real-time nanoparticle detection and analysisNew optical technology aims to expedite and enhance the development of viral vectors and gene therapies