(Press-News.org) Hospital staff spend a significant amount of time working to protect patients from acquiring infections while they are being cared for in the hospital. They employ various methods from hand hygiene to isolation rooms to rigorous environmental sanitation. Despite these efforts, hospital-onset infections still occur—the most common of which is caused by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile, or C. diff, the culprit of almost half a million infections in the U.S. each year.
Surprising findings from a new study in Nature Medicine suggest that the burden of C. diff infection may be less a matter of hospital transmission and more a result of characteristics associated with the patients themselves.
The study team, led by Evan Snitkin, Ph.D. and Vincent Young, M.D., Ph.D., both members of the Departments of Microbiology & Immunology and Internal Medicine/Infectious Diseases at University of Michigan Medical School and Mary Hayden, M.D. of Rush University Medical Center, leveraged ongoing epidemiological studies focused on hospital-acquired infections that enabled them to analyze daily fecal samples from every patient within the intensive care unit at Rush University Medical Center over a nine-month period.
Arianna Miles-Jay, a postdoctoral fellow in Dr. Snitkin’s lab, analyzed the over 1,100 patients in the study, and found that a little over 9% were colonized with C. diff. Using whole genome sequencing at U-M of 425 C. difficile strains isolated from nearly 4000 fecal specimens, she compared the strains to each other to analyze spread.
“By systematically culturing every patient, we thought we could understand how transmission was happening. The surprise was that, based on the genomics, there was very little transmission.”
Essentially, there was very little evidence that the strains of C. diff from one patient to the next were the same, which would imply in-hospital acquisition. In fact, there were only six genomically supported transmissions over the study period. Instead, people who were already colonized were at greater risk of transitioning to infection.
“Something happened to these patients that we still don’t understand to trigger the transition from C. diff hanging out in the gut to the organism causing diarrhea and the other complications resulting from infection,” said Snitkin.
Hayden notes this doesn’t mean hospital infection prevention measures are not needed. In fact, the measures in place in the Rush ICU at the time of the study – high rates of compliance with hand hygiene among healthcare personnel, routine environmental disinfection with an agent active against C diff, and single patient rooms – were likely responsible for the low transmission rate. The current study highlights, though that more steps are needed to identify patients who are colonized and try to prevent infection in them.
Where did the C. diff come from? “They are sort of all around us,” said Young. “C. diff creates spores, which are quite resistant to environmental stresses including exposure to oxygen and dehydration…for example, they are impervious to alcohol-based hand sanitizer.”
However, only about 5% of the population outside of a healthcare setting has C. diff in their gut—where it typically causes no issues.
“We need to figure out ways to prevent patients from developing an infection when we give them tube feedings, antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors—all things which predispose people to getting an actual infection with C. diff that causes damage to the intestines or worse,” said Young.
The team next hopes to build on work investigating the use of A.I. models to predict patients at risk of C. diff infection to identify patients who are likely to be colonized and who could benefit from more focused intervention.
Said Snitkin, “A lot of resources are put into gaining further improvements in preventing the spread of infections, when there is increasing support to redirect some of these resources to optimize the use of antibiotics and identify other triggers that lead patients harboring C diff and other healthcare pathogens to develop serious infections.”
Additional authors include Arianna Miles-Jay, Michael Y. Lin, Teppei Shimasaki, Michael Schoeny, Christine Fukuda, Thelma Dangana, Nicholas Moore, Sarah E. Sansom, Rachel D. Yelin, Pamela Bell, Krishna Rao, Micah Keidan, Alexandra Standke, and Christine Bassis.
Paper cited: “Longitudinal genomic surveillance of carriage and transmission of Clostridioides difficile in an intensive care unit,” Nature Medicine. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-023-02549-4
END
The surprising origin of a deadly hospital infection
C. diff may not result from transmission, but from within the infected patient themselves
2023-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mature sperm lack intact mitochondrial DNA, study finds
2023-09-18
New research provides insight about the bedrock scientific principle that mitochondrial DNA — the distinct genetic code embedded in the organelle that serves as the powerplant of every cell in the body — is exclusively passed down by the mother.
The study, a collaboration among Oregon Health & Science University and other institutions, published today in the journal Nature Genetics.
Scientists have long recognized the fact that mitochondrial DNA, or mtDNA, comes exclusively from egg cells in humans, meaning only the mother contributes the genetic code carried by ...
Research identifies new potential hurdle for nano-based therapies
2023-09-18
HOUSTON ― Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have discovered that certain nano-based cancer therapies may be less effective in younger patients, highlighting the need for further investigation into the impact of aging on the body’s ability to respond to treatment.
The researchers found age-related differences are due to how effectively the liver filters the bloodstream. Younger livers are more efficient at this process, which helps limit toxins in the blood but also filters out beneficial treatments, potentially rendering them ineffective.
The study, published today in ...
Improving the properties of sweeteners for enhanced thermal energy storage
2023-09-18
As we seek more efficient utilization of waste thermal energy, use of “phase change materials (PCMs)” is a good option. PCMs have a large latent heat capacity and the ability to store-and-release heat as they change from one state of matter to another. Among many PCMs, sugar alcohols (SAs), a class of organic compounds commonly used as sweeteners, stand out due to their low cost, non-toxic, non-corrosive, and biodegradable nature. In particular, SAs generally have their melting point in 100–200 °C, which is an important temperature range where a huge amount of waste heat exists but is currently ...
Ohio State leads new global climate center on AI for biodiversity change
2023-09-18
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The Ohio State University will lead a new multimillion dollar international center devoted to using artificial intelligence to help understand climate impacts on biodiversity.
The AI and Biodiversity Change (ABC) Global Climate Center will bring together ecologists and computer scientists from six universities in the United States and Canada, with partners in UK, Europe, and Australia, to develop new AI-enabled, data-supported approaches to study how changes in climate are impacting life – including animals, plants and insects – on Earth.
$5 ...
Ohio State researchers publish national guidelines for ALS genetic testing, counseling
2023-09-18
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine led the creation of evidence-based consensus guidelines for genetic testing and counseling for patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a neurodegenerative disease that affects the cells in the brain and spine.
These evidence-based, consensus guidelines provide clinicians with a framework for the offer of genetic testing and outline the information that should be provided to persons with ALS before and after testing. In addition, the guidelines provide specific recommendations regarding ...
Study: Admissions policies that consider grades and test scores in context of available opportunities are linked to college success
2023-09-18
Indicators of high school grades and standardized test scores that take into account the levels of school, neighborhood, and family resources available to students are strongly associated with those students’ success in college, according to new research published today. The study, published in AERA Open, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association, emerges against the backdrop of the recent Supreme Court decision to ban race-conscious admissions in higher ...
Unlocking urban diversity: The magnetism of complex amenities
2023-09-18
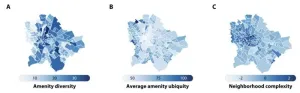
Diversity fuels prosperity in cities, but where do people from diverse backgrounds meet? A study from the Complexity Science Hub now indicates that locations offering a range of rare shops and services may hold the key.
Extensive research consistently underscores a common factor in successful cities: diversity. Encouraging interactions between individuals of different backgrounds fosters the exchange of ideas, leading to innovation and economic success. “However, segregation persists in urban ...
Latest blood cancer treatment updates presented at annual NCCN event during Blood Cancer Awareness Month
2023-09-18
SAN FRANCISCO, CA [September 18, 2023] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) 2023 Annual Congress: Hematologic Malignancies™ returns to San Francisco this week, for the first time since 2019. The meeting features insights from world-renowned experts on providing optimal, evidence-based treatment for various blood cancers, plus best practices for protecting vulnerable populations in a changing healthcare landscape.
The live event is taking place September 22-23, 2023, at the Hilton San Francisco Union Square. ...
How do suicide risk or depression screenings compare to identify patients at risk?
2023-09-18
Editor’s Note: September is National Suicide Prevention Month.
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Research led by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and Wesleyan University found that depression screening tools outperformed suicide risk screenings under most conditions.
“We compared the effectiveness of multiple depression and suicide risk screening methods for the purpose of identifying primary care patients who subsequently attempted suicide. Our findings may generate a lot of discussion within the suicide prevention community, as it contradicts long-held assumptions ...
Atomic layer deposition route to scalable, electronic-grade van der Waals Te thin films
2023-09-18
A research team, led by Professor Joonki Suh in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and the Graduate School of Semiconductor Materials and Devices Engineering at UNIST, has made a significant breakthrough in thin film deposition technology. By employing an innovative atomic layer deposition (ALD) process, Professor Seo successfully achieved regular arrangement of tellurium (Te) atoms at low temperatures as low as 50 degrees Celsius.
The ALD method is a cutting-edge thin film process that enables precise stacking ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Bug beats: caterpillars use complex rhythms to communicate with ants
High-risk patients account for 80% of post-surgery deaths
Celebrity dolphin of Venice doesn’t need special protection – except from humans
Tulane study reveals key differences in long-term brain effects of COVID-19 and flu
The long standing commercialization challenge of lithium batteries, often called the dream battery, has been solved.
New method to remove toxic PFAS chemicals from water
The nanozymes hypothesis of the origin of life (on Earth) proposed
Microalgae-derived biochar enables fast, low-cost detection of hydrogen peroxide
Researchers highlight promise of biochar composites for sustainable 3D printing
Machine learning helps design low-cost biochar to fight phosphorus pollution in lakes
Urine tests confirm alcohol consumption in wild African chimpanzees
Barshop Institute to receive up to $38 million from ARPA-H, anchoring UT San Antonio as a national leader in aging and healthy longevity science
Anion-cation synergistic additives solve the "performance triangle" problem in zinc-iodine batteries
Ancient diets reveal surprising survival strategies in prehistoric Poland
Pre-pregnancy parental overweight/obesity linked to next generation’s heightened fatty liver disease risk
Obstructive sleep apnoea may cost UK + US economies billions in lost productivity
Guidelines set new playbook for pediatric clinical trial reporting
Adolescent cannabis use may follow the same pattern as alcohol use
Lifespan-extending treatments increase variation in age at time of death
From ancient myths to ‘Indo-manga’: Artists in the Global South are reframing the comic
Putting some ‘muscle’ into material design
House fires release harmful compounds into the air
Novel structural insights into Phytophthora effectors challenge long-held assumptions in plant pathology
Q&A: Researchers discuss potential solutions for the feedback loop affecting scientific publishing
A new ecological model highlights how fluctuating environments push microbes to work together
Chapman University researcher warns of structural risks at Grand Renaissance Dam putting property and lives in danger
Courtship is complicated, even in fruit flies
Columbia announces ARPA-H contract to advance science of healthy aging
New NYUAD study reveals hidden stress facing coral reef fish in the Arabian Gulf
36 months later: Distance learning in the wake of COVID-19
[Press-News.org] The surprising origin of a deadly hospital infectionC. diff may not result from transmission, but from within the infected patient themselves