(Press-News.org) About The Study: Increased TV/DVD screen time from age 1 year negatively affected later development in this study of 57,980 children. To reduce the negative consequences of excessive media use, researchers and health care professionals should encourage family media management and recommend social support for parents who tend to rely on the media.
Authors: Midori Yamamoto, Ph.D., of Chiba University in Chiba, Japan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.3643)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.3643?guestAccessKey=db74e19c-7953-493e-8691-cb7b8b0a08fe&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=091823
END
Screen time and developmental performance among children at 1-3 years of age
JAMA Pediatrics
2023-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
School-based health centers, access to care, and income-based disparities
2023-09-18
About The Study: In this study using nationally representative survey data with difference-in-differences analysis of school-based health center (SBHC) adoption, SBHCs were associated with access to care and reduced income-based disparities. These findings support additional SBHC expansion.
Authors: Michel Boudreaux, Ph.D., of the University of Maryland in College Park, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.34532)
Editor’s ...
Buprenorphine dose and time to discontinuation among patients with opioid use disorder in the era of fentanyl
2023-09-18
About The Study: The results of this study of 6,499 patients initiating buprenorphine treatment between 2016 and 2020 suggest that the value of higher buprenorphine doses than currently recommended needs to be considered for improving retention in treatment.
Authors: Laura C. Chambers, Ph.D., M.P.H., of Brown University in Providence, Rhode Island, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.34540)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
Telecare cuts costs, boosts quality of life for dementia patients
2023-09-18
A UCSF telecare program that improves outcomes for patients with dementia and lightens the load for unpaid caregivers also has the surprising bonus of cutting Medicare costs, according to UC San Francisco research.
In the study, publishing in JAMA Internal Medicine on Sept. 18, 2023, researchers, led by UCSF, compared the Medicare costs of 780 patients with dementia. The patients were randomized 2:1 to receive Care Ecosystem support – which included medical and practical assistance – or their usual care for a 12-month period. Both groups were similar in age, severity of dementia ...
Higher buprenorphine doses associated with improved retention in treatment for opioid use disorder
2023-09-18
Individuals with opioid use disorder who were prescribed a lower buprenorphine dose were 20% more likely to discontinue treatment than those on a higher dose, according to a study of patients prescribed buprenorphine in Rhode Island from 2016 to 2020, as fentanyl became widely available. The study, published today in JAMA Network Open, was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), part of the National Institutes of Health, and conducted by researchers at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island; NIDA and the Rhode Island ...
Tracking down the formation of cardenolides in plants
2023-09-18
Plants produce an impressive array of metabolites, including many medically valuable steroids. Well-known examples of this class of substances obtained from plants are cardenolides. As early as 1785, the British physician William Withering (1741-1799) published a book on the red foxglove and its use in medicine (An account of the foxglove, and some of its medical uses: with practical remarks on dropsy, and other diseases. Birmingham 1785). He had found out in experiments that taking extracts ...
The surprising origin of a deadly hospital infection
2023-09-18
Hospital staff spend a significant amount of time working to protect patients from acquiring infections while they are being cared for in the hospital. They employ various methods from hand hygiene to isolation rooms to rigorous environmental sanitation. Despite these efforts, hospital-onset infections still occur—the most common of which is caused by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile, or C. diff, the culprit of almost half a million infections in the U.S. each year.
Surprising findings from a new study in Nature Medicine suggest that the burden of C. diff infection may be less a matter of hospital transmission and more a result of characteristics associated ...
Mature sperm lack intact mitochondrial DNA, study finds
2023-09-18
New research provides insight about the bedrock scientific principle that mitochondrial DNA — the distinct genetic code embedded in the organelle that serves as the powerplant of every cell in the body — is exclusively passed down by the mother.
The study, a collaboration among Oregon Health & Science University and other institutions, published today in the journal Nature Genetics.
Scientists have long recognized the fact that mitochondrial DNA, or mtDNA, comes exclusively from egg cells in humans, meaning only the mother contributes the genetic code carried by ...
Research identifies new potential hurdle for nano-based therapies
2023-09-18
HOUSTON ― Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have discovered that certain nano-based cancer therapies may be less effective in younger patients, highlighting the need for further investigation into the impact of aging on the body’s ability to respond to treatment.
The researchers found age-related differences are due to how effectively the liver filters the bloodstream. Younger livers are more efficient at this process, which helps limit toxins in the blood but also filters out beneficial treatments, potentially rendering them ineffective.
The study, published today in ...
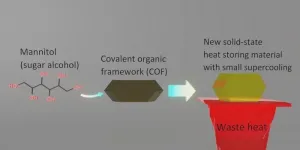
Improving the properties of sweeteners for enhanced thermal energy storage
2023-09-18
As we seek more efficient utilization of waste thermal energy, use of “phase change materials (PCMs)” is a good option. PCMs have a large latent heat capacity and the ability to store-and-release heat as they change from one state of matter to another. Among many PCMs, sugar alcohols (SAs), a class of organic compounds commonly used as sweeteners, stand out due to their low cost, non-toxic, non-corrosive, and biodegradable nature. In particular, SAs generally have their melting point in 100–200 °C, which is an important temperature range where a huge amount of waste heat exists but is currently ...
Ohio State leads new global climate center on AI for biodiversity change
2023-09-18
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The Ohio State University will lead a new multimillion dollar international center devoted to using artificial intelligence to help understand climate impacts on biodiversity.
The AI and Biodiversity Change (ABC) Global Climate Center will bring together ecologists and computer scientists from six universities in the United States and Canada, with partners in UK, Europe, and Australia, to develop new AI-enabled, data-supported approaches to study how changes in climate are impacting life – including animals, plants and insects – on Earth.
$5 ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Housing displacement, employment disruption, and mental health after the 2023 Maui wildfires
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and survival among patients with type 2 diabetes and brain metastases
Solid but fluid: New materials reconfigure their entire crystal structure in response to humidity
New research reveals how development and sex shape the brain
New discovery may improve kidney disease diagnosis in black patients
What changes happen in the aging brain?
Pew awards fellowships to seven scientists advancing marine conservation
Turning cancer’s protein machinery against itself to boost immunity
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
Adults with concurrent hearing and vision loss report barriers and challenges in navigating complex, everyday environments
Breast cancer stage at diagnosis differs sharply across rural US regions
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
[Press-News.org] Screen time and developmental performance among children at 1-3 years of ageJAMA Pediatrics