(Press-News.org)
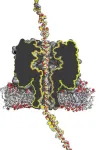
There has been a real race among scientists to create a technology that enables easy protein sequencing. Professor of Chemical Biology Giovanni Maglia of the University of Groningen has now found the missing piece in the puzzle: a way to transport a protein through a nanopore, which allows sequencing of proteins in a simple, handheld device.
DNA sequencing has been a revolution in how we understand life, and sequencing proteins is the next holy grail. Maglia explains: ‘DNA is mostly static. The processes in our cells are executed by proteins: they do the actual work. And by understanding proteins, we will understand even more about how our bodies work.’
The problem of pulling proteins through a hole
There are currently handheld devices on the market that can sequence DNA. These devices use nanopore technology: a single strand of DNA is pulled through a tiny hole (a nanopore) in a membrane, and as they pass through, the sequence of building blocks in the DNA strand can be ‘read’.
There have been steps towards applying the same nanopore technology to proteins, but it was not yet possible to transport a long protein through the tiny hole in the same way as a DNA strand. ‘It’s like cooked spaghetti,’ Maglia explains. ‘These long strands want to be disorganized, they do not want to be pushed through this tiny hole.’
Single-stranded DNA is also a bit like cooked spaghetti, but it can be pulled through with an electric field because DNA itself is electrically charged. But proteins have a weaker charge, and can carry either positive or negative charge. ‘Proteins and DNA are different,’ Maglia explains, ‘so the technology needs to be adapted.’
Going with the flow
To transport a protein through a nanopore, Maglia used a solution of electrically charged particles (ions), which can be pulled through the nanopore with an electric field. When this happens, they drag along the protein. It was not at all trivial to make this work, Maglia explains: ‘we didn’t know whether the flow would be strong enough. Furthermore, these ions want to move both ways, but by attaching a lot of charge on the nanopore itself, we were able to make it directional.’
Maglia engineered a system with the strongest possible flow without proteins. In a collaboration with researchers of the University of Rome Tor Vergata, computer simulations were performed, that revealed that the force of this flow on a protein was comparable to the force of the electric field on DNA. Maglia then tried it on a difficult protein: one with many negative charges, that would make it want to move in the opposite direction of the flow. But even then, the flow was strong enough to pull the protein through the nanopore. Maglia: ‘Previously, only easy to thread proteins were analysed. But we gave ourselves one of the most difficult proteins as a test. And it worked!
‘This proves that there is no fundamental limitation to sequencing proteins anymore,’ Maglia says. With his new startup called Portal Biotech, Maglia intends to make the nanopore technology from his lab available to users, such as labs and doctors. ‘With this latest research result, we have the missing piece that we needed to make protein sequencing happen.’
***
Why would we want to sequence proteins?
DNA is like a blue print for our bodies, but proteins are like the workers that do the actual construction. Based on DNA (the instructions), a range of proteins are formed, that execute various functions throughout our bodies. Just to name a few, proteins are responsible for:
Taking up and releasing oxygen in our blood (hemoglobin)
Defense against pathogens (antibodies)
Transmitting signals, for instance through the nervous system, but also through a cell wall (receptors)
Proteins can also be harmful. Some examples are venom from snakes or spiders, or some pathogens (such as viruses).
We know a lot about the human genome (our DNA). By also studying the proteins in our bodies, scientists hope to gain more insight into how cells operate and what can make them malfunction. Ultimately, this can contribute to new, better treatments against diseases.
END
This month, Ochsner Health is launching a pilot program that uses AI to draft simple messages to patients in the MyOchsner app portal. A small group of Ochsner clinicians will participate in testing a new Epic feature that drafts responses to routine patient requests, which will then be reviewed and edited by the clinicians. The feature is meant to speed up app response time to patients and allows doctors to spend more time with patients.
“Ochsner has long been a leader in using digital tools to improve the patient experience,” said Ochsner ...
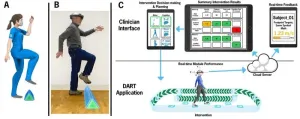
An augmented-reality headset is an effective digital tool for improving posture and gait in people with Parkinson’s disease, according to a recent Cleveland Clinic trial. Findings were published in Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair.
Augmented reality, or AR, allows users to complete digital programs projected into the world around them. The “Dual-task augmented Reality Treatment” (DART) uses the Microsoft HoloLens2 to run patients through dual-task training (DTT), a series of tasks designed to engage the brain and body simultaneously.
Activities ...
A team of UC researchers across three colleges has been awarded an additional $1.5 million state grant to continue research on improving firefighter protective gear.
In 2022, the Ohio Bureau of Workers’ Compensation (BWC) awarded a UC team an initial $1.2 million to provide proof of concept on the development of a firefighter jacket liner that brings a firefighter’s body temperature down through advanced cooling technology and protects the body from other external hazards.
That grant, and the new $1.5 million grant to carry the proof of concept to commercialization, ...
CMAJ headlines:
Pediatric ED visits and hospitalizations for self-harm, suicidal thoughts increased in Canada during pandemic, especially in young adolescent females
"Less is better" is the best message when talking to patients about alcohol
Pediatric ED visits and hospitalizations for self-harm, suicidal thoughts increased in Canada during pandemic, especially in young adolescent females
The COVID-19 pandemic had an outsized impact on the mental health of adolescents, especially young adolescent females, with a higher-than-expected number of emergency department (ED) visits and hospitalizations for self-harm and suicidal ideation, according to two new research ...
Healthcare organizations, in reviewing care delivery opportunities and providing feedback to staff, often focus on what went wrong, but a new study suggests that reversing this perspective may help organizations improve their work culture by understanding what went right. A team of Mass General Brigham researchers analyzed peer-to-peer positive feedback, systematically collected when caring for a dying patient as part of a mandatory mortality review process. They found that standardized collection and sharing of positive feedback — what went right — is a feasible way to increase mutual ...
An international team of scientists has developed a method for simultaneously detecting thousands of lipid molecules that are displayed to T cells in the human immune system. The study, co-led by D. Branch Moody, MD, of the Division of Rheumatology, Immunity and Inflammation at Brigham and Women's Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, represents a collaboration among researchers from Oxford, United Kingdom, Melbourne, Australia and Groningen, Netherlands. Results are published in Cell.
The team developed a new and sensitive method to detect more than 2,000 lipids bound to CD1 ...
The implementation of artificial intelligence-powered large vessel occlusion (LVO) detection software for acute stroke triage can improve endovascular thrombectomy treatment times, according to new research from UTHealth Houston.
The study, which was published today in JAMA Neurology, was led by co-first authors Youngran Kim, PhD, assistant professor of management, policy, and community health with UTHealth Houston School of Public Health; and Juan Carlos Martinez-Gutierrez, MD, a former surgery fellow in the Vivian L. Smith Department of Neurosurgery with McGovern Medical School at UTHealth ...
About The Study: This economic evaluation’s findings indicate that the economic burden of youth violence, including medical care, lost productivity, reduced quality of life from injury morbidity, and avoidable mortality, reached $122 billion in 2020, dominated by male firearm homicides. Prevention strategies can reduce this substantial burden.
Authors: Cora Peterson, Ph.D., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.3235)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: Increased TV/DVD screen time from age 1 year negatively affected later development in this study of 57,980 children. To reduce the negative consequences of excessive media use, researchers and health care professionals should encourage family media management and recommend social support for parents who tend to rely on the media.
Authors: Midori Yamamoto, Ph.D., of Chiba University in Chiba, Japan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.3643)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: In this study using nationally representative survey data with difference-in-differences analysis of school-based health center (SBHC) adoption, SBHCs were associated with access to care and reduced income-based disparities. These findings support additional SBHC expansion.
Authors: Michel Boudreaux, Ph.D., of the University of Maryland in College Park, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.34532)
Editor’s ...