(Press-News.org) The commonly-held belief that attempting to suppress negative thoughts is bad for our mental health could be wrong, a new study from scientists at the University of Cambridge suggests.
Researchers at the Medical Research Council (MRC) Cognition and Brain Sciences Unit trained 120 volunteers worldwide to suppress thoughts about negative events that worried them, and found that not only did these become less vivid, but that the participants’ mental health also improved.
“We’re all familiar with the Freudian idea that if we suppress our feelings or thoughts, then these thoughts remain in our unconscious, influencing our behaviour and wellbeing perniciously,” said Professor Michael Anderson.
“The whole point of psychotherapy is to dredge up these thoughts so one can deal with them and rob them of their power. In more recent years, we’ve been told that suppressing thoughts is intrinsically ineffective and that it actually causes people to think the thought more – it’s the classic idea of ‘Don’t think about a pink elephant’.
These ideas have become dogma in the clinical treatment realm, said Anderson, with national guidelines talking about thought avoidance as a major maladaptive coping behaviour to be eliminated and overcome in depression, anxiety, PTSD, for example.
When COVID-19 appeared in 2020, like many researchers, Professor Anderson wanted to see how his own research could be used to help people through the pandemic. His interest lay in a brain mechanism known as inhibitory control – the ability to override our reflexive responses – and how it might be applied to memory retrieval, and in particular to stopping the retrieval of negative thoughts when confronted with potent reminders to them.
Dr Zulkayda Mamat – at the time a PhD student in Professor Anderson’s lab and at Trinity College, Cambridge – believed that inhibitory control was critical in overcoming trauma in experiences occurring to herself and many others she has encountered in life. She had wanted to investigate whether this was an innate ability or something that was learnt – and hence could be taught.
Dr Mamat said: “Because of the pandemic, we were seeing a need in the community to help people cope with surging anxiety. There was already a mental health crisis, a hidden epidemic of mental health problems, and this was getting worse. So with that backdrop, we decided to see if we could help people cope better.”
Professor Anderson and Dr Mamat recruited 120 people across 16 countries to test whether it might in fact be possible – and beneficial – for people to practice suppressing their fearful thoughts. Their findings are published today in Science Advances.
In the study, each participant was asked to think of a number of scenarios that might plausibly occur in their lives over the next two years – 20 negative ‘fears and worries’ that they were afraid might happen, 20 positive ‘hopes and dreams’, and 36 routine and mundane neutral events. The fears had to be worries of current concern to them, that have repeatedly intruded in their thoughts.
Each event had to be specific to them and something they had vividly imagined occurring. For each scenario, they were to provide a cue word (an obvious reminder that could be used to evoke the event during training) and a key detail (a single word expressing a central event detail). For example:
Negative – visiting one’s parents at the hospital as a result of COVID-19, with the cue ‘Hospital’ and the detail ‘Breathing’.
Neutral – a visit to the opticians, with the cue ‘Optician’ and the detail ‘Cambridge’.
Positive – seeing one’s sister get married, with the cue ‘Wedding’ and the detail ‘Dress’.
Participants were asked to rate each event on a number of points: vividness, likelihood of occurrence, distance in the future, level of anxiety about the event (or level of joy for positive events), frequency of thought, degree of current concern, long-term impact, and emotional intensity.
Participants also completed questionnaires to assess their mental health, though no one was excluded, allowing the researchers to look at a broad range of participants, including many with serious depression, anxiety, and pandemic-related post-traumatic stress.
Then, over Zoom, Dr Mamat took each participant through the 20-minute training, which involved 12 ‘No-imagine’ and 12 ‘Imagine’ repetitions for events, each day for three days.
For No-imagine trials, participants were given one of their cue words, asked to first acknowledge the event in their mind. Then, while continuing to stare directly at the reminder cue, they were asked to stop thinking about the event – they should not try to imagine the event itself or use diversionary thoughts to distract themselves, but rather should try to block any images or thoughts that the reminder might evoke. For this part of the trial, one group of participants was given their negative events to suppress and the other given their neutral ones.
For Imagine trials, participants were given a cue word and asked to imagine the event as vividly as possible, thinking what it would be like and imagining how they would feel at the event. For ethical reasons, no participant was given a negative event to imagine, but only positive or neutral ones.
At the end of the third day and again three months later, participants were once again asked to rate each event on vividness, level of anxiety, emotional intensity, etc., and completed questionnaires to assess changes in depression, anxiety, worry, affect, and wellbeing, key facets of mental health.
Dr Mamat said: “It was very clear that those events that participants practiced suppressing were less vivid, less emotionally anxiety-inducing, than the other events and that overall, participants improved in terms of their mental health. But we saw the biggest effect among those participants who were given practice at suppressing fearful, rather than neutral, thoughts.”
Following training – both immediately and after three months – participants reported that suppressed events were less vivid and less fearful. They also found themselves thinking about these events less.
Suppressing thoughts even improved mental health amongst participants with likely post-traumatic stress disorder. Among participants with post-traumatic stress who suppressed negative thoughts, their negative mental health indices scores fell on average by 16% (compared to a 5% fall for similar participants suppressing neutral events), whereas positive mental health indices scores increased by almost 10% (compared to a 1% fall in the second group).
In general, people with worse mental health symptoms at the outset of the study improved more after suppression training, but only if they suppressed their fears. This finding directly contradicts the notion that suppression is a maladaptive coping process.
Suppressing negative thoughts did not lead to a ‘rebound’, where a participant recalled these events more vividly. Only one person out of 120 showed higher detail recall for suppressed items post-training, and just six of the 61 participants that suppressed fears reported increased vividness for No-Imagine items post-training, but this was in line with the baseline rate of vividness increases that occurred for events that were not suppressed at all.
“What we found runs counter to the accepted narrative,” said Professor Anderson. “Although more work will be needed to confirm the findings, it seems like it is possible and could even be potentially beneficial to actively suppress our fearful thoughts.”
Although participants were not asked to continue practising the technique, many of them chose to do so spontaneously. When Dr Mamat contacted the participants after three months, she found that the benefits in terms of reduced levels of depression and negative emotions, continued for all participants, but were most pronounced among those participants who continued to use the technique in their daily lives.
“The follow up was my favourite time of my entire PhD, because every day was just joyful,” she said. “I didn’t have a single participant who told me ‘Oh, I feel bad’ or ‘This was useless’. I didn't prompt them or ask ‘Did you find this helpful?’ They were just automatically telling me how helpful they found it.”
One participant was so impressed by the technique that she taught her daughter and her own mother how to do it. Another reported how she had moved home just prior to COVID-19 and so felt very isolated during the pandemic.
“She said this study had come exactly at the time she needed it because she was having all these negative thoughts, all these worries and anxiety about the future, and this really, really helped her,” said Dr Mamat. “My heart literally just melted, I could feel goosebumps all over me. I said to her ‘If everyone else hated this experiment, I would not care because of how much this benefited you!’.”
The research was funded by the Medical Research Council of the United Kingdom, and the Mind Science Foundation.
Reference
Mamat, Z, and Anderson, MC. Improving Mental Health by Training the Suppression of Unwanted Thoughts. Sci Adv; 20 Sept 2023; DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adh5292
END
Suppressing negative thoughts may be good for mental health after all, study suggests
2023-09-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ancient Amazonians intentionally created fertile “dark earth”
2023-09-20
The Amazon river basin is known for its immense and lush tropical forests, so one might assume that the Amazon’s land is equally rich. In fact, the soils underlying the forested vegetation, particularly in the hilly uplands, are surprisingly infertile. Much of the Amazon’s soil is acidic and low in nutrients, making it notoriously difficult to farm.
But over the years, archaeologists have dug up mysteriously black and fertile patches of ancient soils in hundreds of sites across the Amazon. This “dark earth” has been found in and around human settlements dating ...
MD Anderson expands breakthrough research campus with groundbreaking of innovative new facility
2023-09-20
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today broke ground on a 600,000-square-foot facility intended to anchor the institution’s expansive south campus research park. The building was purposefully built to enable collaborative science and impactful breakthrough discoveries that will accelerate efforts to end cancer.
A $668 million institutional investment will support the construction of MD Anderson’s South Campus Research Building 5 (SCRB5), a 7-story building designed by Elkus Manfredi Architects with state-of-the-art research facilities and inspiring public spaces to facilitate exceptional science. ...
Genetic biomarker may predict severity of food allergy
2023-09-20
Researchers from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and colleagues reported for the first time that a genetic biomarker may be able to help predict the severity of food allergy reactions. Currently there is no reliable or readily available clinical biomarker that accurately distinguishes patients with food allergies who are at risk for severe life-threatening reactions versus more mild symptoms. Findings were published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Dr. Lang and colleagues found that the presence of an enzyme isoform called α-tryptase, ...
Researchers reveal novel AI-based camera alert system to promote coexistence between tigers and humans
2023-09-20
For decades, wildlife biologists have dreamt of a “smart” camera alerting system capable of detecting tigers and other endangered species on the prowl. Legacy camera-trap technology, while valuable for many research applications, has historically been hindered by false positives and an inability to facilitate rapid responses.
Writing in BioScience, Jeremy Dertien of Clemson University and colleagues announce that for the first time ever, wild tigers and elephants have been detected by an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered, cryptic camera-alert system, TrailGuard AI, that transmits images to the ...
New Mars gravity analysis improves understanding of possible ancient ocean
2023-09-20
The first use of a novel method of analyzing Mars’ gravitational force supports the idea that the planet once had an extensive northern ocean.
In doing so, the method defines the scope of what scientists refer to as the northern Martian paleo-ocean in more detail.
The work was published in July in the journal Icarus, which is affiliated with the American Astronomical Society’s Division for Planetary Sciences.
The research was led by Jaroslav Klokočník, professor emeritus at the Astronomical Institute of the Czech Academy of Sciences. Gunther ...
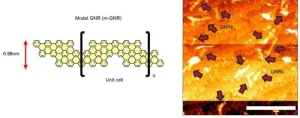
Making contact: Researchers wire up individual graphene nanoribbons
2023-09-20
Researchers have developed a method of “wiring up” graphene nanoribbons (GNRs), a class of one-dimensional materials that are of interest in the scaling of microelectronic devices. Using a direct-write scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) based process, the nanometer-scale metal contacts were fabricated on individual GNRs and could control the electronic character of the GNRs. The researchers say that this is the first demonstration of making metal contacts to specific GNRs with certainty and that those contacts induce device functionality needed for transistor function.
The results of this research, led by electrical and computer engineering (ECE) professor Joseph Lyding, along ...
A new regulatory model which supports and encourages needed to help organizations comply with equalities legislation, study says
2023-09-20
A new type of regulation is needed to support and encourage organisations to comply with equality and human rights law because enforcement alone is ineffective, a new study says.
The introduction of the Public Sector Equality Duty and the Human Rights Act were intended to establish an equality and human rights culture within public authorities. The research highlights how this culture has failed to take hold.
An alternative is needed to the current model of regulation (the enforcement pyramid) under which penalties increasingly progress until noncompliers comply. The study says the current model cannot recognise innovation, ...
Stabilizing precipitate growth at grain boundaries in alloys
2023-09-20
Materials are often considered to be one phase, but many engineering materials contain two or more phases, improving their properties and performance. These two-phase materials have inclusions, called precipitates, embedded in the microstructure. Alloys, a combination of two or more types of metals, are used in many applications, like turbines for jet engines and light-weight alloys for automotive applications, because they have very good mechanical properties due to those embedded precipitates. The average precipitate size, however, tends to increase ...
Researchers discover biomarker for tracking depression recovery
2023-09-20
Using a novel deep brain stimulation (DBS) device capable of recording brain signals, researchers have identified a pattern of brain activity or “biomarker” related to clinical signs of recovery from treatment-resistant depression. The findings from this small study are an important step towards using brain data to understand a patient’s response to DBS treatment. The study was published in Nature and supported by the National Institutes of Health’s Brain Research Through Advancing ...
NIH awards $3.1 million to study human mitochondrial disorders
2023-09-20
The Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development awarded $3.1 million to the University of Arkansas to study a spectrum of pediatric mitochondrial disorders caused by mutations in the mitochondria. These disorders often impact different organs requiring energy and can lead to mitochondria-induced multiple organ disorder syndromes, or MIMODS.
Shilpa Iyer, an associate professor of biological sciences, will serve as the principal investigator on the five-year award. Iyer and her team conduct research on mitochondrial diseases and have received grants from Arkansas ...