(Press-News.org)
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are a class of materials that contain nano-sized pores. These pores give MOFs record-breaking internal surface areas, which make them extremely versatile for a number of applications: separating petrochemicals and gases, mimicking DNA, producing hydrogen, and removing heavy metals, fluoride anions, and even gold from water are just a few examples.
In the gas-separation domain, MOFs are particularly interesting for separating hydrogen from nitrogen, which is crucial for clean energy production, fuel cell efficiency, ammonia synthesis, and various industrial processes. Hydrogen-nitrogen separation also has a number of environmental benefits, making it integral to advancing sustainable technologies and industrial practices.
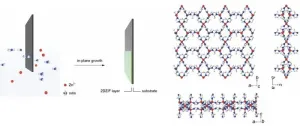
Now, a team of researchers led by Professor Kumar Varoon Agrawal at EPFL’s School of Basic Sciences have developed MOF film with smallest possible thickness that can perform record levels of hydrogen-nitrogen separation. The researchers worked with a type of MOFs known as zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs), which have garnered considerable attention for their potential in molecular separations, sensing, and other applications.
To make the films, the researchers used an innovative crystallization method that capitalizes on the precise alignment of ultra-dilute precursor mixtures with the underlying crystalline substrate. By carefully controlling precursor concentrations and interactions with the substrate, the team were able to suppress out-of-plane growth – a common problem in making thin films.
The approach paid off: Within a matter of minutes, and at room temperature, the scientists were able to fabricate macroscopically uniform two-dimensional (2D) ZIF films with unprecedented thickness: just one structural unit, measuring only two nanometers. The scientists also showed that the process is scalable preparing films with area of hundreds of square centimeters. The breakthrough overcomes conventional methods, which have limited ZIF film thickness to 50 nanometers, making widespread use difficult.
The ZIF film has a unique configuration: a nanometer-thick film with a uniform array of hydrogen-sieving six-membered zinc-imidazolate coordination ring. Kumar Agrawal explains: “This allows for an exceptional combination of hydrogen flux and selectivity, holding immense potential for highly efficient gas-separation applications.”
Other contributors
Johns Hopkins University
King Abdullah University of Science and Technology
Soochow University
Reference
Qi Liu, Yurun Miao, Luis Francisco Villalobos, Shaoxian Li, Heng-Yu Chi, Cailing Chen, Mohammad Tohidi Vahdat, Shuqing Song, Deepu J. Babu, Jian Hao, Yu Han, Michael Tsapatsis, Kumar Varoon Agrawal. Unit-cell-thick zeolitic imidazolate framework films for membrane application. Nature Materials 21 September 2023. DOI: 10.1038/s41563-023-01669-z
END
The team, led by Imperial College London researchers, uncovered the wiring in mouse brains that leads them to begin nesting in preparation for sleep. Published today in Nature Neuroscience, the study reveals that preparing properly for sleep is likely a hard-wired survival feature – one often neglected or overridden by humans.
We all need to sleep, but since we are unconscious when we do so, it makes sense to fall asleep in a safe and warm place. For some animals this is especially important, as a burrow or nest provides a haven from ...
Tumor vaccines can help the body fight cancer. These vaccines alert the patient's immune system to proteins that are carrying cancer-typical alterations. Physicians and cancer researchers from Heidelberg and Mannheim have now treated adult patients with advanced midline gliomas, difficult-to-treat brain tumors, with a peptide vaccine for the first time. The vaccine mimicked a mutational change in a histone protein typical of this type of cancer. The vaccine proved to be safe and induced the desired immune responses directed ...
If you happen to come across plants of the Balanophoraceae family in a corner of a forest, you might easily mistake them for fungi growing around tree roots. Their mushroom-like structures are actually inflorescences, composed of minute flowers.
But unlike some other parasitic plants that extend an haustorium into host tissue to steal nutrients, Balanophora induces the vascular system of their host plant to grow into a tuber, forming a unique underground organ with mixed host-parasite tissue. This ...
An international research team led by scientists in the Center for Genetic Epidemiology at the Keck School of Medicine of USC and USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center has singled out mutations in 11 genes that are associated with aggressive forms of prostate cancer. These findings come from the largest-scale prostate cancer study ever exploring the exome — that is, the key sections of the genetic code that contain the instructions to make proteins. The scientists analyzed samples from about 17,500 prostate cancer ...
Palaeontologists at University College Cork (UCC) in Ireland have discovered X-ray evidence of proteins in fossil feathers that sheds new light on feather evolution.
Previous studies suggested that ancient feathers had a different composition to the feathers of birds today. The new research, however, reveals that the protein composition of modern-day feathers was also present in the feathers of dinosaurs and early birds, confirming that the chemistry of feathers originated much earlier than previously thought.
The research, published today in Nature Ecology and Evolution, was led by palaeontologists ...
MicroRNAs are small molecules that regulate gene activity by binding to and destroying RNAs produced by the genes. More than 60% of all human genes are estimated to be regulated by microRNAs, therefore it is not surprising that these small molecules are involved in many biological processes including diseases such as cancer. To discover the function of a microRNA, it is necessary to find out exactly which RNAs are targeted by it. While such methods exist, they require a lot of material typically in order of millions of cells, to ...
A new form of agricultural pest control could one day take root—one that treats crop infestations deep under the ground in a targeted manner with less pesticide.
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed nanoparticles, fashioned from plant viruses, that can deliver pesticide molecules to soil depths that were previously unreachable. This advance could potentially help farmers effectively combat parasitic nematodes that plague the root zones of crops, all while minimizing costs, pesticide use and environmental toxicity.
Controlling infestations caused by root-damaging nematodes has long been a challenge in agriculture. One reason is that the types of pesticides ...
A research team led by Prof. LIN Nan from the Institute of Psychology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences found that during sentence processing, the neural activity of two canonical language areas, i.e., the left ventral temporoparietal junction (vTPJ) and the lateral anterior temporal lobe (lATL), is associated with social-semantic working memory rather than language processing per se.
The study was published in Nature Human Behaviour on Sept. 21.
Language and social cognition are two deeply interrelated abilities of the human species, but have traditionally been studied ...
On September 17th, 2023, Carbon Future, an international interdisciplinary journal sponsored by Tsinghua University, has been officially inaugurated.
Carbon Future is an open access, peer-reviewed and international interdisciplinary journal that reports carbon-related materials and processes, including carbon materials, catalysis, energy conversion and storage, as well as low carbon emission process and engineering. The journal is published quarterly by Tsinghua University Press, and publicly released on SciOpen, an internationally digital ...
In a groundbreaking study published in Engineering, researchers have developed a revolutionary method for data storage using DNA. The paper titled “Engineering DNA Materials for Sustainable Data Storage Using a DNA Movable-Type System” introduces a novel approach that utilizes DNA fragments, referred to as “DNA movable types,” for data writing, thereby eliminating the need for costly and environmentally hazardous DNA synthesis.
DNA molecules have long been recognized as green materials ...