(Press-News.org) New research analysing the effects of two drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes indicates a consistent lack of cardiovascular and renal benefits in Black populations. Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of severe illness and death associated with type 2 diabetes. Renal disease is also a common complication of type 2 diabetes.
The drugs, called sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2-Is) and glucogen-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RAs), are some of the newer treatments prescribed to lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes.
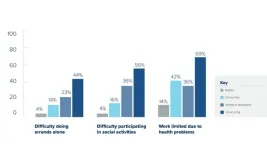
The research findings, published in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, show that for White and Asian populations, SGLT2-Is and GLP1-RAs have beneficial effects on blood pressure, weight control and renal function, and significantly reduce the risk of severe heart problems and kidney disease. However, the research shows no evidence of these beneficial effects in Black populations.
Researchers at the Diabetes Research Centre at the University of Leicester analysed the results of 14 randomised controlled trials of SGLT2-Is and GLP1-RAs reporting cardiovascular and renal outcomes by race, ethnicity and region.
Lead researcher Professor Samuel Seidu, Professor in Primary Care Diabetes and Cardio-metabolic Medicine at the University of Leicester, said: “Given the well-documented evidence that Black and other ethnic minority populations are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes and at a younger age, the consistent lack of benefits we observed among Black populations is concerning.
“Minimising racial and ethnic variations in the cardiovascular and renal complications of type 2 diabetes requires targeted improved access to care and treatment for those most at risk.”
The researchers suggest there are many factors that could have contributed to the lack of evidence of beneficial effects for Black and other non-White populations. Low statistical power due to small sample sizes of these populations may be partly responsible.
“It is quite clear from the current data that some racial/ethnic groups such as Black populations were underrepresented in all the included trials,” pointed out Professor Seidu.
Enrolment in the trials ranged from 66.6% to 93.2% for White populations, 1.2% and 21.6% for Asian populations, and 2.4% to 8.3% for Black populations.
However, the researchers suggest that, given the consistent nature of the significant lack of beneficial effects across the majority of outcomes for Black populations, other factors may also be at play.
“"Whether the differences are due to issues with under-representation of Black populations and low statistical power, or to racial/ethnic variations in the way the body and these drugs interact with each other needs further investigation,” said Professor Seidu. “It is therefore important that prescribers don’t hasten to deny these newer treatments to Black populations on the back of this research.”
ENDS
END
Newer diabetes treatments are understudied in Black populations and may be less beneficial
2023-09-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ochsner offers tuition assistance to aspiring nurses and doctors
2023-09-22
NEW ORLEANS, LOUISIANA – Ochsner Health is again expanding its Ochsner Scholars program for aspiring nurses and physicians ready to fill critical healthcare shortages in local communities and shape the healthcare workforce of the future.
Ochsner is excited to announce tuition assistance for 100 Nurse Scholars pursuing Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN), Licensed Nurse Practitioner (LPN), Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) and Accelerated Bachelor of Science in Nursing (ABSN) degrees this spring to students across Louisiana and Mississippi. Ochsner is also covering tuition for up to 10 Physician Scholars ...
Colorful primates don’t have better color vision, study finds
2023-09-22
Primate species with better colour vision are not more likely to have red skin or fur colouration, as previously thought.
The findings, published this week in the Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, suggest that red skin and/or red-orange fur may be beneficial for use in social communication even in primate species that don't have particularly good colour vision.
It's long been assumed that primates' colourful skin and fur is linked to their enhanced colour vision, and the results may have implications for understanding why these traits exist in different species.
Lead author Robert MacDonald from the University of Bristol explained: ...
Large-scale German study discovers earlier puberty onset in both girls and boys with diabetes
2023-09-22
Puberty in both girls and boys with type 1 diabetes has shifted forward over the last two decades, according to research presented at the 61st Annual European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology Meeting in The Hague. Additionally longer duration of diabetes, bigger waistlines, and lower blood sugar levels were associated with even earlier puberty onset. The findings of this large-scale study highlight a close relationship between type 1 diabetes and puberty onset and the utmost importance of managing diabetes and weight ...
Novel method reveals link between man-made chemicals in everyday products and later puberty
2023-09-22
Children exposed to higher levels of synthetic chemicals in everyday products, such as water-resistant clothes, umbrellas and food packaging, are more likely to mature later during puberty, according to research presented at the 61st Annual European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology Meeting in The Hague. The findings may help better regulate the industrial production and use of these chemicals on a national and international level.
Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), also known ...
Benefit breakdown, 3D printed vs. wood molds
2023-09-21
Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers have conducted a comprehensive life cycle, cost and carbon emissions analysis on 3D-printed molds for precast concrete and determined the method is economically beneficial compared to conventional wood molds.
Precast concrete is used in building construction and produced by pouring the material into a reusable mold. For decades, these molds have been made from wood — a technique that requires a highly specialized skillset. As an alternative, molds made from fiber-reinforced polymer composites can be 3D printed.
“We developed a techno-economic model that compared costs associated with each method, evaluating materials, equipment, ...
Peru’s Operation Mercury stopped most illegal gold mining in one biodiversity hotspot in the Amazon. Then the COVID-19 pandemic hit.
2023-09-21
Artisanal and small-scale gold mining is a lifeline for many who live in Madre de Dios, a region in southeastern Peru, where poverty is high and jobs are scarce. But the economic development in this part of the Amazon basin comes at a cost, as it causes deforestation, build up of sediment in rivers, and mercury contamination in nearby watersheds, threatening public health, Indigenous peoples, and the future of the biodiversity hotspot. And much of the mining activity is unauthorized.
Seeking to eliminate illegal artisanal and small-scale gold mining activity and its many negative impacts, the Peruvian government deployed “Operation Mercury” (Operation Mercurio) in February ...
Texas A&M-led humanities project seeks to preserve an endangered language
2023-09-21
Texas A&M University historian Dr. Daniel Schwartz has devoted the last decade of his professional life to preserving the past — specifically, the culture of a 2,000-year-old language known as Syriac. He and likeminded colleagues from around the world have been working across place, time and cyberspace to safeguard Syriac cultural heritage, painstakingly creating Syriaca.org, a cyberinfrastructure to link Syriac literature to their persons, places, manuscripts and key concepts.
This spring, they received another big assist from the National ...
Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas awards $2 million grant to SMU
2023-09-21
DALLAS (SMU) – The Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) has awarded $2 million to recruit Annika Wylie to SMU and fund five years of her research, which focuses on the p53 gene, a naturally occurring tumor suppressor.
CPRIT is the state agency mandated to create and expedite innovation in the area of cancer research and enhance the potential for a medical or scientific breakthrough in both prevention and cures. CPRIT is now a $6 billion, 20-year initiative – the largest state cancer research investment ...
Study shows millions of people live with co-occuring chronic pain and mental health symptoms
2023-09-21
New University of Arizona Health Sciences research recently published in the journal PAIN found that nearly 1 in 20 adults in the U.S. experience the co-occurrence of chronic pain and anxiety or depression, resulting in functional limitations in daily life.
Prior research has shown that chronic pain along with symptoms of anxiety or depression are biologically linked. This study is one of the few to examine the national prevalence of chronic pain with anxiety or depression symptoms in adults. The results shed light on the fact that millions ...
Cardiovascular organizations pursue new, independent medical board
2023-09-21
Many of the nation’s most prominent cardiovascular organizations, representing tens of thousands of physicians, unite today to pursue the creation of a new Board for cardiovascular medicine. The proposed new Board would be independent of the American Board of Internal Medicine, where the cardiology certification process currently exists. Collectively, the American College of Cardiology (ACC), Heart Failure Society of America (HFSA), Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) and Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) are working together to submit a ...