(Press-News.org) A research team, led by Professor Jong-Beom Baek and his team in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST have achieved a significant breakthrough in battery technology. They have developed an innovative method that enables the safe synthesis of fluorinated carbon materials (FCMs) using polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and graphite.
Fluorinated carbon materials have garnered considerable attention due to their exceptional stability, attributed to the strong C-F bonding—the strongest among carbon single bonds. However, traditional methods of fluorination involve highly toxic reagents such as hydrofluoric acid (HF), making them unsuitable for practical applications.
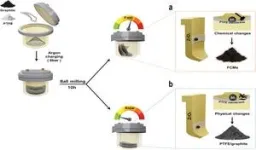
In this study, the research team introduced a straightforward and relatively safe approach for scalable synthesis of FCMs through mechanochemical depolymerization of PTFE—a commonly used compound found in everyday items—and fragmentation of graphite. By utilizing ball-milling techniques that induce both mechanical and chemical reactions, they successfully produced FCMs with significantly improved performance compared to graphite.
The use of hazardous compounds like fluorine gas or HF in conventional carbon fluoride production raises safety concerns, increasing manufacturing costs associated with stringent safety measures. To address these challenges, Professor Baek’s team devised a solid-phase fluorination method using PTFE—an inert polymer known for its stability under atmospheric conditions and harmlessness when consumed orally.
Through experiments, it was observed that subjecting PTFE to higher energy than it can withstand leads to molecular chain breakage and radical formation—initiating a reaction resulting in the production of carbon fluoride complexes. These complexes then adhere to the surface and edges of graphite particles during subsequent processes.
The resulting FCMs demonstrated superior storage capacity and electrochemical stability compared to traditional graphite anodes. At a low charging rate of 50 mA/g, the FCMs exhibited storage capacities 2.5 times higher (951.6 mAh/g) than graphite, while at a high charging rate of 10,000 mA/g, their storage capacity was tenfold higher (329 mAh/g). Remarkably, even after more than 1,000 charge/discharge cycles at a rate of 2,000 mA/g, the FCMs retained 76.6% of their initial capacity compared to only 43.8% for graphite.
“This study highlights not just safe fluorination methods but also the broader potential of solid-phase reactions,” stated Boo-Jae Jang, a researcher in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST.
“This research prompts us to reconsider materials that are commonly found in our surroundings,” added Professor Baek. He further emphasized the significance of understanding solid-phase reactions as it opens doors to developing novel materials that were previously unexplored.
The study findings have been published ahead of their official publication in the online version of Advanced Functional Materials on July 27, 2023. This work has been supported through the U-K Brand and Carbon Neutrality projects of UNIST, and the Creative Research Initiative program through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Journal Reference
Boo-Jae Jang, Qiannan Zhao, Jae-Hoon Baek, et al., “Direct Synthesis of Fluorinated Carbon Materials via a Solid-State Mechanochemical Reaction Between Graphite and PTFE,” Adv. Funct. Mater., (2023).
END
New study unveils direct synthesis of FCMs via solid-state mechanochemical reaction between graphite and PTFE
The study findings have been published ahead of their official publication in the online version of Advanced Functional Materials on July 27, 2023
2023-09-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gold nanoclusters can improve electrochemical water splitting to produce hydrogen
2023-09-22
As energy demand continues to rise, research into new, efficient renewable and clean energy sources is an urgent priority. Currently, renewable energy sources like solar, wind, tide, and geothermal make up less than 40% of the current energy demand. Increasing this percentage and reducing the amount of fossil fuels used will require other, more efficient renewable and clean energy sources.
Hydrogen is a promising alternative, but it is currently produced using steam reforming, which is inefficient and produces CO2 emissions. Electrochemical water splitting, also called ...
Study finds connection between gut microbiome and bone density
2023-09-22
BOSTON – There is growing evidence that a relative abundance of certain gut microbes may be related to skeletal health, according to a new study published in Frontiers in Endocrinology. If confirmed by additional research, the findings could provide the opportunity to alter gut microbiomes to achieve better bone health, as scientists learn more about “osteomicrobiology,” a new term recently used to characterize this relationship.
Due to the lack of large-scale human studies of the gut microbiome and skeletal health, researchers led by Paul C. Okoro, Data Scientist II at Hebrew SeniorLife and Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for ...
A dendritic cell vaccine was safe and induced immune responses in patients with multiple myeloma
2023-09-22
Bottom Line: A dendritic cell vaccine administered before and after autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) was safe and immunogenic and was associated with durable clinical responses in patients with high-risk multiple myeloma.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Authors: Frederick L. Locke, MD, chair of the Blood and Marrow Transplant and Cellular Immunotherapy Department at Moffitt Cancer Center, was the senior author of the study.
Background: “Multiple ...
One-stop implementation from signal detection to processing
2023-09-22
In order to explore brain disorders and discover potential treatments, it is crucial to analyze and interpret the signals transmitted by the brain. Although neural probes attached to the brain can effectively detect subtle bio- signals, they lack the ability to amplify and process these signals, necessitating the use of a separate amplifier. The research team identified a solution in common household “inkjet printers” that have been widely available for a long time.
A collaborative research team led by Professor Sungjune Jung (Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Department of Convergence IT Engineering) with PhD candidate ...
New target to beat cancer drug resistance
2023-09-22
University of Queensland researchers have identified a novel drug target with the potential to overcome drug resistance and prevent tumour regrowth in cancer patients.
Associate Professor Helmut Schaider from UQ’s Frazer Institute said the newly identified molecule was not currently a target for treatment, opening the potential for drug development.
“Drug resistance is the single major cause of death in cancer patients,” Dr Schaider said.
“For example, almost half of patients with lung cancer die ...
Australian research leads to clinical trial for rare women’s cancers
2023-09-22
An international clinical trial exploring a new way to treat rare and aggressive gynaecological cancers has launched in Melbourne.
Based on a WEHI-led discovery, the trial hopes to enhance treatment options for women with two of the most lethal gynaecological cancers – ovarian and uterine carcinosarcomas.
The study will offer a novel combination therapy for women with these relapsing cancers and is now open in Australia, with plans to expand to Canada and the United Kingdom in coming months.
At a glance
New clinical trial launches in Melbourne to test a potential treatment for two aggressive and rare gynaecological ...
Newer diabetes treatments are understudied in Black populations and may be less beneficial
2023-09-22
New research analysing the effects of two drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes indicates a consistent lack of cardiovascular and renal benefits in Black populations. Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of severe illness and death associated with type 2 diabetes. Renal disease is also a common complication of type 2 diabetes.
The drugs, called sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2-Is) and glucogen-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RAs), are some of the newer treatments prescribed to lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes.
The research findings, published in the Journal of the ...
Ochsner offers tuition assistance to aspiring nurses and doctors
2023-09-22
NEW ORLEANS, LOUISIANA – Ochsner Health is again expanding its Ochsner Scholars program for aspiring nurses and physicians ready to fill critical healthcare shortages in local communities and shape the healthcare workforce of the future.
Ochsner is excited to announce tuition assistance for 100 Nurse Scholars pursuing Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN), Licensed Nurse Practitioner (LPN), Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) and Accelerated Bachelor of Science in Nursing (ABSN) degrees this spring to students across Louisiana and Mississippi. Ochsner is also covering tuition for up to 10 Physician Scholars ...
Colorful primates don’t have better color vision, study finds
2023-09-22
Primate species with better colour vision are not more likely to have red skin or fur colouration, as previously thought.
The findings, published this week in the Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, suggest that red skin and/or red-orange fur may be beneficial for use in social communication even in primate species that don't have particularly good colour vision.
It's long been assumed that primates' colourful skin and fur is linked to their enhanced colour vision, and the results may have implications for understanding why these traits exist in different species.
Lead author Robert MacDonald from the University of Bristol explained: ...
Large-scale German study discovers earlier puberty onset in both girls and boys with diabetes
2023-09-22
Puberty in both girls and boys with type 1 diabetes has shifted forward over the last two decades, according to research presented at the 61st Annual European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology Meeting in The Hague. Additionally longer duration of diabetes, bigger waistlines, and lower blood sugar levels were associated with even earlier puberty onset. The findings of this large-scale study highlight a close relationship between type 1 diabetes and puberty onset and the utmost importance of managing diabetes and weight ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
[Press-News.org] New study unveils direct synthesis of FCMs via solid-state mechanochemical reaction between graphite and PTFEThe study findings have been published ahead of their official publication in the online version of Advanced Functional Materials on July 27, 2023