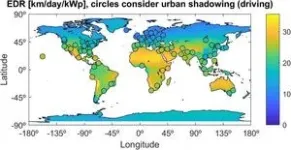
(Press-News.org) A new study, modeling the potential of solar-powered vehicles in the urban context in 100 cities across the world, shows that solar energy provides a range between 11 and 29 km per day, reducing charging needs by half.
Despite the rapid adoption of electric vehicles, the transport sector is still responsible for around a third of global carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions worldwide. Therefore, to achieve decarbonization targets, it is required to significantly decrease the emissions associated with mobility.
Integrating photovoltaic modules into electric vehicles, solar cars, can contribute to this goal, reducing CO2 emissions associated with electricity generation and the charging costs and frequency, with benefits for users and the electrical grid itself.
“Cities are today the main market for electric vehicles and, due to the relatively small travelled distances, are particularly interesting for solar-powered vehicles. However, in urban areas, we have buildings, trees and other obstacles casting shadows onto the roads thus limiting the solar potential of driving or parked vehicles. The purpose of the work was to assess if the impact of these shadows is a significant limitation to the potential of solar cars”, explains Miguel Centeno Brito, first author of this study, researcher at Instituto Dom Luiz – IDL, at the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon (Ciências ULisboa) (Portugal).
The study also finds that the most favorable locations for solar-powered vehicles are cities in Africa, the Middle East, southern Europe and Southeast Asia, although the potential is interesting in other geographies, including China, North America and Australia. Losses associated with shading in the city are around 25%, and therefore relevant, but not an impediment to the large-scale dissemination of this solution.
Meanwhile, the research team launched an experimental campaign with citizen scientists to experimentally validate the model.
With growing urban populations and concerns about environmental sustainability becoming increasingly urgent, solar-powered vehicles could not come at a more opportune time. “Our results can help establish a roadmap for policymakers and the automotive industry to accelerate the transition to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly urban future”, concludes Miguel Centeno Brito.
This worldwide study was developed by researchers from Ciências ULisboa (Portugal), in collaboration with partners in France (Mines Paris - PSL) and Luxembourg (LIST).
END
The potential of solar cars in the world
2023-09-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fruit flies offer clues to how brains make reward-based decisions
2023-09-22
Like many collectors of L.P. records, James Fitzgerald’s brother-in-law has a favorite store where he consistently finds the best vinyl for his collection. But there are times when he spends hours at the store and comes up empty. He also knows that occasionally he should venture to the record store on the other side of town, where he sometimes scores a hard-to-find gem that was stocked since his last visit.
Fitzgerald’s brother-in-law is making a calculation: weighing probable outcomes to guide his behavior. His favorite record store ...
Pioneering health tracker for stroke survivors will use the body to transmit data
2023-09-22
AMHERST, Mass.—An interdisciplinary team led by University of Massachusetts Amherst researchers has been awarded $1.14 million over four years by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to develop a revolutionary way of tracking body movements, with a primary application in stroke survivors’ rehabilitation and huge potential for future applications across a wide range of disciplines, health-related and beyond.
More than 795,000 Americans suffer from strokes annually, and nearly 80% of stroke survivors experience some degree ...
Brazilian researchers develop method of purifying water contaminated by glyphosate
2023-09-22
Researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Brazil have developed a strategy for removing glyphosate, one of the world’s most frequently used herbicides, from water. Inspired by the concept of the circular economy, the technique is based on sugarcane bagasse, a waste material produced by sugar and ethanol plants.
“Isolated and chemically functionalized sugarcane bagasse fibers can be used as adsorbent material. Glyphosate adheres to its surface and is removed as a water contaminant by filtration, decantation or centrifugation,” Maria ...
Vizient awards UCSF Health top marks for quality patient care
2023-09-22
Hospital quality ratings assess safety, equity and effectiveness in hospitals nationwide
Vizient Inc. has named UCSF Health as a Top Performer for its high-quality patient care in the 2023 Bernard A. Birnbaum, MD, Quality Leadership Ranking.
This is the second year in a row that Vizient has recognized UCSF Health as a leader in health care quality. This year, UCSF Health ranked seventh among comprehensive academic medical centers, out of 116 medical centers that were evaluated in that cohort and ...
New research adds evidence to the benefits of ginger supplements for treating autoimmune diseases
2023-09-22
New research has revealed a potentially important role ginger supplements can play in controlling inflammation for people living with autoimmune diseases.
The research published today in JCI Insight focused on studying the impact of ginger supplementation on a type of white blood cell called the neutrophil. The study was especially interested in neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation, also known as NETosis, and what it may mean for controlling inflammation.
The study found ginger consumption by healthy individuals makes their neutrophils more resistant to NETosis. This is important because NETs are microscopic spider web-like structures that propel inflammation and clotting, which ...
The role of the locus coeruleus. A blue stain linked to sleep
2023-09-22
A study conducted by researchers at the University of Liège (BE) Institute, using ultra-high field 7 Tesla MRI, are providing a better understanding of how sleep is regulated.
We've known for a long time that sleep is good for the brain. We also know that light is not just for seeing, but also plays an important role in other aspects such as mood. What we don't know is how all this happens in our brains. Two separate studies, carried out by researchers at the University of Liège using the 7 Tesla MRI on the GIGA-Centre de Recherche du Cyclotron platform, offer the ...
NASA’s Webb finds carbon source on surface of Jupiter’s moon Europa
2023-09-22
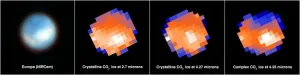
Jupiter’s moon Europa is one of a handful of worlds in our solar system that could potentially harbor conditions suitable for life. Previous research has shown that beneath its water-ice crust lies a salty ocean of liquid water with a rocky seafloor. However, planetary scientists had not confirmed if that ocean contained the chemicals needed for life, particularly carbon.
Astronomers using data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have identified carbon dioxide in a specific region on the icy surface of Europa. Analysis indicates that this carbon likely originated in the subsurface ocean and ...
Wildlife mitigating measures no help for Ottawa’s freshwater turtles
2023-09-22
Local turtles facing extinction within a decade due to urban growth, says uOttawa study.
Urban sprawl and insufficient relief measures have left an Ottawa-area freshwater turtle facing extinction within the decade, says new research from the University of Ottawa and Trent University, which tracked changes to the turtle’s habitat over a 10-year period.
Specifically, the development of Terry Fox Drive in the city’s west end has led to a dangerous decline in the Blanding’s turtle’s (Emydoidea blandingii) habitat, leading to a 70% decline in adult population size, despite mitigating measures such as wildlife fencing, new wetlands ...
A network that spreads light and the role of thalamus in our brain
2023-09-22
New research conducted at the University of Liège, using ultra-high field 7 Tesla MRI, provides a better understanding of how light stimulates our brain and could provide new insights into how it works.
A research team at the ULiège GIGA Institute tried to understand better how light stimulates our cognition. Light acts like a cup of coffee and helps keep us awake. That's why we recommend not using too much light on our smartphones and tablets in the evening. This can disrupt our sleep. On the other hand, the same light can help us during the day. Many studies have shown that good lighting can help students in schools, ...
Unraveling the mysteries of glassy liquids
2023-09-22
Glass, despite its apparent transparency and rigidity, is a complex and intriguing material. When a liquid is cooled to form a glass, its dynamics slows down significantly, resulting in its unique properties.
This process, known as “glass transition”, has puzzled scientists for decades. But one of its intriguing aspects is the emergence of "dynamical heterogeneities," where the dynamics become increasingly correlated and intermittent as the liquid cools down and approaches the glass transition temperature.
In a new study, researchers propose a new theoretical framework to explain these dynamical heterogeneities in glass-forming ...