(Press-News.org) New research has revealed a potentially important role ginger supplements can play in controlling inflammation for people living with autoimmune diseases.
The research published today in JCI Insight focused on studying the impact of ginger supplementation on a type of white blood cell called the neutrophil. The study was especially interested in neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation, also known as NETosis, and what it may mean for controlling inflammation.
The study found ginger consumption by healthy individuals makes their neutrophils more resistant to NETosis. This is important because NETs are microscopic spider web-like structures that propel inflammation and clotting, which contribute to many autoimmune diseases, including lupus, antiphospholipid syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis.
“There are a lot of diseases where neutrophils are abnormally overactive. We found that ginger can help to restrain NETosis, and this is important because it is a natural supplement that may be helpful to treat inflammation and symptoms for people with several different autoimmune diseases,” said senior co-author Kristen Demoruelle, MD, PhD, associate professor of medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine on the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
In a clinical trial, the researchers found that daily intake of a ginger supplement for seven days (20 mg of gingerols/day) by healthy volunteers boosted a chemical inside the neutrophil called cAMP. These high levels of cAMP then inhibited NETosis in response to various disease-relevant stimuli.
“Our research, for the first time, provides evidence for the biological mechanism that underlies ginger’s apparent anti-inflammatory properties in people,” said senior co-author Jason Knight, MD, PhD, associate professor in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of Michigan.
The researchers say that many people with inflammatory conditions are likely to ask their health care providers whether natural supplements could be helpful for them or they already take supplements, like ginger, to help manage symptoms. Unfortunately, the precise impact on disease is often unknown. The researchers hope that providing more evidence about ginger’s benefits, including the direct mechanism by which ginger impacts neutrophils, will encourage health care providers and patients to more strategically discuss whether taking ginger supplements as part of their treatment plan could be beneficial.
“There are not a lot of natural supplements, or prescription medications for that matter, that are known to fight overactive neutrophils. We, therefore, think ginger may have a real ability to complement treatment programs that are already underway. The goal is to be more strategic and personalized in terms of helping to relieve people’s symptoms,” Knight adds.
As a next step, the researchers hope to use this study to unlock funding for clinical trials of ginger in patients with autoimmune and inflammatory diseases where neutrophils are overactive, such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, antiphospholipid syndrome and even COVID-19.
About the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
The University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus is a world-class medical destination at the forefront of transformative science, medicine, education and patient care. The campus encompasses the University of Colorado health professional schools, more than 60 centers and institutes and two nationally ranked independent hospitals - UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital and Children's Hospital Colorado - that treat more than two million adult and pediatric patients each year. Innovative, interconnected and highly collaborative, the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus delivers life-changing treatments, patient care and professional training and conducts world-renowned research fueled by over $690 million in research grants. For more information, visit www.cuanschutz.edu.
END
New research adds evidence to the benefits of ginger supplements for treating autoimmune diseases
Study looked at the impact of ginger supplements on people’s white blood cell function
2023-09-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The role of the locus coeruleus. A blue stain linked to sleep
2023-09-22
A study conducted by researchers at the University of Liège (BE) Institute, using ultra-high field 7 Tesla MRI, are providing a better understanding of how sleep is regulated.
We've known for a long time that sleep is good for the brain. We also know that light is not just for seeing, but also plays an important role in other aspects such as mood. What we don't know is how all this happens in our brains. Two separate studies, carried out by researchers at the University of Liège using the 7 Tesla MRI on the GIGA-Centre de Recherche du Cyclotron platform, offer the ...
NASA’s Webb finds carbon source on surface of Jupiter’s moon Europa
2023-09-22
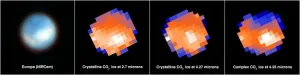
Jupiter’s moon Europa is one of a handful of worlds in our solar system that could potentially harbor conditions suitable for life. Previous research has shown that beneath its water-ice crust lies a salty ocean of liquid water with a rocky seafloor. However, planetary scientists had not confirmed if that ocean contained the chemicals needed for life, particularly carbon.
Astronomers using data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have identified carbon dioxide in a specific region on the icy surface of Europa. Analysis indicates that this carbon likely originated in the subsurface ocean and ...
Wildlife mitigating measures no help for Ottawa’s freshwater turtles
2023-09-22
Local turtles facing extinction within a decade due to urban growth, says uOttawa study.
Urban sprawl and insufficient relief measures have left an Ottawa-area freshwater turtle facing extinction within the decade, says new research from the University of Ottawa and Trent University, which tracked changes to the turtle’s habitat over a 10-year period.
Specifically, the development of Terry Fox Drive in the city’s west end has led to a dangerous decline in the Blanding’s turtle’s (Emydoidea blandingii) habitat, leading to a 70% decline in adult population size, despite mitigating measures such as wildlife fencing, new wetlands ...
A network that spreads light and the role of thalamus in our brain
2023-09-22
New research conducted at the University of Liège, using ultra-high field 7 Tesla MRI, provides a better understanding of how light stimulates our brain and could provide new insights into how it works.
A research team at the ULiège GIGA Institute tried to understand better how light stimulates our cognition. Light acts like a cup of coffee and helps keep us awake. That's why we recommend not using too much light on our smartphones and tablets in the evening. This can disrupt our sleep. On the other hand, the same light can help us during the day. Many studies have shown that good lighting can help students in schools, ...
Unraveling the mysteries of glassy liquids
2023-09-22
Glass, despite its apparent transparency and rigidity, is a complex and intriguing material. When a liquid is cooled to form a glass, its dynamics slows down significantly, resulting in its unique properties.
This process, known as “glass transition”, has puzzled scientists for decades. But one of its intriguing aspects is the emergence of "dynamical heterogeneities," where the dynamics become increasingly correlated and intermittent as the liquid cools down and approaches the glass transition temperature.
In a new study, researchers propose a new theoretical framework to explain these dynamical heterogeneities in glass-forming ...
Can cloud-based quantum computing really offer a quantum advantage?
2023-09-22
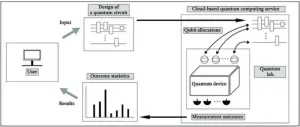
A quantum machine can drastically speed up certain kinds of computation, but only if two or more quantum bits in the machine are entangled---that is, capable of displaying related behavior despite being separated. Seeking a way for users of cloud-based quantum computing services to detect qubit entanglement, Jiheon Seong and Joonwoo Bae of the Korea Advanced Institute of science and Technology developed and tested an entanglement witness circuit. It works to certify entanglement even when the cloud-based service allows only limited control ...
UNC-Chapel Hill research presents new development model for the world's third-longest river
2023-09-22
A new research paper published in Science Advances reveals how changes in the size of the Yangtze River watershed may have led to the carving of deep canyons.
In this study, UNC-Chapel Hill professor Eric Kirby and his co-authors explore the impact of drainage basin expansion on the growth of the Yangtze River.
“This study presents a new model for when and how the Yangtze River was born,” said Kirby, “The Yangtze is one of the world’s great rivers, rising on the Tibetan Plateau at altitudes over 17,000 feet and descending ...
Why are you better at recognizing upright faces? Clues from a person who sees the world differently
2023-09-22
When you see a familiar face upright, you’ll recognize it right away. But if you saw that same face upside down, it’s much harder to place. Now researchers who’ve studied Claudio, a 42-year-old man whose head is rotated back almost 180 degrees such that it sits between his shoulder blades, suggest that the reason people are so good at processing upright faces has arisen through a combination of evolution and experience. The findings appear September 22 in the journal iScience.
“Nearly everyone has far more experience with upright faces and ancestors whose reproduction ...
Jellyfish shown to learn from past experience for the first time
2023-09-22
Even without a central brain, jellyfish can learn from past experiences like humans, mice, and flies, scientists report for the first time on September 22 in the journal Current Biology. They trained Caribbean box jellyfish (Tripedalia cystophora) to learn to spot and dodge obstacles. The study challenges previous notions that advanced learning requires a centralized brain and sheds light on the evolutionary roots of learning and memory.
No bigger than a fingernail, these seemingly simple jellies have a complex visual system with 24 eyes embedded in their bell-like body. Living ...
Jellyfish are smarter than you think
2023-09-22
Jellyfish are more advanced than once thought. A new study from the University of Copenhagen has demonstrated that Caribbean box jellyfish can learn at a much more complex level than ever imagined – despite only having one thousand nerve cells and no centralized brain. The finding changes our fundamental understanding of the brain and could enlighten us about our own mysterious brains.
After more than 500 million years on Earth, the immense evolutionary success of jellyfish is undeniable. Still, we've always thought of them as simple creatures with very limited learning abilities.
The prevailing opinion is that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
[Press-News.org] New research adds evidence to the benefits of ginger supplements for treating autoimmune diseasesStudy looked at the impact of ginger supplements on people’s white blood cell function