(Press-News.org) Researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Brazil have developed a strategy for removing glyphosate, one of the world’s most frequently used herbicides, from water. Inspired by the concept of the circular economy, the technique is based on sugarcane bagasse, a waste material produced by sugar and ethanol plants.
“Isolated and chemically functionalized sugarcane bagasse fibers can be used as adsorbent material. Glyphosate adheres to its surface and is removed as a water contaminant by filtration, decantation or centrifugation,” Maria Vitória Guimarães Leal, told Agência FAPESP. She is the first author of an article on the research published in the journal Pure and Applied Chemistry. Adsorption is a process whereby molecules dispersed in a liquid or gaseous medium adhere to a solid insoluble surface, which is typically porous.
Owing to its low cost and high potential to raise crop yields, glyphosate is widely used to control the growth of unwanted plants, such as weeds, invasive species and agricultural pests, but scientific studies have shown that it can be a human health hazard and in particular may pose a cancer risk. Application of glyphosate-containing products is restricted or banned in Austria, Bulgaria, Colombia, Costa Rica, Denmark, El Salvador, Germany and Greece, among other countries. In Brazil, however, annual use of such products averages 173,150.75 metric tons. Part of them is borne away by rain into rivers, wells and other aquatic environments.
With FAPESP’s support via three projects (14/50869-6, 20/06577-1 and 21/09773-9), scientists at UNESP’s School of Sciences and Technology (FCT) in Presidente Prudente found a way to remove glyphosate products from water in research led by postdoctoral fellow Guilherme Dognani and Aldo Eloizo Job, a professor at FCT-UNESP.
How it works
Dognani explained the procedure. “The bagasse is shredded and the cellulose isolated by separating it from the hemicellulose and lignin. The cellulose fibers are then functionalized by adding quaternary ammonia groups to their surface so that the material is positively charged. The resulting cationic cellulose microfibers bind easily to glyphosate,” he said.
Leal added that there are certain favorable conditions, such as pH variation, which was the focus of the study. “When pH is varied, both the adsorbent material and the glyphosate display different molecular configurations. The most efficient level for interaction between them, inducing the most adsorption and hence optimal removal, is pH 14,” he said.
To evaluate adsorption capacity, the researchers prepared fractions of a glyphosate solution with pH 2, 6, 10 and 14, measured using a pH meter. They then added to each fraction identical amounts of functionalized cellulose microfiber. The flasks with the solution contaminated by glyphosate plus cellulose were agitated for 24 hours. In accordance with the procedure described in the literature, they were then heated in a water bath until the reaction occurred, cooled to room temperature and analyzed by visible light spectrophotometry. Removal efficiency was calculated as a ratio of initial to final glyphosate levels in each sample, and adsorption capacity was calculated as a function of pH.
About São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP)
The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) is a public institution with the mission of supporting scientific research in all fields of knowledge by awarding scholarships, fellowships and grants to investigators linked with higher education and research institutions in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. FAPESP is aware that the very best research can only be done by working with the best researchers internationally. Therefore, it has established partnerships with funding agencies, higher education, private companies, and research organizations in other countries known for the quality of their research and has been encouraging scientists funded by its grants to further develop their international collaboration. You can learn more about FAPESP at www.fapesp.br/en and visit FAPESP news agency at www.agencia.fapesp.br/en to keep updated with the latest scientific breakthroughs FAPESP helps achieve through its many programs, awards and research centers. You may also subscribe to FAPESP news agency at http://agencia.fapesp.br/subscribe.
END
Brazilian researchers develop method of purifying water contaminated by glyphosate
The technique uses functionalized cellulose fibers from sugarcane bagasse to remove residues of the herbicide from an aqueous medium
2023-09-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Vizient awards UCSF Health top marks for quality patient care
2023-09-22
Hospital quality ratings assess safety, equity and effectiveness in hospitals nationwide
Vizient Inc. has named UCSF Health as a Top Performer for its high-quality patient care in the 2023 Bernard A. Birnbaum, MD, Quality Leadership Ranking.
This is the second year in a row that Vizient has recognized UCSF Health as a leader in health care quality. This year, UCSF Health ranked seventh among comprehensive academic medical centers, out of 116 medical centers that were evaluated in that cohort and ...
New research adds evidence to the benefits of ginger supplements for treating autoimmune diseases
2023-09-22
New research has revealed a potentially important role ginger supplements can play in controlling inflammation for people living with autoimmune diseases.
The research published today in JCI Insight focused on studying the impact of ginger supplementation on a type of white blood cell called the neutrophil. The study was especially interested in neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation, also known as NETosis, and what it may mean for controlling inflammation.
The study found ginger consumption by healthy individuals makes their neutrophils more resistant to NETosis. This is important because NETs are microscopic spider web-like structures that propel inflammation and clotting, which ...
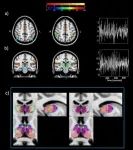
The role of the locus coeruleus. A blue stain linked to sleep
2023-09-22
A study conducted by researchers at the University of Liège (BE) Institute, using ultra-high field 7 Tesla MRI, are providing a better understanding of how sleep is regulated.
We've known for a long time that sleep is good for the brain. We also know that light is not just for seeing, but also plays an important role in other aspects such as mood. What we don't know is how all this happens in our brains. Two separate studies, carried out by researchers at the University of Liège using the 7 Tesla MRI on the GIGA-Centre de Recherche du Cyclotron platform, offer the ...
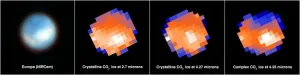
NASA’s Webb finds carbon source on surface of Jupiter’s moon Europa
2023-09-22
Jupiter’s moon Europa is one of a handful of worlds in our solar system that could potentially harbor conditions suitable for life. Previous research has shown that beneath its water-ice crust lies a salty ocean of liquid water with a rocky seafloor. However, planetary scientists had not confirmed if that ocean contained the chemicals needed for life, particularly carbon.
Astronomers using data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have identified carbon dioxide in a specific region on the icy surface of Europa. Analysis indicates that this carbon likely originated in the subsurface ocean and ...
Wildlife mitigating measures no help for Ottawa’s freshwater turtles
2023-09-22
Local turtles facing extinction within a decade due to urban growth, says uOttawa study.
Urban sprawl and insufficient relief measures have left an Ottawa-area freshwater turtle facing extinction within the decade, says new research from the University of Ottawa and Trent University, which tracked changes to the turtle’s habitat over a 10-year period.
Specifically, the development of Terry Fox Drive in the city’s west end has led to a dangerous decline in the Blanding’s turtle’s (Emydoidea blandingii) habitat, leading to a 70% decline in adult population size, despite mitigating measures such as wildlife fencing, new wetlands ...
A network that spreads light and the role of thalamus in our brain
2023-09-22
New research conducted at the University of Liège, using ultra-high field 7 Tesla MRI, provides a better understanding of how light stimulates our brain and could provide new insights into how it works.
A research team at the ULiège GIGA Institute tried to understand better how light stimulates our cognition. Light acts like a cup of coffee and helps keep us awake. That's why we recommend not using too much light on our smartphones and tablets in the evening. This can disrupt our sleep. On the other hand, the same light can help us during the day. Many studies have shown that good lighting can help students in schools, ...
Unraveling the mysteries of glassy liquids
2023-09-22
Glass, despite its apparent transparency and rigidity, is a complex and intriguing material. When a liquid is cooled to form a glass, its dynamics slows down significantly, resulting in its unique properties.
This process, known as “glass transition”, has puzzled scientists for decades. But one of its intriguing aspects is the emergence of "dynamical heterogeneities," where the dynamics become increasingly correlated and intermittent as the liquid cools down and approaches the glass transition temperature.
In a new study, researchers propose a new theoretical framework to explain these dynamical heterogeneities in glass-forming ...
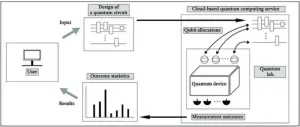
Can cloud-based quantum computing really offer a quantum advantage?
2023-09-22
A quantum machine can drastically speed up certain kinds of computation, but only if two or more quantum bits in the machine are entangled---that is, capable of displaying related behavior despite being separated. Seeking a way for users of cloud-based quantum computing services to detect qubit entanglement, Jiheon Seong and Joonwoo Bae of the Korea Advanced Institute of science and Technology developed and tested an entanglement witness circuit. It works to certify entanglement even when the cloud-based service allows only limited control ...
UNC-Chapel Hill research presents new development model for the world's third-longest river
2023-09-22
A new research paper published in Science Advances reveals how changes in the size of the Yangtze River watershed may have led to the carving of deep canyons.
In this study, UNC-Chapel Hill professor Eric Kirby and his co-authors explore the impact of drainage basin expansion on the growth of the Yangtze River.
“This study presents a new model for when and how the Yangtze River was born,” said Kirby, “The Yangtze is one of the world’s great rivers, rising on the Tibetan Plateau at altitudes over 17,000 feet and descending ...
Why are you better at recognizing upright faces? Clues from a person who sees the world differently
2023-09-22
When you see a familiar face upright, you’ll recognize it right away. But if you saw that same face upside down, it’s much harder to place. Now researchers who’ve studied Claudio, a 42-year-old man whose head is rotated back almost 180 degrees such that it sits between his shoulder blades, suggest that the reason people are so good at processing upright faces has arisen through a combination of evolution and experience. The findings appear September 22 in the journal iScience.
“Nearly everyone has far more experience with upright faces and ancestors whose reproduction ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
[Press-News.org] Brazilian researchers develop method of purifying water contaminated by glyphosateThe technique uses functionalized cellulose fibers from sugarcane bagasse to remove residues of the herbicide from an aqueous medium