(Press-News.org) Loma Linda University (LLU) researchers found microbial contamination in common sources of drinking water in the Eastern Coachella Valley, including soda fountains at fast-food restaurants. Their findings revealed that 41% of the water samples researchers collected from these soda fountains contained total coliforms, an indicator of water contamination.
Molecular analysis of the water samples revealed traces of genetic material found in bacteria, including Salmonella spp (Salmonella), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Escherichia coli (E. coli). Given these findings, study authors advise soda fountain owners to regularly clean and flush the dispensers as a way to prevent water contamination.
“To the best of our knowledge, our study is the first to assess the water quality from soda fountains, water vending machines, swabs, and tap water, especially in the Eastern Coachella Valley,” said Thomas Hile, PhD, MSc, an LLU affiliated researcher and lead author of the study.
The study, “Microbial contamination analysis of drinking water from bulk dispensers and fast-food restaurants in the Eastern Coachella Valley, California,” was published last month in Water Supply, the International Water Association’s peer-reviewed journal.
Researchers collected 72 water samples from fast-food soda fountains, water vending machines, and tap water from outdoor sources in the Eastern Coachella Valley. They measured physico-chemical parameters on site and brought samples back to the laboratory to perform conventional cultivable methods and molecular analysis.
Analysis of the water samples indicated the presence of biofilms — organized communities of organisms widely present in nature that represent serious problems in environmental, industrial, and medical settings. In several cases, the amounts of bacteria in soda fountain samples exceeded the maximum permissible levels set by the Environmental Protection Agency.
“The presence of pathogenic microorganisms in drinking water is a serious public health concern and cannot be overemphasized,” the authors stated in their journal article.
Based on the results, the authors contend that biofilm forms over time in water distribution systems, mainly made of plastic piping, funneling water to fast-food soda fountains and water vending machines. Additionally, they say the soda fountains' filtration systems, when not maintained, do not effectively prevent water contamination.
East Coachella Valley is an environmental justice area and includes the city of Coachella and the unincorporated communities of Thermal, Oasis, Mecca, and North Shore. These communities are primarily Latino, made up of migrant and agricultural-worker families that struggle for access to safe drinking water.
“The study collected water samples from an underserved area, where there generally aren’t routine checks of water quality and lack of maintenance for soda fountains or water vending machines,” said Ryan Sinclair, PhD, MPH, the study’s last author and an associate professor at Loma Linda University School of Public Health and School of Medicine.
He says the study reinforces the importance of developing surveillance and regulations that target fast-food soda fountains and water dispensers. He and study authors recommend that owners regularly clean and flush dispensers and use antimicrobial tubes inside water dispensers to control the growth of biofilms.
The study’s researchers plan to perform a risk assessment to determine whether the levels of microbes they identified and quantified in their water samples pose a health hazard or are tied to any health conditions.
The study was funded by Loma Linda University School of Medicine.
For more information about research at LLU, visit researchaffairs.llu.edu or call 909-558-8544.
END
Loma Linda University researchers find contaminated water in fast-food soda fountains
LLU study authors advise regular cleaning of water dispensers
2023-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Uncovering novel mechanisms of endocytosis and intracellular trafficking
2023-09-25
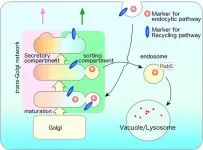
Endocytosis is an important cellular process through which cells internalize substances such as water and nutrients. These substances are first transported as cargo to the initial sorting compartment (endosomes) before being degraded (endo-lysosomal pathway) or recycled (recycling pathway of the plasma membrane). The trans-Golgi network (TGN), which lies adjacent to the Golgi apparatus, is a key mediator of this intracellular transport. Endocytosis mediates the infection of harmful pathogens such as bacteria and virus, and its disruption may lead to several diseases. It is, ...
Transforming the cacao sector: introducing the guide for the assessment of cacao quality and flavor
2023-09-25
[Rome, 25 September] - The cacao sector has long grappled with challenges stemming from the absence of commonly agreed standardised protocols for evaluating cacao quality and flavour, as well as the lack of a common language to describe the sensory experience of cacao. These issues have impeded effective communication and understanding between producers and buyers, disproportionately affecting farmers in developing countries who strive to cultivate and sell superior quality cacao deserving of higher prices.
Today, Cacao of Excellence is proud to unveil a groundbreaking initiative aimed at addressing these long-standing issues — the Guide for the Assessment of Cacao Quality and Flavour. ...
Genetic code of rare kidney cancer cracked
2023-09-25
GENETIC CODE OF RARE KIDNEY CANCER CRACKED
The genetic code of a rare form of kidney cancer, called reninoma, has been studied for the first time. In the new paper, published today (25th September) in Nature Communications, researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Great Ormond Street Hospital and The Royal Free Hospital also revealed a new drug target that could serve as an alternative treatment if surgery is not recommended.
There are around 100 cases of reninoma reported to date worldwide (1), and it is amongst the rarest of tumours in humans. Although it can usually be cured with surgery, ...
Waterfleas hold key to cleaner environment and better human health
2023-09-25
Tiny waterfleas could play a pivotal role in removing persistent chemical pollutants from wastewater – making it safe to use in factories, farms and homes, a new study reveals.
Rapid urbanisation, population growth, unsustainable food production and climate change have put unprecedented pressure on water resources, culminating in a global water crisis. The sustainable management and reuse of water resources is paramount for ensuring societal, economic, and environmental well-being.
Persistent chemical pollutants, originating from domestic and industrial processes, ...
Researchers pioneer safe chemotherapy methods for treating bacterial infections
2023-09-25
Antibiotic resistant bacteria are a threat to human lives, and yet the development of new drugs to treat bacterial infections is slow. A group of proven drugs used in cancer treatment for decades could possibly be the solution. A new class of antibiotics is now being developed by researchers at Linköping University, Sweden.
Many drugs and drug candidates have proven highly effective in killing bacteria or tumour cells. The problem is that they also harm the patient, and they are therefore used very sparingly or not at all. When used to treat for instance cancer, they are delivered directly into the blood and spread throughout the body. ...
New insights on a potentially serious side effect of the cancer drug alpelisib
2023-09-25
New research has uncovered elevated rates of high blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, among patients with breast cancer who are treated with the oral medication alpelisib. The results are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Alpelisib targets the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) protein that is involved in cell growth and when mutated can contribute to cancer. In 2019, the US Food and Drug Administration approved the use of this drug in combination with fulvestrant, ...
Holidays back to the home country could help bilingual children hold on to their family’s original language
2023-09-25
It's hard to keep a language in the family. Many people who migrate to different countries find that their language of origin has become a heritage language, passed on to future generations with varying degrees of success. These languages come under pressure from the dominant language in a country as well as the lack of opportunities to practice and fluent speakers to practice with. So how do kids use or retain heritage languages? And can visits to their parents’ countries of origin help them increase their fluency?
“The role of parental language use in the country of residence is well-established,” ...
ETRI unveiled hyper-realistic technologies for the metaverse world
2023-09-25
For the upcoming hyper-realistic metaverse world in the era of digital transformation, domestic researchers are showcased their achievements in the development of display and stereoscopic imaging technologies.
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute(ETRI) participated in consecutive events, starting from the 16th August at COEX in Seoul for 'K-Display 2023,' followed by 'IMID 2023' at BEXCO in Busan from the 23rd, where they exhibited a variety of innovative technologies capable of realizing a truly realistic metaverse world.
At this exhibition, ETRI unveiled a total of 11 technologies across four categories, including ▲hyper-realistic ...
New guideline to promote health equity in Canada
2023-09-25
A comprehensive new guideline with 16 preventive care recommendations aims to promote health equity for people disadvantaged because of racism, sexism and other forms of discrimination.
The guideline, created by a diverse team of clinicians from across Canada with patient involvement, is published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal): https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230237
Some key recommendations:
Colorectal cancer — prioritize colorectal cancer screening for patients starting at age 45 years ...
Global study provides new insights into barriers to effective cardiovascular rehabilitation for women and why women are less likely to participate
2023-09-25
Philadelphia, September 25, 2023 – Cardiovascular rehabilitation (CR) improves health outcomes and well-being and can reduce death and re-hospitalization rates by 20%. However, programs are underutilized and women are much less likely to participate than men, so they do not reap these benefits. This first global comparative study into barriers to using CR in men and women assesses the extent of these barriers and discusses ways in which patients can overcome them. It determined that women and men face some common, but also many different barriers, and barriers differ by global region. The study appears in the Canadian ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Loma Linda University researchers find contaminated water in fast-food soda fountainsLLU study authors advise regular cleaning of water dispensers