(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO — Sept. 25, 2023 —Southwest Research Institute and The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) are collaborating to study the “felt heat” of San Antonio’s historic West Side. The prevalence of paved surfaces creates an environment that feels considerably hotter than the rest of the city.
The work, led by Principal Scientist Dr. Stuart Stothoff of SwRI’s Chemistry and Chemical Engineering Division and Dr. Esteban Lopez Ochoa of the Margie and Bill Klesse College of Engineering and Integrated Design at UTSA, is supported by a $125,000 grant from the Connecting through Research Partnerships (Connect) Program.
“If you look back in time, the West Side has always been somewhat neglected,” Lopez Ochoa said. “The consideration was not there to keep green spaces, which are cooler and offer more shade than pavement, which absorbs heat. It’s just easier to pave. When you compare different areas of the city, that area does lack vegetation much more than other areas of San Antonio.”
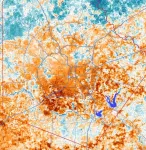
As a result of the greater amount of paved surfaces on the West Side, people there experience considerably more heat than in the rest of the city. Recent measurements by Lopez Ochoa showed temperatures as high as 154 degrees Fahrenheit just above the pavement.
“We’re working to precisely characterize what’s going on in this unusually hot area of the city, so that eventually a solution can be found to alleviate it,” Stothoff said.
Over the next year, SwRI and UTSA will place sensors in representative locations around the West Side to measure the felt heat in various environments. The sensors will gather data on air flow, wind speeds, relative humidity, air temperatures and dew points.
“The publicly available information about the heat measured on the West Side is satellite data, derived from visible or infrared wavelengths. It’s useful, but it doesn’t characterize the actual felt heat,” Stothoff said. “Satellite data also doesn’t allow you to see underneath the trees, in the shade. By placing our sensors in various key locations, we can measure the temperatures people actually feel.”
Stothoff and Lopez are also considering putting sensors inside homes on the West Side and are working with the Historic Westside Neighborhood Association and the Esperanza Peace and Justice Center to connect with residents who might be willing to participate.
Once the data gathering is complete, SwRI will create an energy balance model to comprehensively evaluate the felt environment and adapt publicly available weather data to better represent ambient temperatures and overall thermal comfort on the West Side.
SwRI’s Executive Office and UTSA’s Office of the Vice President for Research, Economic Development, and Knowledge Enterprise sponsor the Connect program, which offers grant opportunities to enhance greater scientific collaboration between the two institutions.
For more information, visit https://www.swri.org/industries/oceans-land-climate.
END
SwRI, UTSA collaborate to measure the felt heat on San Antonio’s West Side
Researchers will gather data with sensors to fill gap left by satellite measurements
2023-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rivers contain hidden sinks and sources of microplastics
2023-09-25
Significant quantities of microplastic particles are being trapped in riverbed sediments or carried through the air along major river systems, a new study has shown.
The research, conducted along the length of the Ganges River in South Asia, found on average about 41 microplastic particles per square metre per day settled from the atmosphere. .
In addition, analysis by scientists found 57 particles per kilogram on average in sediment from the riverbed as well as one particle in every 20 litres of ...
By air, rain and land: How microbes return after a wildfire
2023-09-25
Highlights:
Ecological disturbances like wildfires disrupt microbial communities.
Researchers studied microbial succession for a year in a field, following a fire.
They found that dispersal played a pivotal role in re-establishing surface-level communities.
Dispersal from wind or rain explained the return of most fungal species. Bacterial communities were influenced by both air and deeper bulk soil.
Washington, D.C. — The disruption brought by wildfires reaches everything that lives in or near a burning field or forest—including microbes. A better understanding ...
Companies may benefit from transparency about racial diversity efforts
2023-09-25
WASHINGTON – Companies that reveal their struggles to increase racial diversity in their workforces are perceived as more trustworthy and committed to diversity than companies that remain silent, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“We suspect that many companies fear that revealing lagging diversity numbers will undermine their reputation and credibility, so they don’t disclose that information, but that strategy may be misplaced,” said lead researcher Evan ...
Social impact entrepreneurs: Funding available for local health equity solutions in Houston
2023-09-25
HOUSTON, September 25, 2023 – In Houston, people who live south of downtown in the Sunnyside neighborhood can expect to live an average of 21 years less than those who live just nine miles away in the more affluent Bellaire community[1]. This life expectancy gap is nearly equivalent to the difference in life expectancy between low-income and high-income countries. The science tells us that physical conditions in which people live explain in part why some are healthier than others[2].
To sustainably remove the social and economic barriers preventing access to equitable health for everyone ...
New study sheds light on the impact of in-stream video advertising on ad information encoding
2023-09-25
The effects of in-stream video advertising on ad information encoding have long remained a mystery. A recent study, led by Professor Sung-Phil Kim and his research team in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at UNIST sheds light on this subject. By integrating the negative emotion–memory model (NEMM) and the limited capacity model of motivated–mediated message processing (LC4MP), researchers investigated how advertising content is encoded within the context of in-stream video advertising.
The ...
Political independents are more negative than partisans
2023-09-25
COLUMBUS, Ohio – In this era of extreme partisanship, the people who express the most negativity in their political choices are those we may least expect: independents.
In a new paper, researchers conducted five studies in which they found that independents were more likely than partisans to frame their position in terms of opposition to one party, candidate, message or option rather than in support of the other choice.
And it’s not just in politics: One study found that “independents” ...
Loma Linda University researchers find contaminated water in fast-food soda fountains
2023-09-25
Loma Linda University (LLU) researchers found microbial contamination in common sources of drinking water in the Eastern Coachella Valley, including soda fountains at fast-food restaurants. Their findings revealed that 41% of the water samples researchers collected from these soda fountains contained total coliforms, an indicator of water contamination.
Molecular analysis of the water samples revealed traces of genetic material found in bacteria, including Salmonella spp (Salmonella), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Escherichia coli (E. coli). Given these findings, ...
Uncovering novel mechanisms of endocytosis and intracellular trafficking
2023-09-25
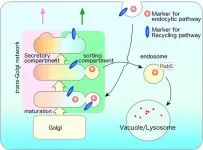
Endocytosis is an important cellular process through which cells internalize substances such as water and nutrients. These substances are first transported as cargo to the initial sorting compartment (endosomes) before being degraded (endo-lysosomal pathway) or recycled (recycling pathway of the plasma membrane). The trans-Golgi network (TGN), which lies adjacent to the Golgi apparatus, is a key mediator of this intracellular transport. Endocytosis mediates the infection of harmful pathogens such as bacteria and virus, and its disruption may lead to several diseases. It is, ...
Transforming the cacao sector: introducing the guide for the assessment of cacao quality and flavor
2023-09-25
[Rome, 25 September] - The cacao sector has long grappled with challenges stemming from the absence of commonly agreed standardised protocols for evaluating cacao quality and flavour, as well as the lack of a common language to describe the sensory experience of cacao. These issues have impeded effective communication and understanding between producers and buyers, disproportionately affecting farmers in developing countries who strive to cultivate and sell superior quality cacao deserving of higher prices.
Today, Cacao of Excellence is proud to unveil a groundbreaking initiative aimed at addressing these long-standing issues — the Guide for the Assessment of Cacao Quality and Flavour. ...
Genetic code of rare kidney cancer cracked
2023-09-25
GENETIC CODE OF RARE KIDNEY CANCER CRACKED
The genetic code of a rare form of kidney cancer, called reninoma, has been studied for the first time. In the new paper, published today (25th September) in Nature Communications, researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Great Ormond Street Hospital and The Royal Free Hospital also revealed a new drug target that could serve as an alternative treatment if surgery is not recommended.
There are around 100 cases of reninoma reported to date worldwide (1), and it is amongst the rarest of tumours in humans. Although it can usually be cured with surgery, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] SwRI, UTSA collaborate to measure the felt heat on San Antonio’s West SideResearchers will gather data with sensors to fill gap left by satellite measurements