(Press-News.org) (Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Wind energy is, by far, the most common type of clean energy. And transitioning to clean energy is critical to addressing the climate crisis. Yet local opposition poses a significant barrier to the deployment of wind energy projects.
A study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) by researchers from UC Santa Barbara, the University of Michigan and Gallup Inc. examined wind energy projects throughout the United States and Canada to determine how common opposition is and what factors predict it. The study found that nearly one in five projects faced opposition (17% of wind projects in the U.S. and 18% in Canada). It also found that opposition to wind farms involved small groups of local opponents, and was more likely in whiter communities in the United States and wealthier communities in Canada.
“Most research on opposition to wind energy projects focuses on specific case studies or small geographic areas,” said Leah Stokes, lead author and the Anton Vonk Associate Professor of Environmental Politics in the Department of Political Science at UCSB. “We wanted to take a comprehensive look at political opposition across North America to understand how common opposition is and what predicts it.”
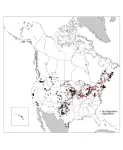
The study collected over 35,000 news articles to analyze 1,415 North American wind energy projects between 2000 and 2016. Political opposition to projects was defined as physical protests, legal actions, legislation and letters to the editor. In total, 17% of wind projects in the United States and 18% in Canada faced significant opposition, with rates of opposition increasing in both countries over time.
In the U.S., opposition was concentrated in the Northeast, and in areas with a higher proportion of white residents and a lower proportion of Hispanic residents. In addition, the names of the people who opposed wind projects were overwhelmingly likely (92.4%) to be white. In Canada, opposition was concentrated in Ontario and in wealthy communities. In both countries, larger projects were more likely to face opposition than smaller projects. The number of people engaging in opposition was small at a given project: the median number of protestors was 23 in the U.S. and 34 in Canada.
“Fossil fuel plants are predominantly located in poorer communities and communities of color,” Stokes explained. “These plants create pollution. We need to replace fossil fuel power plants with clean energy, like wind and solar. When wealthier, whiter communities oppose wind energy projects in their backyards, they extend the lifetime of fossil fuel projects. This is an injustice.”
In the study, researchers used the term “energy privilege” to describe this environmental justice challenge: opposing clean energy is a privilege because wealthy white communities can continue to consume goods and services from burning fossil fuels while lower-income communities and communities of color bear the brunt of that pollution.
END
Wind energy projects in North America are more likely to be opposed by white, wealthy communities
2023-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Naming and shaming can be effective to get countries to act on climate
2023-09-25
Enforcement is one of the biggest challenges to international cooperation on mitigating climate change in the Paris Agreement. The agreement has no formal enforcement mechanism; instead, it is designed to be transparent so countries that fail to meet their obligations will be named and thus shamed into changing behavior. A new study from the University of California San Diego's School of Global Policy and Strategy shows that this naming-and-shaming mechanism can be an effective incentive for many countries to uphold their pledges ...
Scientists develop method of identifying life on other worlds
2023-09-25
Humankind is looking for life on other planets, but how will we recognise it when we see it? Now a group of US scientists have developed an artificial-intelligence-based system which gives 90% accuracy in discovering signs of life.
The work was presented to scientists for the first time at the Goldschmidt Geochemistry Conference in Lyon on Friday 14th July, where it received a positive reception from others working in the field. The details have now been published in the peer-reviewed journal PNAS (see notes for details).
Lead researcher Professor Robert Hazen, of the Carnegie Institution’s Geophysical ...
Caribbean parrots thought to be endemic are actually relicts of millennial-scale extinction
2023-09-25
In a new study published in PNAS, researchers have extracted the first ancient DNA from Caribbean parrots, which they compared with genetic sequences from modern birds. Working with fossils and archaeological specimens, they showed that two species thought to be endemic to particular islands were once more widespread and diverse. The results help explain how parrots rapidly became the world’s most endangered group of birds, with 28% of all species considered to be threatened. This is especially true for parrots that inhabit islands.
On ...
CSIC contributes to deciphering the enigmatic global distribution of fairy circles
2023-09-25
One of the most impressive and mysterious natural formations that we can observe in the arid areas of our planet are the fairy circles. These are enigmatic circular patterns of bare soil surrounded by plants generating rings of vegetation, which until now had only been described in Namibia and Australia. Over the years, multiple hypotheses have been proposed to explain their formation, which have given rise to numerous discussions about the mechanisms that give rise to them. However, until now, we did not know the global dimension of this type of phenomena and the environmental ...
Insilico Medicine and University of Cambridge present new approach to discover targets for Alzheimer’s and other diseases with protein phase separation
2023-09-25
New York and Cambridge, UK -- Recent research demonstrates that protein phase separation (PPS) is widely present in cells and drives a variety of important biological functions. Protein phase separation at the wrong place or time could create clogs or aggregates of molecules linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, and poorly formed cellular condensates could contribute to cancers and might help explain the aging process.
Given the emerging association between human disease and the PPS process, scientists have been looking for ways to identify potential targets for therapeutic interventions based on PPS regulation. Today, Insilico ...
Antibiotics can help some bacteria survive for longer
2023-09-25
Scientists have found a surprising effect of some antibiotics on certain bacteria – that the drugs can sometimes benefit bacteria, helping them live longer.
Until now, it has been widely acknowledged that antibiotics kill bacteria or stop them growing, making them widely used as blanket medication for bacterial infections. In recent years, the rise of antibiotic resistance has stopped some antibiotics from working, meaning that untreatable infections could be the biggest global cause of death by 2050.
Now, researchers at the University of Exeter have shown for the first time that antibiotics ...
New method can improve assessing genetic risks for non-white populations
2023-09-25
A team led by researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and the National Cancer Institute has developed a new algorithm for genetic risk-scoring for major diseases across diverse ancestry populations that holds promise for reducing health care disparities.
Genetic risk-scoring algorithms are considered a promising method to identify high-risk groups of individuals who could benefit from preventive interventions for various diseases and conditions, such as cancers and heart diseases. ...
Wearable devices show who may need more help managing diabetes
2023-09-25
A new Dartmouth study in the journal Science Advances suggests that how well people with diabetes manage their blood sugar depends on their experience with the condition and their overall success in controlling their glucose levels, as well as on the season and time of day. The findings could help physicians identify those patients who could benefit from more guidance in regulating their blood sugar, particularly at certain times of year.
The researchers accessed data from wearable glucose monitors that showed how 137 people in the U.S. aged 2 to 76 living primarily with type 1, aka juvenile, diabetes managed their blood sugar on a daily basis. By analyzing more ...
Light and sound waves reveal negative pressure
2023-09-25
As a physical quantity pressure is encountered in various fields: atmospheric pressure in meteorology, blood pressure in medicine, or even in everyday life with pressure cookers and vacuum-sealed foods. Pressure is defined as a force per unit area acting perpendicular to a surface of a solid, liquid, or gas. Depending on the direction in which the force acts within a closed system, very high pressure can lead to explosive reactions in extrem cases, while very low pressure in a closed system can cause the implosion of the system itself. Overpressure ...
Predicting how climate change affects infrastructure without damaging the subject
2023-09-25
A digital twin may sound like something out of a science fiction film, but Pitt engineers are developing new technology to make them a reality in our campus and beyond.
Digital twins – a model that serves as a real-time computational counterpart – can be used to help simulate the effects of multiple types of conditions, such as weather, traffic, and even climate change. Still, life-cycle assessments (LCAs) of climate change’s effects on infrastructure are still a work-in-progress, leaving a need ...