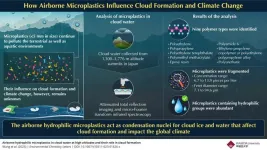
Plastic particles less than 5 mm in size are called “microplastics.” These tiny bits of plastic are often found in industrial effluents, or form from the degradation of bulkier plastic waste. Research shows that large amounts of microplastics are ingested or inhaled by humans and animals alike and have been detected in multiple organs such as lung, heart, blood, placenta, and feces. Ten million tons of these plastic bits end up in the ocean, released with the ocean spray, and find their way into the atmosphere. This implies that microplastics may have become an essential component of clouds, contaminating nearly everything we eat and drink via “plastic rainfall.” While most studies on microplastics have focused on aquatic ecosystems, few have looked into their impact on cloud formation and climate change as “airborne particles.”
In a new study led by Hiroshi Okochi, Professor at Waseda University, a group of Japanese researchers has explored the path of airborne microplastics (AMPs) as they circulate in the biosphere, adversely impacting human health, and the climate. Their study was recently published in the journal Environmental Chemistry Letters with contributions from co-authors Yize Wang from Waseda University and Yasuhiro Niida from PerkinElmer Japan Co. Ltd. “Microplastics in the free troposphere are transported and contribute to global pollution. If the issue of 'plastic air pollution' is not addressed proactively, climate change and ecological risks may become a reality, causing irreversible and serious environmental damage in the future,” explains Okochi.
To investigate the role of these tiny plastic particles in the troposphere and the atmospheric boundary layer, the team collected cloud water from the summit of Mount (Mt.) Fuji, south-eastern foothills of Mt. Fuji (Tarobo), and the summit of Mt. Oyama – regions at altitudes ranging between 1300-3776 meters. Using advanced imaging techniques like attenuated total reflection imaging and micro-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (µFTIR ATR imaging), the researchers determined the presence of microplastics in the cloud water, and examined their physical and chemical properties.
They identified nine different types of polymers and one type of rubber in the AMPs detected. Notably, most of the polypropylene that was detected in the samples was degraded and had carbonyl (C=O) and/or hydroxyl (OH) groups. The Feret diameters of these AMPs ranged between 7.1 – 94.6 µm, the smallest seen in the free troposphere. Moreover, the presence of hydrophilic (water loving) polymers in the cloud water was abundant, suggesting that they were removed as “cloud condensation nuclei.” These findings confirm that AMPs play a key role in rapid cloud formation, which may eventually affect the overall climate.
Accumulation of AMPs in the atmosphere, especially in the polar regions, could lead to significant changes in the ecological balance of the planet, leading to severe loss of biodiversity. Okochi concludes by saying “AMPs are degraded much faster in the upper atmosphere than on the ground due to strong ultraviolet radiation, and this degradation releases greenhouse gases and contributes to global warming. As a result, the findings of this study can be used to account for the effects of AMPs in future global warming projections.”
***
Reference
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01626-x
Authors: Yize Wang1, Hiroshi Okochi1, Yuto Tani1, Hiroshi Hayami1, Minami Yukiya2, Naoya Katsumi2, Masaki Takeuchi3, Atsuyuki Sorimachi4, Yusuke Fujii5, Mizuo Kajino6, Kouji Adachi6, Yasuhiro Ishihara7, Yoko Iwamoto7, Yasuhiro Niida8
Affiliations:
Graduate School of Creative Science and Engineering, Waseda University
Faculty of Bioresources and Environmental Science, Ishikawa Prefectural University
Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Tokushima University
Faculty of Science and Engineering, Toyo University
Graduate School of Humanities and Sustainable System Sciences, Osaka Prefecture University
Meteorological Research Institute
Graduate School for Integrated Sciences for Life, Hiroshima University
PerkinElmer Japan Co. Ltd., Kanagawa, Japan
About Waseda University
Located in the heart of Tokyo, Waseda University is a leading private research university that has long been dedicated to academic excellence, innovative research, and civic engagement at both the local and global levels since 1882. The University has produced many changemakers in its history, including nine prime ministers and many leaders in business, science and technology, literature, sports, and film. Waseda has strong collaborations with overseas research institutions and is committed to advancing cutting-edge research and developing leaders who can contribute to the resolution of complex, global social issues. The University has set a target of achieving a zero-carbon campus by 2032, in line with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by the United Nations in 2015.
To learn more about Waseda University, visit https://www.waseda.jp/top/en
About Professor Hiroshi Okochi from Waseda University
Hiroshi Okochi is a Professor at the Faculty of Creative Science and Engineering, at the Waseda University, Japan. He completed his Doctor of Engineering degree from the University of Tokyo. He is currently a faculty of Science and Engineering in the Department of Environmental Resources Engineering and leads the Environmental Chemistry Laboratory, at the Waseda University. His research group focusses on health management of the planet by understanding processes of water and material circulation. Their studies are based in various geographical areas of interest at Mt. Fuji, Tanzawa, Ikuta, Fukushima, and Cambodia. His research interests span various topics in climate science, surrounding the atmosphere and the hydrosphere.
END