(Press-News.org) Over 40 per cent of Canadians have used at least one risk-associated alternative health-care treatment in the past 12 months, says a new UBC study published in PLOS One.
The researchers explored alternative health-care therapies where the proven benefits do not justify the risks involved. They found that people who access these therapies tend to be wealthier, like novelty and taking risks, and are also more likely to distrust conventional medicine.
The multidisciplinary study between UBC School of Nursing and the University of Alberta Health Law Institute involved a survey of 1,492 Canadians ages 16 and over and is the first to explore risk-associated alternative health care use in Canada, said UBC professor Dr. Bernie Garrett.
“Many alternative health-care therapies are harmless, but few can result in physical injuries or death. As people are now more frequently accessing riskier alternative health care, we wanted to understand why they would use unproven and potentially harmful therapeutics instead of medically established ones,” said Dr. Garrett. “Our aim was also to establish factors that might predict engagement behaviours.”
Susceptible to persuasion, and skeptical of science
Among those who engaged in risky alternative health care, physical manipulative therapies such as cervical chiropractic manipulation, and potentially toxic herbal and nutritional supplement use, were the most common. They were accessed by 68 per cent and 55 per cent respectively. At least one in 10 users engaged in higher-risk invasive or untested procedures such as injecting potentially harmful substances into veins.
The researchers also used a variety of existing psychometric tools to see if they could predict the likelihood of engagement with riskier alternative health care. They found two tools were particularly effective: one that measures susceptibility to advertising techniques, and another that assesses trust in science.
Individuals who had more trust in science were less likely to engage in alternative health care than those who had negative attitudes about science and scientific authority. People who were more likely to use risky alternative medicine were more susceptible to social pressure, had positive attitudes towards advertising, a greater desire for novelty, and a higher tolerance of risk generally.
“This study provides key evidence of the role played by advertising and social media marketing in promoting alternative health care. This type of marketing is less regulated, and the advertisements can be very persuasive, often using positive role models like celebrities and influencers. They hardly mention side effects while promising the ability to control one’s own health outside of conventional medicine," said Dr. Garrett.
Gender and wealth also play a part
Riskier alternative health care uptake in the Canadian public was also found to be influenced by socioeconomic factors, including gender, age and wealth:
Women were more likely to choose alternative health care, likely due to targeted advertising that capitalizes on idealized body images and their role as primary caregivers.
Older respondents, particularly those over 55, were more hesitant, possibly because they are more experienced.
Wealthier individuals and those with higher education were more likely to use alternative health care, likely due to associated costs of such treatments.
Contrary to some other findings, Canadians of Asian descent were less likely to use risky alternative health care. Reasons for this were unclear, although experience and financial barriers may be a factor.
As engagement in risk-associated alternative health care increases, the researchers emphasize that health-care practices and the advertisement of health-care therapies should be based on scientific evidence and subject to better advertising regulations to protect Canadians from potential harm.
“Identifying and educating the public on the significant risks encountered with some alternative health-care practices is an important part of Canadian public health promotion. It isn’t all harmless,” Dr. Garrett said.
END
People who use alternative medicine favor risk and novelty, and distrust science
2023-09-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
SARS-CoV-2 infects coronary arteries, increases plaque inflammation
2023-09-28
SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, can directly infect the arteries of the heart and cause the fatty plaque inside arteries to become highly inflamed, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke, according to a study funded by the National Institutes of Health. The findings, published in the journal Nature Cardiovascular Research, may help explain why certain people who get COVID-19 have a greater chance of developing cardiovascular disease, or if they already have it, develop more heart-related complications.
In the study, researchers focused on older people with fatty buildup, known as atherosclerotic plaque, who ...
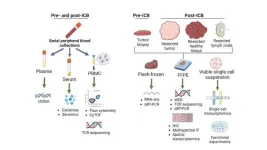
Immune checkpoint blockade prior to surgery promising in multiple cancer types
2023-09-28
Treating cancer with immunotherapies known as an immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) prior to surgery (so-called neoadjuvant immunotherapy) has been a rapidly growing area of research, but the scientific community is just scratching the surface of what is possible, according to a review article co-authored by several current and former investigators from the Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy and the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
“We consider this approach to cancer immunotherapy to be a gold mine ...
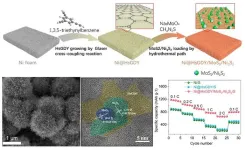
HsGDY on Ni foam for loading MoS2/Ni3S2 to enhance the performance on lithium-sulfur batteries
2023-09-28
They published their work on Sep. 26 in Energy Material Advances.
"The booming progress of electric vehicles demands next-generation energy storage technologies with high energy density, low cost, and longevity." said Lu, a professor at the college of chemistry and chemical engineering in Shantou university. "Lithium-sulfur batteries are identified as a promising energy storage system because of their high ultrahigh energy density and large theoretical capacity. However, they are limited by the poor electronic conductivity of sulfur, volume changes of the cathode, and shuttle effect."
Lu explained that the conversion of polysulfides (Li2Sn, ...
Brief dialysis may be best for some kidney patients
2023-09-28
Patients with acute kidney injury requiring outpatient dialysis after hospital discharge receive the same care as those with the more common end-stage kidney disease, according to a study led by UC San Francisco.
But while patients with the latter diagnosis – typically caused by long-standing hypertension or diabetes – must remain on lifelong dialysis or receive a new kidney, some patients on dialysis for acute kidney injury have the potential to recover, the researchers reported in their study in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology on Sept. 28, 2023.
“For ...
COOPERATE: Empowering minoritized patients with chronic back and other musculoskeletal pain to receive the care they need
2023-09-28
INDIANAPOLIS – A new study led by a U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine researcher focuses on empowering minoritized patients with chronic back and other musculoskeletal pain to receive care best suited to their individual values and preferences. Black patients continue to experience greater pain severity, worse pain outcomes and inadequate pain treatment compared to White patients, despite national priorities focused on health equity.
COOPERATE (Communication and Activation in Pain to Enhance Relationships ...
Novel battery technology with negligible voltage decay developed at CityU, a world’s first
2023-09-28
A pivotal breakthrough in battery technology that has profound implications for our energy future has been achieved by a joint-research team led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU).
The new development overcomes the persistent challenge of voltage decay and can lead to significantly higher energy storage capacity.
Lithium-ion batteries (LiBs) are widely used in electronic devices, while lithium-(Li) and manganese-rich (LMR) layered oxides are a promising class of cathodes for LiBs due to their high ...
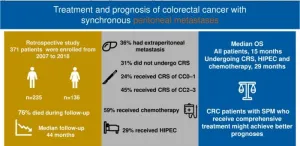
Comprehensive treatment strategy could change CRC with SPM
2023-09-28
Colorectal cancer (CRC) with synchronous peritoneal metastases (SPM) is a challenging disease to treat, with a relatively poor prognosis. However, recent advances in treatment strategies have led to improved outcomes for patients with SPM.
The optimal treatment approach for CRC with SPM remains controversial. A growing body of evidence suggests that comprehensive treatment, including cytoreductive surgery (CRS), chemotherapy, and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC), may improve patient outcomes.
A ...
Unlocking the potential of silicon anode materials for commercialized batteries
2023-09-28
In a groundbreaking review published in Nature Energy, Professor Jaephil Cho from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST presents an analysis protocol to evaluate silicon cathode materials applicable to commercialized batteries. The study delves deep into the characteristics and challenges surrounding silicon anode materials—the focus of significant attention as secondary battery components.
Silicon has emerged as a promising alternative to conventional graphite anodes in high-energy lithium-ion batteries due to its exceptional gravimetric capacity. However, intrinsic issues such as severe volume expansion during cycling have hindered the widespread ...
Mount Sinai Rehabilitation Centers ranked among the best in the United States by Newsweek
2023-09-28
Two Mount Sinai Health System hospitals are among the top-ranked for “America’s Best Physical Rehabilitation Centers for 2023” by Newsweek/Statista.
The Mount Sinai Hospital is ranked No. 2 in New York State for inpatient rehabilitation care, with stroke care designated as a “Standout Program.” Mount Sinai Morningside, on Manhattan’s Upper West Side, is ranked No. 5 for inpatient rehabilitation. These prestigious accolades highlight the exceptional quality of care and follow-up care, along with accommodations and amenities that are part of the rehabilitation ...
For the lonely, a blurred line between real and fictional people
2023-09-28
COLUMBUS, Ohio – In lonely people, the boundary between real friends and favorite fictional characters gets blurred in the part of the brain that is active when thinking about others, a new study found.
Researchers scanned the brains of people who were fans of “Game of Thrones” while they thought about various characters in the show and about their real friends. All participants had taken a test measuring loneliness.
The difference between those who scored highest on loneliness and those who ...