(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON (Sept. 28, 2023) — Grandmother was right: Scrubbing behind the ears and between the toes may help keep the skin in those regions healthy, or so says a new study by a team at the George Washington University.
The microbiome, or the collection of microbes living on and in the human body, are known to play a role in human health and the skin is no different. A new study by a team at the George Washington University has shown that the composition of the skin microbiome varies across dry, moist and oily regions of the skin.
Researchers at the GW Computational Biology Institute wanted to take a closer look at the skin microbiome of healthy people. Marcos Pérez-Losada, an associate professor of biostatistics and bioinformatics at the GW Milken Institute School of Public Health, and his team were interested in testing what they call “the Grandmother Hypothesis.”
Keith Crandall, Director of the Computational Biology Institute and professor of biostatistics and bioinformatics at GW says his grandmother always instructed the kids in his family to “scrub behind the ears, between the toes and in the belly button.” Crandall posited that these hotspots are normally washed less often compared to the skin on the arms or legs and thus may harbor different types of bacteria.
But would the Grandmother Hypothesis hold up if put to the test? Pérez-Losada and Crandall designed an innovative genomics course and then unleashed a team of students to help them find out.
The 129 graduate and undergraduate students were taught to collect their own data–by swabbing certain moist and oily hotspots, behind the ears, between the toes and in the naval. They also collected samples from control dry areas like the calves and forearms.
The students then learned how to extract and sequence the DNA in the skin samples in order to compare the microbes living in the hotspots to those in the control regions.
The researchers found that forearms and calves which are often cleaned more thoroughly at bath time had a greater diversity and thus potentially a healthier collection of microbes compared to the samples taken in the hotspots.
When certain trouble-making microbes take over the microbiome they can shift the balance away from health, Crandall says. If the microbiome tips in favor of detrimental microbes, skin diseases like eczema or acne can be the result, he says.
The students proved the grandmother hypothesis and their results suggested that cleaning habits can change the microbes living on your skin and consequently its health status, Crandall says.
This research, including an earlier study by the same team, is one of the first to look at the diversity of sites across the skin microbiome in healthy adult subjects and may provide a reference point for future research. Crandall says the study of how the collection of microbes on the skin leads to health or disease is in the early stages.
The new study “Spatial diversity of the skin bacteriome,” was published Sept. 19 in the journal Frontiers in Microbiology.
-GW-
END
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Every person hosts trillions of microorganisms, like bacteria and viruses, on their skin and in organs including those that make up the digestive tract, like their mouth, that collectively make up their microbiome. Microbiome research can lead to medical breakthroughs to treat diseases like inflammatory bowel syndrome and diabetes. According to Laura Weyrich, associate professor of anthropology and bioethics at Penn State, microbiome samples from Indigenous communities have played an important role in furthering Western ...
URBANA, Ill. – Family mealtimes are important for parents and children as a space to communicate, socialize, and build attachment relationships. But it can be difficult for busy parents to balance family and work life. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign explores how parents’ job stress influences their attendance at family mealtimes, and in turn, children’s socioemotional development.
“We all struggle to maintain the balance between work life and family life. But this might ...
Forget walking 10,000 steps a day. Taking at least 50 steps climbing stairs each day could significantly slash your risk of heart disease, according to a new study from Tulane University.
The study, published in Atherosclerosis, found that climbing more than five flights of stairs daily could reduce risk of cardiovascular disease by 20%.
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) along with coronary artery disease and stroke are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide.
“Short bursts of high-intensity stair climbing are a time-efficient ...
The first ethical framework for conducting human research on commercial spaceflight was proposed today in an article in Science by an international team that included Hastings Center president Vardit Ravitsky. Ravitsky’s contribution focused on promoting diversity among the researchers and participants, which is essential to ensuring the research benefits society at large.
Human research on commercial spaceflight is expected to expand significantly in the near future, and yet there are no rules for ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – New research suggests that ultrasound may have potential in treating a group of harmful chemicals known as PFAS to eliminate them from contaminated groundwater.
Invented nearly a century ago, per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances, also known as “forever chemicals,” were once widely used to create products such as cookware, waterproof clothing and personal care items. Today, scientists understand that exposure to PFAS can cause a number of human health issues such as birth defects and cancer. But because the bonds inside these chemicals don’t break down easily, they’re notoriously ...
Bottom Line: Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) reduced the risk of severe infections by 90% in patients with multiple myeloma undergoing treatment with an anti-BCMA bispecific antibody.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Blood Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Author: Guido Lancman, MD, a clinical associate at the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre of the University Health Network and an adjunct assistant professor at the University of Toronto
Background: Bispecific antibodies targeting the BCMA ...
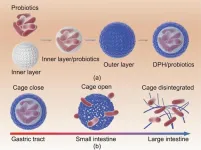
In a groundbreaking study, a research team led by Changhu Xue and Xiangzhao Mao from the Ocean University of China has developed a remarkable double-layer polysaccharide hydrogel (DPH) that promises to revolutionize the field of intestine-targeted oral delivery of probiotics. The team’s findings, published in Engineering, demonstrate the potential of DPH to enhance the bioavailability, intestinal colonization, and overall effectiveness of probiotics in treating various diseases.
The research team’s study focused on addressing the challenges posed by the harsh gastrointestinal environment and the short retention ...
New guidelines are needed to assure that research on human subjects performed on commercial spaceflights is conducted ethically, a panel of experts say in a commentary appearing in the September 28 issue of the journal Science.
Their paper is titled Ethically cleared to launch?
Private companies are expected to fly thousands of people into space in the coming decades. Those aboard will include workers and passengers who will have the opportunity to participate in research studies. Such research is not only essential to assure the safety of future space travelers but often also addresses critical issues of human health in general.
Buț ...
Large differences in flower characteristics between wildflowers with different pollinators are achieved by a few key genetic differences, according to a study by Carolyn Wessinger at the University of South Carolina, US, and colleagues, publishing September 28th in the open access journal PLOS Biology.
Plants that rely on animal pollinators, such as insects or birds, have evolved distinctive suites of flower characteristics — known as “pollination syndromes” — that are tailored to the pollinator. For example, most plants in the ...
To help resolve the scientific debate over whether it was a giant asteroid or volcanic eruptions that wiped out the dinosaurs and most other species 66 million years ago, Dartmouth researchers tried a new approach — they removed scientists from the debate and let the computers decide.
The researchers report in the journal Science a new modeling method powered by interconnected processors that can work through reams of geological and climate data without human input. They tasked nearly 130 processors with analyzing the fossil record in reverse to pinpoint the events and conditions that led to the Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event that ...