(Press-News.org) URBANA, Ill. – Family mealtimes are important for parents and children as a space to communicate, socialize, and build attachment relationships. But it can be difficult for busy parents to balance family and work life. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign explores how parents’ job stress influences their attendance at family mealtimes, and in turn, children’s socioemotional development.
“We all struggle to maintain the balance between work life and family life. But this might be especially challenging for parents, who are engaging in childcare after a busy and stressful day at work. And when it comes to co-parenting in dual-earner families, which comprises 65% of families with children in United States, we do not know much about how mothers and fathers share caregiving roles under work stress,” said lead author Sehyun Ju, doctoral student in the Department of Human Development and Family Studies (HDFS) in the College of Agricultural, Consumer and Environmental Sciences (ACES) at U. of I.
The study included data from more than 1,400 dual-earner families, consisting of heterosexual married couples with children, in a nationally representative survey that traced children’s development across family, home, child care, and school environments from 9 months to kindergarten. The researchers focused on the interplay of child characteristics, family mealtimes, and parents’ job and financial dissatisfaction.
“We found that children of parents who expressed higher work-related stress when the children were 2 years old had lower socioemotional competency at age 4 to 5, measured by lower positive and higher negative social behaviors,” Ju explained.
There were significant differences regarding the impact of mothers’ and fathers’ work stress. For mothers, higher job dissatisfaction did not impact frequency of family mealtimes; however, it was directly associated with lower socioemotional competency in their children.
On the other hand, fathers who had higher job and financial dissatisfaction were less likely to attend family mealtimes with their children, and this in turn resulted in the children having lower socioemotional competency at age 4 to 5.
“Even when the mother increased her mealtime presence to compensate for the father’s absence, the child’s socioemotional development was still negatively impacted. This indicates fathers may have a unique influence that cannot be replaced by the mother. Future intervention programs should help both parents obtain a better balance between work and family, and highlight the importance of family routines to promote healthy child development,” stated co-author Qiujie Gong, a doctoral student in HDFS.
The findings speak to the pervasiveness of traditional gender roles, added Karen Kramer, associate professor in HDFS and co-author on the study. “Mothers are considered primary caregivers, and they are expected to be present and feed their children no matter what. The study showed they didn't adjust their mealtime frequencies in response to job dissatisfaction as fathers did.”
Kramer notes the study is unique in combining topics from different disciplines, including psychology, sociology, economics, and nutrition, and connecting them in a holistic way that provides insights for policy measures.
“We have to acknowledge the challenges that families face in creating consistent routines. It’s not just an outcome of individual influences. Outside factors, such as parents’ work environment and financial situation can affect their interactions, mealtimes, and child development. For example, dinner time for young kids is typically around five or six o'clock, but the expectation that parents are home early in the day doesn’t align with being an ideal worker. Policy initiatives to help provide a work environment and community support that facilitate family mealtimes would be important,” Kramer concluded.
The paper, “Association of parents’ work-related stress and children’s socioemotional competency: Indirect effects of family mealtimes” is published in Journal of Family Psychology. [DOI: 10.1037/fam0001147]. Authors are Sehyun Ju, Qiujie Gong, and Karen Z. Kramer. The research was supported by the National Institute of Food and Agriculture, Grant ILLU-793-914
END
How parents’ work stress affects family mealtimes and children’s development
2023-09-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Walking more than five flights of stairs a day can cut risk of heart disease by 20%, study says
2023-09-28
Forget walking 10,000 steps a day. Taking at least 50 steps climbing stairs each day could significantly slash your risk of heart disease, according to a new study from Tulane University.
The study, published in Atherosclerosis, found that climbing more than five flights of stairs daily could reduce risk of cardiovascular disease by 20%.
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) along with coronary artery disease and stroke are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide.
“Short bursts of high-intensity stair climbing are a time-efficient ...
Global team recommends ethical rules for human research in commercial spaceflight
2023-09-28
The first ethical framework for conducting human research on commercial spaceflight was proposed today in an article in Science by an international team that included Hastings Center president Vardit Ravitsky. Ravitsky’s contribution focused on promoting diversity among the researchers and participants, which is essential to ensuring the research benefits society at large.
Human research on commercial spaceflight is expected to expand significantly in the near future, and yet there are no rules for ...
Ultrasound may rid groundwater of toxic ‘forever chemicals’
2023-09-28
COLUMBUS, Ohio – New research suggests that ultrasound may have potential in treating a group of harmful chemicals known as PFAS to eliminate them from contaminated groundwater.
Invented nearly a century ago, per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances, also known as “forever chemicals,” were once widely used to create products such as cookware, waterproof clothing and personal care items. Today, scientists understand that exposure to PFAS can cause a number of human health issues such as birth defects and cancer. But because the bonds inside these chemicals don’t break down easily, they’re notoriously ...
Intravenous immunoglobulin may prevent severe infections associated with anti-BCMA therapy for multiple myeloma
2023-09-28
Bottom Line: Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) reduced the risk of severe infections by 90% in patients with multiple myeloma undergoing treatment with an anti-BCMA bispecific antibody.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Blood Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Author: Guido Lancman, MD, a clinical associate at the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre of the University Health Network and an adjunct assistant professor at the University of Toronto
Background: Bispecific antibodies targeting the BCMA ...
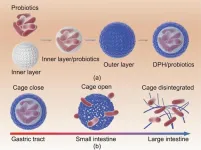
Innovative double-layer polysaccharide hydrogel revolutionizes intestine-targeted oral delivery of probiotics
2023-09-28
In a groundbreaking study, a research team led by Changhu Xue and Xiangzhao Mao from the Ocean University of China has developed a remarkable double-layer polysaccharide hydrogel (DPH) that promises to revolutionize the field of intestine-targeted oral delivery of probiotics. The team’s findings, published in Engineering, demonstrate the potential of DPH to enhance the bioavailability, intestinal colonization, and overall effectiveness of probiotics in treating various diseases.
The research team’s study focused on addressing the challenges posed by the harsh gastrointestinal environment and the short retention ...
Ethics rules needed for human research on commercial spaceflights, panel says
2023-09-28
New guidelines are needed to assure that research on human subjects performed on commercial spaceflights is conducted ethically, a panel of experts say in a commentary appearing in the September 28 issue of the journal Science.
Their paper is titled Ethically cleared to launch?
Private companies are expected to fly thousands of people into space in the coming decades. Those aboard will include workers and passengers who will have the opportunity to participate in research studies. Such research is not only essential to assure the safety of future space travelers but often also addresses critical issues of human health in general.
Buț ...
A few essential genetic differences tailor flowers to bee or hummingbird pollinators
2023-09-28
Large differences in flower characteristics between wildflowers with different pollinators are achieved by a few key genetic differences, according to a study by Carolyn Wessinger at the University of South Carolina, US, and colleagues, publishing September 28th in the open access journal PLOS Biology.
Plants that rely on animal pollinators, such as insects or birds, have evolved distinctive suites of flower characteristics — known as “pollination syndromes” — that are tailored to the pollinator. For example, most plants in the ...
Dartmouth study removes human bias from debate over dinosaurs' demise
2023-09-28
To help resolve the scientific debate over whether it was a giant asteroid or volcanic eruptions that wiped out the dinosaurs and most other species 66 million years ago, Dartmouth researchers tried a new approach — they removed scientists from the debate and let the computers decide.
The researchers report in the journal Science a new modeling method powered by interconnected processors that can work through reams of geological and climate data without human input. They tasked nearly 130 processors with analyzing the fossil record in reverse to pinpoint the events and conditions that led to the Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event that ...
Cleared to launch? Ethical guidelines needed for human research in commercial spaceflight
2023-09-28
HOUSTON – (Sept. 28, 2023) – The commercial spaceflight industry is expanding opportunities for scientific research in space, but the industry needs clear ethical guidelines before human research is ready for liftoff. In a new policy paper published in Science, a global, multidisciplinary team of bioethicists, health policy experts, space health researchers, commercial spaceflight professionals and government regulators outlines potential ethical concerns facing the future of commercial space research and provides guiding principles ...
Genome-wide study of staghorn coral identifies genomic markers of disease resistance
2023-09-28
A genome-wide survey of highly endangered staghorn coral in the Caribbean has identified 10 genomic regions associated with resilience against white band disease – an emergent infectious disease responsible for killing up to 95% of Caribbean Acropora species, including staghorn corals (A. cervicornis). The findings could be used as a conservation tool to improve disease resistance in the wild and nursery stocks of staghorn corals used to repopulate damaged coral reefs throughout Caribbean waters. Over the last several decades, Earth’s reef corals have experienced unprecedented declines. Increased anthropogenic ...