(Press-News.org) A top UVA Health cancer expert is highlighting how a new drug could transform how doctors treat a brain tumor that typically strikes younger people.
David Schiff, MD, the co-director of UVA Cancer Center’s Neuro-Oncology Center, has authored an editorial in the prestigious New England Journal of Medicine describing the potential significance of the drug vorasidenib for patients with tumors known as “grade 2 IDH-mutant gliomas.” The drug, when tested in the INDIGO clinical trial, was found to slow tumor growth significantly and extended the average time until the tumor started growing from 11.1 months to more than 27 months.
If the drug receives approval from the federal Food and Drug Administration, it would become the first targeted therapy for low-grade gliomas. But Schiff notes that there are also other recent advances that are improving our understanding of such gliomas.
“It used to be that we thought of all gliomas as being on a spectrum,” Schiff said. “We now understand that those with the IDH gene mutation have a markedly different biology, outcome and, as this study shows, vulnerabilities that new therapies can exploit.”
About IDH-Mutant Gliomas
Approximately 2,500 Americans with a median age of only 40 are diagnosed with grade 2 IDH-mutant gliomas each year. The tumors often affect the patients’ ability to think and hold a job, as well as interfere with other aspects of daily life. Eventually the tumors become resistant to treatment options and typically prove fatal.
Because of the limited treatment options available, doctors usually take a “watch and wait” approach to managing the gliomas, holding off on treatment until after the tumor progresses. But vorasidenib could change that, Schiff notes. The drug could offer the first early treatment for the cancer, giving patients an important new option that could extend their lives.
In the INDIGO trial, more than 300 patients were randomized to receive vorasidenib or a harmless placebo. Neither the patients nor their doctors knew which the patients were receiving. Schiff, in his editorial, describes the results as “striking.” Not only did the patients receiving vorasidenib live longer, but they did not need more toxic treatments, such as radiation and chemotherapy, as quickly as the patients receiving placebos.
Schiff was so impressed by the success of the drug that he writes that vorasidenib could “put a nail in the coffin” of the watch-and-wait approach.
“There are still many unanswered questions about how we can best utilize this new medication if and when it receives FDA approval,” Schiff said. “Nonetheless, considering that existing standard therapies for these tumors [radiation and chemotherapy] are tough on patients, with short- and long-term side effects, it will be wonderful to have a useful and very well-tolerated treatment option.”
Findings Published
Both the results of the INDIGO trial and Schiff’s editorial have been published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
To keep up with the latest medical research news from UVA, subscribe to the Making of Medicine blog at http://makingofmedicine.virginia.edu.
END
New drug a breakthrough for brain tumor that strikes young people: NEJM editorial
2023-09-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Genome study reveals 30 years of Darwin’s finch evolution
2023-09-29
An international team of researchers has released a landmark study on contemporary evolutionary change in natural populations. Their study uses one of the largest genomic datasets ever produced for animals in their natural environment, comprising nearly 4,000 Darwin’s finches. The study has revealed the genetic basis of adaptation in this iconic group. The results are published in the journal Science.
Ever since Darwin wrote about the finches of the Galápagos Islands, biologists have studied these small songbirds to understand the mechanisms of evolution. One ancestral species has evolved into 18 different species in the last million years. ...
Ghent University’s research team envisions a bright future with active machine learning in chemical engineering
2023-09-29
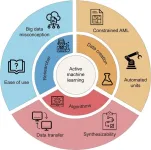
Chemical engineering researchers have a powerful new tool at their disposal: active machine learning. In a recent perspective article published in Engineering, Kevin M. Van Geem’s research team at Ghent University explores the potential of active machine learning in revolutionizing the field of chemical engineering. By combining machine learning with the design of experiments, active machine learning promises to enhance the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of research, spanning all length scales of chemical engineering.
Active machine learning algorithms ...
Climate change and carnivores: shifts in the distribution and effectiveness of protected areas in the Amazon
2023-09-29
A new article published in PeerJ Life & Environment, authored by Camila Ferreira Leão at Universidade Federal do Pará sheds light on the effects of climate change on carnivorous mammals in the Amazon and their representation within Protected Areas (PAs). "Climate change and carnivores: shifts in the distribution and effectiveness of protected areas in the Amazon," reveals alarming findings about the vulnerable status of these animals and the effectiveness of conservation measures.
Carnivorous ...
Can ChatGPT help us form personal narratives?
2023-09-29
Research has shown that personal narratives—the stories we tell ourselves about our lives—can play a critical role in identity and help us make sense of the past and present. Research has also shown that by helping people reinterpret narratives, therapists can guide patients toward healthier thoughts and behaviors.
Now, researchers from the Positive Psychology Center at the University of Pennsylvania have tested the ability of ChatGPT-4 to generate individualized personal narratives based on stream-of-consciousness thoughts and demographic details ...
An intelligent control method reduces carbon emissions in energy-intensive equipment
2023-09-29
A research team led by Professor Tianyou Chai from Northeastern University, China, has developed an innovative intelligent control method for the low-carbon operation of energy-intensive equipment. This groundbreaking research, published in the journal Engineering, presents a significant step towards reducing carbon emissions in the process industry.
The research team’s method combines mechanism analysis with deep learning, linking control and optimization with prediction, and integrating decision-making ...
Groundbreaking control method reduces carbon emissions from zinc oxide rotary kilns, boosting profits for zinc smelting industry
2023-09-29
A research team from Central South University in China develops innovative control method to reduce carbon emissions from zinc oxide rotary kilns.
The zinc smelting industry is facing new challenges in meeting China’s carbon peak and carbon neutrality targets. To address these challenges, researchers from Central South University in China have developed a groundbreaking control method that reduces carbon emissions from zinc oxide rotary kilns while maintaining high profits. Their findings have been published in the journal Engineering.
Zinc oxide rotary kilns play a crucial role in the zinc smelting process. ...
Small but mighty new gene editor
2023-09-29
A new CRISPR-based gene-editing tool has been developed which could lead to better treatments for patients with genetic disorders. The tool is an enzyme, AsCas12f, which has been modified to offer the same effectiveness but at one-third the size of the Cas9 enzyme commonly used for gene editing. The compact size means that more of it can be packed into carrier viruses and delivered into living cells, making it more efficient. Researchers created a library of possible AsCas12f mutations and then combined selected ones to engineer an AsCas12f ...
Study finds SARS-CoV-2-associated sepsis was more common, deadly than previously thought
2023-09-29
Using data from Mass General Brigham’s electronic health records, Brigham researchers quantified the burden of SARS-CoV-2-associated sepsis early in the pandemic
New research suggests that the virus responsible for COVID-19 was a more common and deadly cause of sepsis during the initial period of the pandemic than previously assumed. The study, led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, used electronic health record (EHR) data from five Mass General Brigham hospitals to track the rate of SARS-CoV-2-associated ...
Use of electronic clinical data to track incidence and mortality for SARS-CoV-2–associated sepsis
2023-09-29
About The Study: The results of this study of 431,000 inpatient encounters at five Massachusetts hospitals suggest that SARS-CoV-2–associated sepsis was common and had higher mortality than presumed bacterial sepsis early in the COVID-19 pandemic. These findings highlight the high burden of SARS-CoV-2–associated sepsis and demonstrate the utility of electronic health record-based algorithms to conduct surveillance for viral and bacterial sepsis.
Authors: Claire N. Shappell, M.D., M.P.H., of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
Misinformation, trust, and use of ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19
2023-09-29
About The Study: In this 50-state survey study of 13,438 adults who reported probable or definite COVID-19 infection, endorsement of misinformation about the COVID-19 pandemic, lack of trust in physicians or scientists, conspiracy-mindedness, and the nature of news sources were associated with receiving non–evidence-based treatment for COVID-19. These results suggest that the potential harms of misinformation may extend to the use of ineffective and potentially toxic treatments in addition to avoidance of health-promoting behaviors.
Authors: Roy ...