Use of electronic clinical data to track incidence and mortality for SARS-CoV-2–associated sepsis
JAMA Network Open
2023-09-29
(Press-News.org)
About The Study: The results of this study of 431,000 inpatient encounters at five Massachusetts hospitals suggest that SARS-CoV-2–associated sepsis was common and had higher mortality than presumed bacterial sepsis early in the COVID-19 pandemic. These findings highlight the high burden of SARS-CoV-2–associated sepsis and demonstrate the utility of electronic health record-based algorithms to conduct surveillance for viral and bacterial sepsis.
Authors: Claire N. Shappell, M.D., M.P.H., of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.35728)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.35728?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=092923
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-09-29
About The Study: In this 50-state survey study of 13,438 adults who reported probable or definite COVID-19 infection, endorsement of misinformation about the COVID-19 pandemic, lack of trust in physicians or scientists, conspiracy-mindedness, and the nature of news sources were associated with receiving non–evidence-based treatment for COVID-19. These results suggest that the potential harms of misinformation may extend to the use of ineffective and potentially toxic treatments in addition to avoidance of health-promoting behaviors.
Authors: Roy ...
2023-09-29
About The Study: In this study of Black and white U.S. adults ages 45 and older, neighborhood-level factors, including safety and physical and social environments, and individual-level factors, including discrimination, attenuated racial disparities in cardiovascular health. Interventional approaches to improve ideal cardiovascular health that separately target neighborhood context and discrimination by gender and race are warranted.
Authors: Anika L. Hines, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the ...
2023-09-29
Children with mental health issues are more likely to have poor mental and physical health in their late teens and early 20s, and are at greater risk of social isolation, low educational attainment, financial difficulties and heavy substance use. That’s according to new research led by RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, which examined a wide range of data from more than 5,000 children and young adults in Ireland.
The findings, published today in JAMA Network Open, are drawn from the ‘Growing up in Ireland’* study. The researchers from Ireland, the UK, and Australia followed trends of mental health throughout childhood (ages 9-13) for 5,141 ...
2023-09-29
Language is the most important tool for human communication and essential for life in our society. “Despite a great deal of neuroscientific research on the representation of language, little is known about the organisation of language in the human brain. Much of what we do know comes from single studies with small numbers of subjects and has not been confirmed in follow-up studies,” says Dr Sabrina Turker from the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig. This meta-analysis aims to help change that.
Based on more than 400 ...
2023-09-29
Study by LMU psychologists shows that distractor objects can help the visual system develop more effective search strategies.
People are continuously provided with an overwhelming stream of events flooding the sensory organs. However, while the brain has impressive processing capabilities, its capacity is strongly limited. Thus, an observer cannot consciously experience all the events and information available at any one time, but has to focus on some limited subset of the whole.
For many decades, researchers have investigated the neuro-cognitive mechanisms of this selective attention through the use of visual search and have shown that contextual cueing plays ...
2023-09-29
Diagnosis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria using rapid diagnostic tests and treatment with artemisinin derivatives, the main component of the malaria treatments recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO), are under threat in the Horn of Africa. Scientists from the Laboratory of Parasitology and Medical Mycology at the University of Strasbourg and Strasbourg University Hospital, in collaboration with the Eritrean Ministry of Health, the Institut Pasteur, Columbia University in New York and WHO, have detected the emergence and spread in Eritrea of parasites with both artemisinin resistance and genome modifications ...
2023-09-29
Tsukuba, Japan—Proteins are subject to post-translational chemical modifications that result in functional diversity. Methylation is one such modification that is generally believed to occur on lysine and arginine residues. Recently, this modification has been shown to occur on histidine residues as well. Furthermore, it has been suggested that histidine methylation occurs in a wide range of proteins. However, many details remain unknown: for example, which are the proteins that are methylated and ...
2023-09-29
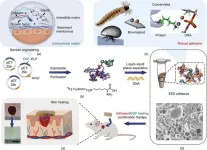
A team of researchers from China has made a significant breakthrough in biomedical engineering by developing a novel adhesive that promises to revolutionize wound management and tissue repair. The research, published in Engineering, unveils a biocomposite adhesive that exhibits robust adhesion and real-time skin healing properties.
Adhesives have long been recognized as a valuable tool in biomedical engineering. However, current adhesive systems face challenges in achieving strong and durable adhesion, limiting their effectiveness in wound healing. ...
2023-09-29
A research team led by Changjiang Wu at SINOPEC (Beijing) Research Institute of Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. in China has made important progress in understanding the polymerization behavior and thermal properties of copolymers formed through ethylene copolymerization with linear and end-cyclized olefins. The findings, published in the journal Engineering, shed light on the potential of utilizing different comonomers in olefin solution polymerization to obtain high-performance polyolefin materials.
Polyolefin elastomers (POEs) are widely used in various industries due to their exceptional properties. However, the high cost ...
2023-09-29
Researchers at Stanford University School of Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, and the Hospital for Special Surgery Research Institute have uncovered new details about how the immune system prevents the production of antibodies that can recognize and damage the body’s own, healthy tissues. The study, to be published September 29 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), also reveals how this process is impaired in autoimmune disorders such as systemic sclerosis and systemic lupus ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Use of electronic clinical data to track incidence and mortality for SARS-CoV-2–associated sepsis
JAMA Network Open