(Press-News.org) Language is the most important tool for human communication and essential for life in our society. “Despite a great deal of neuroscientific research on the representation of language, little is known about the organisation of language in the human brain. Much of what we do know comes from single studies with small numbers of subjects and has not been confirmed in follow-up studies,” says Dr Sabrina Turker from the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig. This meta-analysis aims to help change that.
Based on more than 400 neuroscientific experiments using functional imaging and involving more than 7000 subjects, the analysis provides in-depth insights into how the brain organises language. A quantitative, coordinate-based meta-analysis was used to integrate the many findings from different studies in the most complete and objective way possible. This makes it possible to see where the brain is activated when particular language processes occur. This approach provides insights into fundamental principles of how the brain organises language processing. The researchers not only studied language as a process in general, but also explicitly addressed subordinate processes: the meaning of language at the level of words and sentences (semantics); the phonetic structure of language (phonology); grammar and the arrangement of linguistic elements (syntax); and the phonetic structure of language at sentence level, including melody, intonation and rhythm (prosody).
In addition to the classical language regions in the left hemisphere of the brain, the authors of the study found that structures in the brain regions below the cerebral cortex and the cerebellum play a key role in language processes.
“These regions have been rather neglected in previous neuroscientific research on language,” says Gesa Hartwigsen, Professor of Cognitive and Biological Psychology at Leipzig University. “In particular, the left and right cerebellum are involved in processes related to the meaning of language and the processing of sounds. Similarly, phonetic patterns that transcend individual words and also convey emotional meaning are associated with activation in the right amygdala, a paired core area of the brain.” She points out that this part influences emotion and memory.
Professor Gesa Hartwigsen adds: “Our findings may serve future studies involving language recovery after brain injury, for example caused by stroke. And they could help to refine models of language processing.”
END
New insights into how the human brain organises language
Leipzig scientists publish largest meta-analysis on language processing to date
2023-09-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Visual search: Context facilitates more effective strategies
2023-09-29
Study by LMU psychologists shows that distractor objects can help the visual system develop more effective search strategies.
People are continuously provided with an overwhelming stream of events flooding the sensory organs. However, while the brain has impressive processing capabilities, its capacity is strongly limited. Thus, an observer cannot consciously experience all the events and information available at any one time, but has to focus on some limited subset of the whole.
For many decades, researchers have investigated the neuro-cognitive mechanisms of this selective attention through the use of visual search and have shown that contextual cueing plays ...
Malaria: Treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria patients under threat in the Horn of Africa
2023-09-29
Diagnosis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria using rapid diagnostic tests and treatment with artemisinin derivatives, the main component of the malaria treatments recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO), are under threat in the Horn of Africa. Scientists from the Laboratory of Parasitology and Medical Mycology at the University of Strasbourg and Strasbourg University Hospital, in collaboration with the Eritrean Ministry of Health, the Institut Pasteur, Columbia University in New York and WHO, have detected the emergence and spread in Eritrea of parasites with both artemisinin resistance and genome modifications ...
New post-translational modification of the glycolytic enzyme enolase
2023-09-29
Tsukuba, Japan—Proteins are subject to post-translational chemical modifications that result in functional diversity. Methylation is one such modification that is generally believed to occur on lysine and arginine residues. Recently, this modification has been shown to occur on histidine residues as well. Furthermore, it has been suggested that histidine methylation occurs in a wide range of proteins. However, many details remain unknown: for example, which are the proteins that are methylated and ...
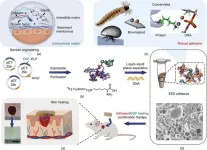
New frontier in biomedical engineering: Protein coacervates engineered into adhesive for unprecedented skin repair speed
2023-09-29
A team of researchers from China has made a significant breakthrough in biomedical engineering by developing a novel adhesive that promises to revolutionize wound management and tissue repair. The research, published in Engineering, unveils a biocomposite adhesive that exhibits robust adhesion and real-time skin healing properties.
Adhesives have long been recognized as a valuable tool in biomedical engineering. However, current adhesive systems face challenges in achieving strong and durable adhesion, limiting their effectiveness in wound healing. ...
New study unveils insights into ethylene copolymerization with linear and end-cyclized olefins using a metallocene catalyst
2023-09-29
A research team led by Changjiang Wu at SINOPEC (Beijing) Research Institute of Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. in China has made important progress in understanding the polymerization behavior and thermal properties of copolymers formed through ethylene copolymerization with linear and end-cyclized olefins. The findings, published in the journal Engineering, shed light on the potential of utilizing different comonomers in olefin solution polymerization to obtain high-performance polyolefin materials.
Polyolefin elastomers (POEs) are widely used in various industries due to their exceptional properties. However, the high cost ...
Study identifies new pathway to suppressing autoimmunity
2023-09-29
Researchers at Stanford University School of Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, and the Hospital for Special Surgery Research Institute have uncovered new details about how the immune system prevents the production of antibodies that can recognize and damage the body’s own, healthy tissues. The study, to be published September 29 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), also reveals how this process is impaired in autoimmune disorders such as systemic sclerosis and systemic lupus ...
Diabetes may accelerate blood cancer growth, yet survival outcomes differ by race
2023-09-29
(WASHINGTON, Sept. 29, 2023) – Patients with multiple myeloma, a blood cancer of plasma cells in the bone marrow, who also have diabetes have a reduced overall survival when compared to those without diabetes. In a subgroup analysis, this difference in survival due to diabetes was seen in white patients but not in Black patients, according to a study published today in Blood Advances.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, diabetes affects 13% of the U.S. population, and this prevalence is growing rapidly. Multiple myeloma is the second most common blood cancer in the U.S. and disproportionately ...
Groundbreaking mathematical proof: new insights into typhoon dynamics unveiled
2023-09-29
In a remarkable breakthrough in the field of Mathematical Science, Professor Kyudong Choi from the Department of Mathematical Sciences at UNIST has provided an irrefutable proof that certain spherical vortices exist in a stable state. This groundbreaking discovery holds significant implications for predicting weather anomalies and advancing weather prediction technologies.
A vortex is a rotating region of fluid, such as air or water, characterized by intense rotation. Common examples include typhoons and tornadoes frequently observed in news reports. Professor Choi’s mathematical proof establishes the stability of specific ...
Teams invent a new metallization method of modified tannic acid photoresist patterning
2023-09-29
The micro/nano metal pattern formation is a key step in the assembly of various devices. However, ex situ approaches of metal patterning limited their industrial applications due to the poor stability and dispersion of metal nanoparticles. The in situ electroless deposition after lithography patterning may be a better choice for avoiding the growth and aggregation of metal particles in the polymers. Tannic acid is rich in natural products, having an adjacent tri-hydroxyl structure, which can realize the in situ reduction of metal ions on the photoresist pattern. A team of scientists ...
MoMFs could be central to liver regeneration
2023-09-29
The liver is a vital organ that plays a role in many essential functions, including digestion, detoxification, and metabolism. When the liver is damaged, it has the remarkable ability to regenerate itself. However, the process of liver regeneration is not fully understood.
A critical aspect of liver regeneration is removing dead tissue and necrotic lesions. In a recent study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, Feng et al. showed that monocyte-derived macrophages (MoMFs) play a crucial role in this process. MoMFs are a type of white blood cell that is recruited to the liver in response to injury. Once in the liver, MoMFs engulf dead cells ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] New insights into how the human brain organises languageLeipzig scientists publish largest meta-analysis on language processing to date