(Press-News.org) Study by LMU psychologists shows that distractor objects can help the visual system develop more effective search strategies.
People are continuously provided with an overwhelming stream of events flooding the sensory organs. However, while the brain has impressive processing capabilities, its capacity is strongly limited. Thus, an observer cannot consciously experience all the events and information available at any one time, but has to focus on some limited subset of the whole.
For many decades, researchers have investigated the neuro-cognitive mechanisms of this selective attention through the use of visual search and have shown that contextual cueing plays a role: If the searched-for target object is situated within a certain spatial arrangement of other objects, then it is located more quickly. That is to say, people react faster to a target object when it is embedded in a stable arrangement of distractor objects. According to the prevailing theory, this is because people store the relative position of the target stimulus in relation to the distractor stimuli in their long-term memory.
Using a novel eyetracking scanpath analysis, a team led by Professor Thomas Geyer from the Department of Psychology at LMU has now shown that contextual cueing is caused less by display-specific memories. Rather, they aid the visual system in developing new capabilities and learning more effective scanning strategies. The authors thus see the contextual facilitation of visual search as a byproduct of this effect. “This has strong implications on how we can understand visual search and adaptive behavior in general,” says Geyer. “Our results suggest that visual scanning strategies are learnable and act as a ‘gatekeeper’ between a plethora of sensory information and attentional selection.” This also means that eye movements are not just the consequence of a focused shifting of attention, but that they proactively support the orienting of attention toward objects that will most likely contain relevant information for further processing – before the actual attentional selection takes place.
END
Visual search: Context facilitates more effective strategies
2023-09-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Malaria: Treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria patients under threat in the Horn of Africa
2023-09-29
Diagnosis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria using rapid diagnostic tests and treatment with artemisinin derivatives, the main component of the malaria treatments recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO), are under threat in the Horn of Africa. Scientists from the Laboratory of Parasitology and Medical Mycology at the University of Strasbourg and Strasbourg University Hospital, in collaboration with the Eritrean Ministry of Health, the Institut Pasteur, Columbia University in New York and WHO, have detected the emergence and spread in Eritrea of parasites with both artemisinin resistance and genome modifications ...
New post-translational modification of the glycolytic enzyme enolase
2023-09-29
Tsukuba, Japan—Proteins are subject to post-translational chemical modifications that result in functional diversity. Methylation is one such modification that is generally believed to occur on lysine and arginine residues. Recently, this modification has been shown to occur on histidine residues as well. Furthermore, it has been suggested that histidine methylation occurs in a wide range of proteins. However, many details remain unknown: for example, which are the proteins that are methylated and ...
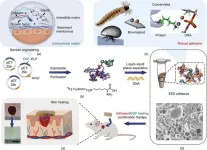
New frontier in biomedical engineering: Protein coacervates engineered into adhesive for unprecedented skin repair speed
2023-09-29
A team of researchers from China has made a significant breakthrough in biomedical engineering by developing a novel adhesive that promises to revolutionize wound management and tissue repair. The research, published in Engineering, unveils a biocomposite adhesive that exhibits robust adhesion and real-time skin healing properties.
Adhesives have long been recognized as a valuable tool in biomedical engineering. However, current adhesive systems face challenges in achieving strong and durable adhesion, limiting their effectiveness in wound healing. ...
New study unveils insights into ethylene copolymerization with linear and end-cyclized olefins using a metallocene catalyst
2023-09-29
A research team led by Changjiang Wu at SINOPEC (Beijing) Research Institute of Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. in China has made important progress in understanding the polymerization behavior and thermal properties of copolymers formed through ethylene copolymerization with linear and end-cyclized olefins. The findings, published in the journal Engineering, shed light on the potential of utilizing different comonomers in olefin solution polymerization to obtain high-performance polyolefin materials.
Polyolefin elastomers (POEs) are widely used in various industries due to their exceptional properties. However, the high cost ...
Study identifies new pathway to suppressing autoimmunity
2023-09-29
Researchers at Stanford University School of Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, and the Hospital for Special Surgery Research Institute have uncovered new details about how the immune system prevents the production of antibodies that can recognize and damage the body’s own, healthy tissues. The study, to be published September 29 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), also reveals how this process is impaired in autoimmune disorders such as systemic sclerosis and systemic lupus ...
Diabetes may accelerate blood cancer growth, yet survival outcomes differ by race
2023-09-29
(WASHINGTON, Sept. 29, 2023) – Patients with multiple myeloma, a blood cancer of plasma cells in the bone marrow, who also have diabetes have a reduced overall survival when compared to those without diabetes. In a subgroup analysis, this difference in survival due to diabetes was seen in white patients but not in Black patients, according to a study published today in Blood Advances.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, diabetes affects 13% of the U.S. population, and this prevalence is growing rapidly. Multiple myeloma is the second most common blood cancer in the U.S. and disproportionately ...
Groundbreaking mathematical proof: new insights into typhoon dynamics unveiled
2023-09-29
In a remarkable breakthrough in the field of Mathematical Science, Professor Kyudong Choi from the Department of Mathematical Sciences at UNIST has provided an irrefutable proof that certain spherical vortices exist in a stable state. This groundbreaking discovery holds significant implications for predicting weather anomalies and advancing weather prediction technologies.
A vortex is a rotating region of fluid, such as air or water, characterized by intense rotation. Common examples include typhoons and tornadoes frequently observed in news reports. Professor Choi’s mathematical proof establishes the stability of specific ...
Teams invent a new metallization method of modified tannic acid photoresist patterning
2023-09-29
The micro/nano metal pattern formation is a key step in the assembly of various devices. However, ex situ approaches of metal patterning limited their industrial applications due to the poor stability and dispersion of metal nanoparticles. The in situ electroless deposition after lithography patterning may be a better choice for avoiding the growth and aggregation of metal particles in the polymers. Tannic acid is rich in natural products, having an adjacent tri-hydroxyl structure, which can realize the in situ reduction of metal ions on the photoresist pattern. A team of scientists ...
MoMFs could be central to liver regeneration
2023-09-29
The liver is a vital organ that plays a role in many essential functions, including digestion, detoxification, and metabolism. When the liver is damaged, it has the remarkable ability to regenerate itself. However, the process of liver regeneration is not fully understood.
A critical aspect of liver regeneration is removing dead tissue and necrotic lesions. In a recent study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, Feng et al. showed that monocyte-derived macrophages (MoMFs) play a crucial role in this process. MoMFs are a type of white blood cell that is recruited to the liver in response to injury. Once in the liver, MoMFs engulf dead cells ...
A lethal parasite’s secret weapon: Infecting non-immune cells
2023-09-29
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The organisms that cause visceral leishmaniasis, a potentially deadly version of the parasitic disease that most often affects the skin to cause disfiguring disease, appear to have a secret weapon, new research suggests: They can infect non-immune cells and persist in those uncommon environments.
Researchers found the Leishmania donovani parasites in blood-related stem cells in the bone marrow of chronically infected mice – precursor cells that can regenerate all types of cells in the blood-forming system. The finding may help explain why some people who develop visceral leishmaniasis, which is ...