(Press-News.org) EAST LANSING, Mich. — Developing biofuel from native perennials instead of corn in the Midwest's rolling grasslands would better protect threatened bird populations, Michigan State University research suggests.
Federal mandates and market forces both are expected to promote rising biofuel production, MSU biologist Bruce Robertson says, but the environmental consequences of turning more acreage over to row crops for fuel are a serious concern.
Ethanol in America is chiefly made from corn, but research is focusing on how to cost-effectively process cellulosic sources such as wood, corn stalks and grasses. Perennial grasses promise low cost and energy inputs – planting, fertilizing, watering – and the new study quantifies substantial environmental benefits.
"Native perennial grasses might provide an opportunity to produce biomass in ways that are compatible with the conservation of biodiversity and important ecosystem services such as pest control," Robertson said. "This work demonstrates that next-generation biofuel crops have potential to provide a new source of habitat for a threatened group of birds."
With its rich variety of ecosystems, including historic prairie, southern Michigan provided a convenient place to compare bird populations in 20 sites of varying size for each of the three fuel feedstocks. Grassland birds are of special concern, Robertson said, having suffered more dramatic population losses than any other group of North American birds.
In the first such empirical comparison and the first to simultaneously study grassland bird communities across habitat scales, Robertson and colleagues found that bugs and the birds that feed on them thrive more in mixed prairie grasses than in corn. Almost twice as many species made their homes in grasses, while plots of switchgrass, a federally designated model fuel crop, fell between the two in their ability to sustain biodiversity.
The larger the plot of any type, researchers found, the greater the concentration of birds supported. But if grasslands offer conservation and biofuel opportunities, Robertson said, the biodiversity benefits could decrease as biofuel grass feedstocks are bred and cultivated for commercial uniformity.
INFORMATION:
Robertson was a research associate at MSU's W.K. Kellogg Biological Station in Kalamazoo County during the two-year research project. Today he is an MSU adjunct entomology professor and a postdoctoral fellow at the Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute Migratory Bird Center in Washington, D.C. His research colleagues included John A. Hannah Distinguished Professor of plant biology Douglas Schemske and research associate Liz Loomis, both at the Kellogg Biological Station; Patrick Doran of The Nature Conservancy in Lansing; and statistician J. Roy Robertson of Battle Creek.
The research was funded by the U.S. Department of Energy Great Lakes Bioenergy Research Center with support from The Nature Conservancy's Great Lakes Fund for Partnership in Conservation Science and Economics. Results were recently published in the scientific journal GCB (Global Change Biology) Bioenergy.
Michigan State University has been advancing knowledge and transforming lives through innovative teaching, research and outreach for more than 150 years. MSU is known internationally as a major public university with global reach and extraordinary impact. Its 17 degree-granting colleges attract scholars worldwide who are interested in combining education with practical problem solving.
Biofuel grasslands better for birds than ethanol staple corn, researchers find
Diverse ecosystems promote diverse avian populations
2011-01-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Story tips from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory January 2011
2011-01-07
FORENSICS -- The telltale bone
Technology developed more than 100 years ago to wirelessly transmit electricity is being adapted to locate clandestine graves. Oak Ridge National Laboratory's Charles Van Neste and colleagues are transmitting electromagnetic waves to penetrate the ground and set up a resonance in buried bones. "The system consists of a transmitter and a receiver that collects the surface waves and passively integrates them through resonance over time," Van Neste said. He and colleagues Arpad Vass, Marc Wise and Lee Hively have discovered that human bone ...
Sulphur proves important in the formation of gold mines
2011-01-07
Collaborating with an international research team, an economic geologist from The University of Western Ontario has discovered how gold-rich magma is produced, unveiling an all-important step in the formation of gold mines.
The findings were published in the December issue of Nature Geoscience.
Robert Linnen, the Robert Hodder Chair in Economic Geology in Western's Department of Earth Sciences conducts research near Kirkland Lake, Ontario and says the results of the study could lead to a breakthrough in choosing geographic targets for gold exploration and making exploration ...
CMU research finds regional dialects are alive and well on Twitter
2011-01-07
PITTSBURGH—Microbloggers may think they're interacting in one big Twitterverse, but researchers at Carnegie Mellon University's School of Computer Science find that regional slang and dialects are as evident in tweets as they are in everyday conversations.
Postings on Twitter reflect some well-known regionalisms, such as Southerners' "y'all," and Pittsburghers' "yinz," and the usual regional divides in references to soda, pop and Coke. But Jacob Eisenstein, a post-doctoral fellow in CMU's Machine Learning Department, said the automated method he and his colleagues have ...
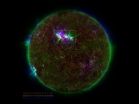
Hotspots in fountains on the sun's surface help explain coronal heating mystery
2011-01-07
GREENBELT, Md. -- Observations from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and the Japanese satellite Hinode show that some gas in the giant, fountain-like jets in the sun's atmosphere known as spicules can reach temperatures of millions of degrees. The finding offers a possible new framework for how the sun's high atmosphere gets so much hotter than the surface of the sun.
What makes the high atmosphere, or corona, so hot – over a million degrees, compared to the sun surface's 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit -- remains a poorly understood aspect of the sun's complicated space ...
Study finds energy limits global economic growth
2011-01-07
A study that relates global energy use to economic growth, published in the January issue of BioScience, finds strong correlations between these two measures both among countries and within countries over time. The research leads the study's authors to infer that energy use limits economic activity directly. They conclude that an "enormous" increase in energy supply will be required to meet the demands of projected world population growth and lift the developing world out of poverty without jeopardizing standards of living in most developed countries.
The study, which ...
Evidence lacking for widespread use of costly antipsychotic drugs, says Stanford researcher
2011-01-07
STANFORD, Calif. — Many prescriptions for the top-selling class of drugs, known as atypical antipsychotic medications, lack strong evidence that the drugs will actually help, a study by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine and University of Chicago has found. Yet, drugs in this class may cause such serious effects as weight gain, diabetes and heart disease, and cost Americans billions of dollars.
"Because these drugs have safety issues, physicians should prescribe them only when they are sure patients will get substantial benefits," said Randall Stafford, ...
Statistical analysis can estimate crop performance
2011-01-07
Madison, WI December 23, 2010 – Scientists at Rothamsted Research, United Kingdom, in collaboration with the International Center for Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA), Syria have developed a method of accounting for spatial trend in single crop field trials. Spatial trend refers to the variations in crop yield and other characteristics observed when repeating this single crop field trial.
Usually plant breeders will grow several replicate plots to assess the breed line in different environments and then compare the results to commercial or standard varieties ...
Glaucoma Eye Test Through Eyelid Supports National Glaucoma Awareness Month - BiCOM sets up Free Eye Exam and Glaucoma Educational Events Worldwide
2011-01-07
BiCOM Inc. home of Glaucoma Eye Test Diat throug the eylid supports National Glaucoma Awareness Month this January. It is imperative to get regular eye pressure (IOP) test. Vision loss caused by Glaucoma can be slowed or halted with the proper medication. Getting an eye pressure screening has never been easier or safer with painless, hand-held through the eyelid Tonometer Diaton aka Glaucoma Eye Test.
The start of a new year signifies a new beginning to most, many people making resolutions to better their lives. Improving health is usually a top priority - but, visual ...
Shaw Capital Business Asset Based Loan Financing - The Perfect Solution for Cash Flow
2011-01-07
Shaw Capital Management and Financing provide same-day-funding. We can help you meet your cash flow needs immediately without entering into a long term factoring relationship. The money you get for the freight bills we purchase is payment in full. You are a Canadian business owner and financial manager looking for info and guidance on a business asset based loan. What is asset based loan financing, sometimes called cash flow factoring - how does it work, and why could it be the best solution for your firm's working capital challenges.
Let's cover off the basics and find ...
Millionaire Dating Service for Successful Singles, Millionaires Launched
2011-01-07
Last month, a brand-new high class dating service WantsMillionaire.com, which caters for those singles who are still trying online dating with the aim of finding serious and successful mates and life-time relationship partners, was lunched. Unlike other dating services, this Wants Millionaire dating club pursues successful dating and relationships for high class singles including CEOs, investors, entrepreneurs, beauty queens, fitness models and Hollywood celebrities, to name a few. Hookers, players, other gold diggers can hardly be approved on this website. With a short ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
[Press-News.org] Biofuel grasslands better for birds than ethanol staple corn, researchers findDiverse ecosystems promote diverse avian populations