(Press-News.org) Large health systems are acquiring smaller physician practices at what some consider an alarming rate, leaving fewer independent practices. When the COVID-19 pandemic occurred, it was unclear whether the independent practices would be able to “keep up” (maintain the same level of patient care) with larger practices, which have more resources, and if care for patients with chronic conditions might be disrupted by the pandemic.
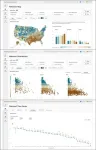
A new study from Associate Dean of Research Alison Cuellar found that independent practices experienced a smaller drop in patient volume than their larger counterparts during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. This was true for patients with and without chronic conditions. However, doctors in larger group practices had a higher proportion of telehealth visits initially, but the differences between group and independent practices declined with time.
These findings also show that both integrated physician practices and independent practices can still thrive and help their patients during times of crisis and stress for the public.
“Policymakers have raised concerns about the increased consolidation of physicians into large practices. This study finds that doctors at large practices had fewer patients and higher rates of telehealth visits in the early pandemic compared to independent practices. This may indicate that integrated physician practices faced less financial pressure, had greater resources to implement new technologies such as telehealth, or that they have fundamentally different practice cultures,” said Cuellar, the principal investigator.
"Volume of Care for Primary Care Physicians in Integrated vs Independent Practices Through the COVID-19 Pandemic" was published in JAMA Health Forum in September 2023. Cuellar was funded by the National Institute of Health Care Management. Anupam Jena of Harvard Medical School is the co-investigator and co-author. For this study, Cuellar and Jena analyzed administrative data using claims data from FAIR Health.
END
Independent physician practices can keep up with larger consolidated practices in a pandemic
Independent practices experienced a smaller drop in patient volume than consolidated practices during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic
2023-10-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Join GSA in Tampa for the Nation’s Premier Aging Conference!
2023-10-03
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) invites all journalists to attend its 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting — the country’s largest interdisciplinary conference in the field of aging — from November 8 to 12 in Tampa, Florida. Qualified media representatives intending to cover the meeting may register free of charge.
More than 3,000 professionals are expected to attend the five-day gathering at the Tampa Convention Center. The theme for 2023 is “Building Bridges > Catalyzing Research > Empowering All Ages,” and the program schedule contains ...
Female animals may learn mate preferences based on what sets other females’ choices apart from the crowd
2023-10-03
Females may infer what makes a male attractive by observing the choices of more experienced females, and the context of those choices matters, according to a mathematical model publishing October 3rd in the open access journal PLOS Biology. Rather than simply copying their peers, females might learn to prefer rare traits that set successful males apart from others, Emily DuVal at Florida State University, US, and colleagues report.
Sexual selection — where traits become more common because of their attractiveness to the opposite sex — can produce strange and elaborate characteristics, such as huge antlers, bright plumage, and ...
Despite increasing rates of tuberculosis in prisons across the globe, current WHO TB prevention guidelines fail to reach incarcerated populations
2023-10-03
Despite increasing rates of tuberculosis in prisons across the globe, current WHO TB prevention guidelines fail to reach incarcerated populations. Programs should instead prioritize them, argue a group of researchers from Stanford, Harvard, UCL and a range of other global institutions.
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Medicine: http://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1004288
Article Title: Prioritizing persons deprived of liberty in global guidelines for tuberculosis preventive treatment
Author Countries: United States
Funding: ...
Computer model predicts who needs lung cancer screening
2023-10-03
A machine learning model equipped with only data on people’s age, smoking duration and the number of cigarettes smoked per day can predict lung cancer risk and identify who needs lung cancer screening, according to a new study publishing October 3rd in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Thomas Callender of University College London, UK, and colleagues.
Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer death worldwide, with poor survival in the absence of early detection. Screening for lung cancer among those at highest risk could reduce ...
Rural counties showing steeper decline in health measures compared to urban counties in 2015 versus 2019—though all areas showed declines in health measures over time
2023-10-03
Residents of rural counties have overall worse health outcomes than their urban counterparts. A study published in PLOS Global Public Health by William Weeks at Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, Washington, United States and colleagues introduces a Health Equity Dashboard for policy makers to visualize health disparities in specific locations, and to examine the relationship between health-related measures and socio-demographic characteristics.
Despite overall decreasing mortality rates prior to 2020, health disparities between rural and urban areas in the United States have increased. To better understand inequities in health-related measures between rural and non-rural populations, ...
Interconnected factors increase household food insecurity in Brazil
2023-10-03
Food insecurity is four times higher in Brazilian households headed by single women of colour than those headed by married white men, according to research published in the open access journal PLOS Global Public Health. Gender inequities, skin colour and children in the home increase the risk of food insecurity and the authors argue that policy makers need to consider intersectionality in programmes to reduce it.
In 2021 there were 2.37 billion people suffering from food insecurity, with prevalence higher among women than men. The gender gap has increased in recent years, especially in the economic crisis triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic. ...
Real-world study confirms reliability of tool assessing 10-year risk prediction of heart disease
2023-10-03
ROCHESTER, Minn. — A recent study based on real-world community patient data confirms the effectiveness of the Pooled Cohort Equation (PCE), developed by the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology in 2013. The PCE is used to estimate a person's 10-year risk of developing clogged arteries, also known as atherosclerosis, and guide heart attack and stroke prevention efforts. Study findings are published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The new study highlights to patients and clinicians the continued reliability and effectiveness of the PCE as a tool for assessing cardiovascular risk, regardless of statin use to lower ...
Newly established Bulgarian Barcode of Life to support biodiversity conservation in the country
2023-10-03
On 27 September 2023, during a specialised symposium on DNA barcoding at the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, the Bulgarian Barcode of Life (BgBOL), a Bulgarian DNA barcoding consortium, was founded. By becoming the latest national node to join the International Barcode of Life Consortium (iBOL), the main task before BgBOL will be to coordinate, support, and promote DNA barcoding research in Bulgaria, with a primary focus on the study and preservation of the country's biodiversity.
“The Bulgarian Barcode of Life opens up new horizons and opportunities to study and understand the biodiversity ...
On-Yee Lo, PhD, receives NAM Healthy Longevity Catalyst Award for work on brain stimulation to improve physical and cognitive functions in older adults
2023-10-03
On-Yee Lo, PhD, Assistant Scientist II at the Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research at Hebrew SeniorLife and Instructor in Medicine at Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, is among the awardees of the 2023 Healthy Longevity Catalyst Awards by the National Academy of Medicine (NAM) together with eight global collaborators representing over 50 countries and territories.
Lo, the principal investigator, and her colleagues were honored for the work with brain stimulation targeting shared networks to improve physical and cognitive ...
New recommendation on meningitis vaccines for infants in sub-Saharan Africa
2023-10-03
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers, as part of the Infectious Diseases Clinical Research Consortium (IDCRC), provided an interim analysis showing that the pentavalent (NmCV-5) meningitis vaccine is safe for use in 9-month-old infants in the meningitis belt of sub-Saharan Africa. They presented their results to the World Health Organization’s (WHO) Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) on Immunization on September 26.
SAGE recommended that all countries in the African meningitis belt introduce the novel pentavalent meningococcal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The world’s largest brain research prize awarded for groundbreaking discoveries on how we sense touch and pain
Magnetofluids help to overcome challenges in left atrial appendage occlusion
Brain-clearing cells offer clues to slowing Alzheimer’s disease progression
mRNA therapy restores fertility in genetically infertile mice
Cloaked stem cells evade immune rejection in mice, pointing to a potential universal donor cell line
Growth in telemedicine has not improved mental health care access in rural areas, study finds
Pitt scientists engineer “living eye drop” to support corneal healing
Outcomes of older adults with advanced cancer who prefer quality of life vs prolonging survival
Lower music volume levels in fitness class and perceived exercise intensity
Of crocodiles, counting and conferences
AERA announces 2026 award winners in education research
Saving two lives with one fruit drop
Photonic chips advance real-time learning in spiking neural systems
Share of migratory wild animal species with declining populations despite UN treaty protections worsens from 44% to 49% in two years; 24% face extinction, up 2%
One in 20 babies experiences physical abuse, global review finds
Tundra tongue: The science behind a very cold mistake
Targeting a dangerous gut infection
Scientists successfully harvest chickpeas from “moon dirt”
Teen aggression a warning sign for faster aging later in life
Study confirms food fortification is highly cost-effective in fighting hidden hunger across 63 countries
Special issue elevates disease ecology in marine management
A kaleidoscope of cosmic collisions: the new catalogue of gravitational signals from LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
[Press-News.org] Independent physician practices can keep up with larger consolidated practices in a pandemicIndependent practices experienced a smaller drop in patient volume than consolidated practices during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic